Chapter 3 - Department Of Computer Science
... opposite reaction Whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal (in magnitude) and opposite (in direction) force on the first object action = opposite reaction F1 = - F2 ...
... opposite reaction Whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal (in magnitude) and opposite (in direction) force on the first object action = opposite reaction F1 = - F2 ...
King Abdulaziz University
... Q. 42 A civil engineer wishes to design a curved exit ramp for a highway in such a way that a car will not have to rely on friction to round the curve without skidding. In other words, a car moving at the designated speed can negotiate the curve even when the road is covered with ice. Such a ramp is ...
... Q. 42 A civil engineer wishes to design a curved exit ramp for a highway in such a way that a car will not have to rely on friction to round the curve without skidding. In other words, a car moving at the designated speed can negotiate the curve even when the road is covered with ice. Such a ramp is ...
Chapter 3: The Basics of Classical Mechanics
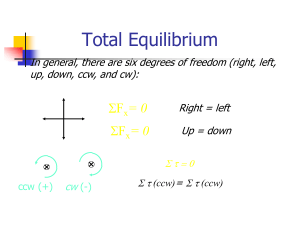
... the virtual displacements δ ri in contrast to the case for real displacements. For a system in equilibrium, the forces on the individual particles vanish and therefore so does the virtual work. For a dynamical system subject to Newton's laws of motion we can say that the forces are balanced by the a ...
... the virtual displacements δ ri in contrast to the case for real displacements. For a system in equilibrium, the forces on the individual particles vanish and therefore so does the virtual work. For a dynamical system subject to Newton's laws of motion we can say that the forces are balanced by the a ...
Math Practice Problems 2nd 8 weeks
... 3. Determine the acceleration of a car that moves from rest to 15.0 m/s in 10.0 seconds. 4. Determine the average speed of a truck that makes a 285-mile trip in 5.0 hours? 5. An object moves 3.5 cm west from a point of zero origin. It then moves 2.8 cm north. (a) Draw the corresponding vectors and t ...
... 3. Determine the acceleration of a car that moves from rest to 15.0 m/s in 10.0 seconds. 4. Determine the average speed of a truck that makes a 285-mile trip in 5.0 hours? 5. An object moves 3.5 cm west from a point of zero origin. It then moves 2.8 cm north. (a) Draw the corresponding vectors and t ...
Rotational Motion
... Wrap your fingers in the direction of rotation Your thumb points in the direction of ω ...
... Wrap your fingers in the direction of rotation Your thumb points in the direction of ω ...
Chapter 8 - RHIG - Wayne State University
... • Periodic motion in U(r) implies the orbit is closed; I.e. loops on itself after a certain number of excursions about the center of force. • The change in q while going from rmin to rmax is a function of the potential and need not be 180o. • It can be calculated! • Because the motion is symmetric ...
... • Periodic motion in U(r) implies the orbit is closed; I.e. loops on itself after a certain number of excursions about the center of force. • The change in q while going from rmin to rmax is a function of the potential and need not be 180o. • It can be calculated! • Because the motion is symmetric ...
Powerpoint - Northern Highlands
... The more massive an object is, the more force required to get the same change in motion ...
... The more massive an object is, the more force required to get the same change in motion ...
Standard EPS Shell Presentation
... A moving body will continue moving in the same direction with the same speed until some net force acts on it. A body at rest will remain at rest unless a net force acts on it. Summing it up: It takes a net force to change a body’s velocity. ...
... A moving body will continue moving in the same direction with the same speed until some net force acts on it. A body at rest will remain at rest unless a net force acts on it. Summing it up: It takes a net force to change a body’s velocity. ...
Sponge - A 200 kg hockey player pushes a 150 kg official after
... Ex. 8 - In a circus balancing act, a woman performs a headstand on top of a man’s head. The woman weighs 490 N, and the man’s head and neck weigh 50 N. It is primarily the seventh cervical vertebra in the spine that supports all the weight above the shoulders. What is the normal force that this ver ...
... Ex. 8 - In a circus balancing act, a woman performs a headstand on top of a man’s head. The woman weighs 490 N, and the man’s head and neck weigh 50 N. It is primarily the seventh cervical vertebra in the spine that supports all the weight above the shoulders. What is the normal force that this ver ...
Chapter 11 Biology Study Guide
... sometimes greater than, sometimes less than its weight on Earth’s surface. 15. Newton’s third law of motion describes a. action and reaction forces. c. b. balanced forces. d. ...
... sometimes greater than, sometimes less than its weight on Earth’s surface. 15. Newton’s third law of motion describes a. action and reaction forces. c. b. balanced forces. d. ...
Newton`s Laws and the Nature of Matter
... influence of the gravity of another mass. Gravity and Newton's laws explain orbits. In circular motion the acceleration is given by the expression a=V2/d where V is the velocity and d is the radius of the orbit. This is the centrifugal force you feel when you turn a corner at high speed: because of ...
... influence of the gravity of another mass. Gravity and Newton's laws explain orbits. In circular motion the acceleration is given by the expression a=V2/d where V is the velocity and d is the radius of the orbit. This is the centrifugal force you feel when you turn a corner at high speed: because of ...
12.1 Powerpoint
... wagon stops? (Hint: Consider what it takes to change the velocity of the wagon and the marble.) ...
... wagon stops? (Hint: Consider what it takes to change the velocity of the wagon and the marble.) ...
Physics/Graphing Notes
... An object in motion will remain in motion or an object at rest will remain at rest, unless an unbalanced force acts upon it. Example: A car slamming into a telephone pole. The driver is thrown from the vehicle. This is because the person stays in motion because there is not an unbalanced force to st ...
... An object in motion will remain in motion or an object at rest will remain at rest, unless an unbalanced force acts upon it. Example: A car slamming into a telephone pole. The driver is thrown from the vehicle. This is because the person stays in motion because there is not an unbalanced force to st ...
Chapter 4: Newton`s Laws of Motion
... In some circumstances when objects that are in physical contact are moving as one unit (both have the same acceleration) it is acceptable, and in fact useful, to draw a composite force diagram for the objects. In this case the forces exerted on one object by the other do not appear on the diagram be ...
... In some circumstances when objects that are in physical contact are moving as one unit (both have the same acceleration) it is acceptable, and in fact useful, to draw a composite force diagram for the objects. In this case the forces exerted on one object by the other do not appear on the diagram be ...
Center of Mass, Angular Momentum
... It always bothered me that if the same impulsive force were applied on the bar between the two masses, i.e. at the CM, the barbell would move at the SAME speed we just calculated for the CM, but without rotation. From energy considerations, it seems that applying the same force in two locations impa ...
... It always bothered me that if the same impulsive force were applied on the bar between the two masses, i.e. at the CM, the barbell would move at the SAME speed we just calculated for the CM, but without rotation. From energy considerations, it seems that applying the same force in two locations impa ...
Literacy - TECC Science
... resist the change in motion of the car. Also, when the car’s brakes are applied from a high speed, your body is thrown forward due to its inertia in motion – it wants to continue moving and opposes the change that is trying to slow it down. Newton’s Second Law: A resultant, or net, external force F ...
... resist the change in motion of the car. Also, when the car’s brakes are applied from a high speed, your body is thrown forward due to its inertia in motion – it wants to continue moving and opposes the change that is trying to slow it down. Newton’s Second Law: A resultant, or net, external force F ...