Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... stopped the driver’s body from moving too far forward. Newton’s third law says that for every action force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force. The driver’s body exerted an action force on the seat belt. The seat belt exerted a reaction force on the driver that stopped her motion. ...
... stopped the driver’s body from moving too far forward. Newton’s third law says that for every action force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force. The driver’s body exerted an action force on the seat belt. The seat belt exerted a reaction force on the driver that stopped her motion. ...
forces introduction
... alone, will cause the motion of the system or object to change. If a system or object at rest is subjected to a non-zero force it will start to move. ...
... alone, will cause the motion of the system or object to change. If a system or object at rest is subjected to a non-zero force it will start to move. ...
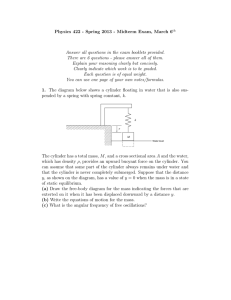
Physics 422 - Spring 2013 - Midterm Exam, March 6
... (a) Draw the free-body diagram for the mass indicating the forces that are exterted on it when it has been displaced downward by a distance y. (b) Write the equations of motion for the mass. (c) What is the angular frequency of free oscillations? ...
... (a) Draw the free-body diagram for the mass indicating the forces that are exterted on it when it has been displaced downward by a distance y. (b) Write the equations of motion for the mass. (c) What is the angular frequency of free oscillations? ...
PHY 101 Lecture 4 - Force
... The technical definition of the concept of “Force” started with Isaac Newton, in the Three Laws of Motion. /1/ If the net force acting on an object is 0, then the object moves with constant velocity. /2/ If the net force is F, then the object undergoes acceleration; a = F /m where m is the mass. /3/ ...
... The technical definition of the concept of “Force” started with Isaac Newton, in the Three Laws of Motion. /1/ If the net force acting on an object is 0, then the object moves with constant velocity. /2/ If the net force is F, then the object undergoes acceleration; a = F /m where m is the mass. /3/ ...
AP 1 Ch. 4 Review w/answers
... 13. A rope is tied around a tree. One person pulls with a force of 40.0 N, north while another person pulls with a force of 60.0 N, west. What is the resultant force on the tree? ...
... 13. A rope is tied around a tree. One person pulls with a force of 40.0 N, north while another person pulls with a force of 60.0 N, west. What is the resultant force on the tree? ...
Day 1 Notes: Dealing with projectiles in two dimensions. There are
... D. Diagonal forces can be split into x axis and y axis. Then, using trig functions, a student simply can plug the net force value in to Newton’s second law formula. E. When a student is encountered with an off centered plane questions, simply make diagonal lines x and y axis. Then, the original hori ...
... D. Diagonal forces can be split into x axis and y axis. Then, using trig functions, a student simply can plug the net force value in to Newton’s second law formula. E. When a student is encountered with an off centered plane questions, simply make diagonal lines x and y axis. Then, the original hori ...
Example 2.1. on pg 30
... 2. simplifying equations and substituting one equation into another is a common practice in AP physics 3. all students are expected to have a working knowledge of advanced algebra and trigonometry 4. all tests will consist of 3 questions (15 pts. constructed response) from old AP physics tests and 3 ...
... 2. simplifying equations and substituting one equation into another is a common practice in AP physics 3. all students are expected to have a working knowledge of advanced algebra and trigonometry 4. all tests will consist of 3 questions (15 pts. constructed response) from old AP physics tests and 3 ...
Newton`s Three Laws of Motion
... Newton’s Second Law: Law of Unbalanced Forces Unbalanced forces (the net force) cause objects to accelerate. Fnet = ma The greater the net force on a mass, the greater the acceleration. If the same size force is applied to two different objects, the object with the greater mass experiences a smalle ...
... Newton’s Second Law: Law of Unbalanced Forces Unbalanced forces (the net force) cause objects to accelerate. Fnet = ma The greater the net force on a mass, the greater the acceleration. If the same size force is applied to two different objects, the object with the greater mass experiences a smalle ...
File - Mrs. Haug`s Website
... when objects move in two dimensions (x and y) In these cases, the x- and y- components are conserved separately. Use vector addition to solve! Remember: by definition p is in the same direction as v ...
... when objects move in two dimensions (x and y) In these cases, the x- and y- components are conserved separately. Use vector addition to solve! Remember: by definition p is in the same direction as v ...
Paper Reference(s)
... In the boxes on the answer book, write the name of the examining body (Edexcel), your centre number, candidate number, the unit title (Mechanics M1), the paper reference (6677), your surname, other name and signature. Whenever a numerical value of g is required, take g = 9.8 m s2. When a calculator ...
