Chapter 5
... Figure 5.4-8 A point mass m and a distributed mass M are rotating at a uniform angular velocity . The linear momentum of a mass m moving in the x direction with a velocity Vx is mVx. The angular momentum (L) of a point mass m rotating with an angular velocity rad/s in an arc having a radius of c ...
... Figure 5.4-8 A point mass m and a distributed mass M are rotating at a uniform angular velocity . The linear momentum of a mass m moving in the x direction with a velocity Vx is mVx. The angular momentum (L) of a point mass m rotating with an angular velocity rad/s in an arc having a radius of c ...
Ch. 13 Quiz - westscidept
... A) acceleration B) friction C) density D) gravity _____ 4. The type of friction that exists for a shark swimming in the ocean is A) sliding B) hydraulic C) rolling D) fluid _____ 5. The property of matter that resists a change in its motion is A) inertia B) friction C) gravity D) weight _____ 6. Acc ...
... A) acceleration B) friction C) density D) gravity _____ 4. The type of friction that exists for a shark swimming in the ocean is A) sliding B) hydraulic C) rolling D) fluid _____ 5. The property of matter that resists a change in its motion is A) inertia B) friction C) gravity D) weight _____ 6. Acc ...
What did the boy cat say to the girl cat on
... acceleration = force mass •The SI unit for force is the Newton. •Let’s say a 4N force acts on a 2kg mass. What is the acceleration? •What if we increase the force to 8N? •What if we increase the mass to 4kg? ...
... acceleration = force mass •The SI unit for force is the Newton. •Let’s say a 4N force acts on a 2kg mass. What is the acceleration? •What if we increase the force to 8N? •What if we increase the mass to 4kg? ...
Unit 4
... terms of its mass and the net force applied (Newton’s second law- the law of acceleration), • Apply proportional reasoning to determine the effect of changing one quantity while another is held constant – if the force on a mass is doubled, the resulting acceleration would be doubled (direct proporti ...
... terms of its mass and the net force applied (Newton’s second law- the law of acceleration), • Apply proportional reasoning to determine the effect of changing one quantity while another is held constant – if the force on a mass is doubled, the resulting acceleration would be doubled (direct proporti ...
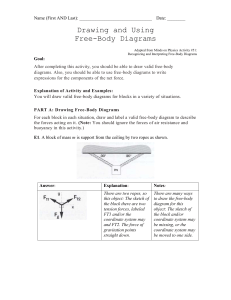
Drawing and Using
... What if the acceleration of the object is non-zero? Sometimes, we do not know the magnitude of the acceleration, particularly before we have solved the problem! Often we want to solve for the acceleration of an object. Even if we do not yet know the magnitude of the acceleration, sometimes we know i ...
... What if the acceleration of the object is non-zero? Sometimes, we do not know the magnitude of the acceleration, particularly before we have solved the problem! Often we want to solve for the acceleration of an object. Even if we do not yet know the magnitude of the acceleration, sometimes we know i ...
On A Roll! Theoretical Background
... In the first project this semester, you calculated the time required for a bead to slide down a wire connecting two points, and then tried to find a fast path between the points. The calculation of descent time began with the statement of conservation of energy —the potential energy lost as the bead ...
... In the first project this semester, you calculated the time required for a bead to slide down a wire connecting two points, and then tried to find a fast path between the points. The calculation of descent time began with the statement of conservation of energy —the potential energy lost as the bead ...
template - charlestuttle
... 8. For the interval from a to b the train is: a. speeding up. b. slowing down. c. moving at constant speed. d. moving in the negative direction. 9. Is the net force on the train equal to zero at any time? Explain. ...
... 8. For the interval from a to b the train is: a. speeding up. b. slowing down. c. moving at constant speed. d. moving in the negative direction. 9. Is the net force on the train equal to zero at any time? Explain. ...
Outcomes Survey Begi.. - Aerospace Engineering Courses page
... the following 18 concepts and skills related to the application of engineering mechanics. The course outcomes are listed below. Please indicate your level of understanding of each of these outcomes (concepts and skills) at the beginning of the semester according to the following scale (indicate by c ...
... the following 18 concepts and skills related to the application of engineering mechanics. The course outcomes are listed below. Please indicate your level of understanding of each of these outcomes (concepts and skills) at the beginning of the semester according to the following scale (indicate by c ...
Force And Work
... In order for work to take place, the following conditions must be fulfilled: i. ii. iii. ...
... In order for work to take place, the following conditions must be fulfilled: i. ii. iii. ...
Force and Motion Section 6.1
... direction and magnitude of the force. • Because forces are vectors, the total force on an object is the vector sum of all forces exerted on the object. • You are looking for the net force on the object. ...
... direction and magnitude of the force. • Because forces are vectors, the total force on an object is the vector sum of all forces exerted on the object. • You are looking for the net force on the object. ...
Physics Practice Exam Solutions
... Now find x, y, and z components in ratios to the magnitude, which gives you the unit vector, so i= -4/√141=-0.33, j=5/√141=0.42, k=10/√141=0.84 3. [B] If you draw a free-body diagram, you have: sum of F=ma, if she weighs 1000N, then her mass is 1000N/(9.8m/s²) =102.04 kg, and her acceleration is 4.9 ...
... Now find x, y, and z components in ratios to the magnitude, which gives you the unit vector, so i= -4/√141=-0.33, j=5/√141=0.42, k=10/√141=0.84 3. [B] If you draw a free-body diagram, you have: sum of F=ma, if she weighs 1000N, then her mass is 1000N/(9.8m/s²) =102.04 kg, and her acceleration is 4.9 ...
UNIT 2
... magnitude of the force of friction on block X is 24 N. ( = 9.81 m/s2 [down]) Which of the following statements is correct? a. The acceleration of block X to the right is less than the acceleration of block Y downward because of the friction on block X. b. The acceleration of block X to the right has ...
... magnitude of the force of friction on block X is 24 N. ( = 9.81 m/s2 [down]) Which of the following statements is correct? a. The acceleration of block X to the right is less than the acceleration of block Y downward because of the friction on block X. b. The acceleration of block X to the right has ...
Chapter 11 - UCF Physics
... space, orbiting their center of mass at speeds of 5.00 m/s. Treating the astronauts as particles, calculate (a) the magnitude of the angular momentum of the system and (b) the rotational energy of the system. By pulling on the rope, one of the astronauts shortens the distance between them to 5.00 m. ...
... space, orbiting their center of mass at speeds of 5.00 m/s. Treating the astronauts as particles, calculate (a) the magnitude of the angular momentum of the system and (b) the rotational energy of the system. By pulling on the rope, one of the astronauts shortens the distance between them to 5.00 m. ...
Vector - DEP
... Displacement is vector quantity :- Aero plane and ship required a fixed direction to go ahead as there are no roads in the sky or in ocean. So distance cover by then is known as displacement , which is vector quantity. Distance is scalar quantity :In roads Bus generally moves according to zig-zag pa ...
... Displacement is vector quantity :- Aero plane and ship required a fixed direction to go ahead as there are no roads in the sky or in ocean. So distance cover by then is known as displacement , which is vector quantity. Distance is scalar quantity :In roads Bus generally moves according to zig-zag pa ...