... In the boxes on the answer book, write the name of the examining body (Edexcel), your centre number, candidate number, the unit title (Mechanics M1), the paper reference (6677), your surname, other name and signature. Whenever a numerical value of g is required, take g = 9.8 m s2. When a calculator ...
Export To Word
... 1. Conservation of linear momentum: Conservation laws play an extremely important role in many aspects of physics. The idea that a certain property of a system is maintained before and after something happens is quite central to many principles in physics. In the pool example, we concentrate on the ...
... 1. Conservation of linear momentum: Conservation laws play an extremely important role in many aspects of physics. The idea that a certain property of a system is maintained before and after something happens is quite central to many principles in physics. In the pool example, we concentrate on the ...
hp1f2013_class04_3d
... Choosing coordinates well is important A tennis ball is hit at 50 mps at an angle of 5 degrees above the horizontal. The initial height is 2 m. Neglecting air drag, how far does the ball go before hitting the ground? Choose +x to be in the direction the ball starts at. Choose +y to be at right angle ...
... Choosing coordinates well is important A tennis ball is hit at 50 mps at an angle of 5 degrees above the horizontal. The initial height is 2 m. Neglecting air drag, how far does the ball go before hitting the ground? Choose +x to be in the direction the ball starts at. Choose +y to be at right angle ...
Newton’s Laws of Motion - Wayne State University
... • A reference frame can be considered inertial if a body subject to no external force, moves in a straight line with constant velocity in that frame. • If Newton’s laws are valid in a given reference frame, then they are also valid in any reference in uniform motion relative to that first frame. • A ...
... • A reference frame can be considered inertial if a body subject to no external force, moves in a straight line with constant velocity in that frame. • If Newton’s laws are valid in a given reference frame, then they are also valid in any reference in uniform motion relative to that first frame. • A ...
What does a force do? Part I
... a) Fill in the table below by changing the value of the force Fman on object and finding the value of the acceleration. Force (N) Acceleration (m/s/s) ...
... a) Fill in the table below by changing the value of the force Fman on object and finding the value of the acceleration. Force (N) Acceleration (m/s/s) ...
Part I - Otterbein
... • We need to know the position of the object in the moment at which we want to calculate its velocity • We need to know the initial velocity of the object to calculate its velocity at time t • This equation is only true if the acceleration of the object is constant. • The equation is only true for p ...
... • We need to know the position of the object in the moment at which we want to calculate its velocity • We need to know the initial velocity of the object to calculate its velocity at time t • This equation is only true if the acceleration of the object is constant. • The equation is only true for p ...
2013 Q6 - Loreto Balbriggan
... (iv) Name the type of acceleration that the ISS experiences as it travels in a circular orbit around the earth. What force provides this acceleration? Centripetal acceleration. Gravity. (v) Calculate the attractive force between the earth and the ISS. Hence or otherwise, calculate the mass of the ea ...
... (iv) Name the type of acceleration that the ISS experiences as it travels in a circular orbit around the earth. What force provides this acceleration? Centripetal acceleration. Gravity. (v) Calculate the attractive force between the earth and the ISS. Hence or otherwise, calculate the mass of the ea ...
Collins_PTI_BiomechanicsGuestLecture - Patho-DPT
... – Components are at right angles to one another – Coordinate system can be local or global ...
... – Components are at right angles to one another – Coordinate system can be local or global ...
5.3 Newton`s Third Law
... If the net force is zero, an object at rest will stay at rest. If an object is acted upon by unbalanced forces, its motion will change. ...
... If the net force is zero, an object at rest will stay at rest. If an object is acted upon by unbalanced forces, its motion will change. ...
Lecture04
... “The Law of Inertia”: A body’s velocity is constant (i.e., a = 0) if the net force acting on it equals zero Alternate statement: A body remains in uniform motion along a straight line at constant speed (or remains at rest) unless it is acted on by a net external force. Above assume an “inertial refe ...
... “The Law of Inertia”: A body’s velocity is constant (i.e., a = 0) if the net force acting on it equals zero Alternate statement: A body remains in uniform motion along a straight line at constant speed (or remains at rest) unless it is acted on by a net external force. Above assume an “inertial refe ...
3 newton`s laws of motion notes
... – Force causes acceleration – Mass resists acceleration – The acceleration you get is equal to the ratio of force over mass ...
... – Force causes acceleration – Mass resists acceleration – The acceleration you get is equal to the ratio of force over mass ...