Dynamics and Statics
... and tries to pull it away from Mary. Is Sarah pulls horizontally on the pillow with a force of 10N and Mary pulls with a horizontal force of 11N, what is the horizontal acceleration of the pillow? ...
... and tries to pull it away from Mary. Is Sarah pulls horizontally on the pillow with a force of 10N and Mary pulls with a horizontal force of 11N, what is the horizontal acceleration of the pillow? ...
Introductory Physics
... For example, if you lean up against a wall, the wall is pushing up against you to keep you from falling over. ...
... For example, if you lean up against a wall, the wall is pushing up against you to keep you from falling over. ...
Types of Variation
... In physics and other sciences, many experiments are performed to obtain or test a relationship between two variables (manipulated and responding). Once the evidence is collected and analyzed, the relationship is expressed clearly and concisely using the concepts and language of mathematics. The math ...
... In physics and other sciences, many experiments are performed to obtain or test a relationship between two variables (manipulated and responding). Once the evidence is collected and analyzed, the relationship is expressed clearly and concisely using the concepts and language of mathematics. The math ...
V - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... Many problems involving the motion of systems of particles can be solved by applying simultaneously the principle of impulse and momentum and the principle of conservation of energy or by expressing that the linear momentum, angular momentum, and energy of the system are conserved. ...
... Many problems involving the motion of systems of particles can be solved by applying simultaneously the principle of impulse and momentum and the principle of conservation of energy or by expressing that the linear momentum, angular momentum, and energy of the system are conserved. ...
Types of Variation
... In physics and other sciences, many experiments are performed to obtain or test a relationship between two variables (manipulated and responding). Once the evidence is collected and analyzed, the relationship is expressed clearly and concisely using the concepts and language of mathematics. The math ...
... In physics and other sciences, many experiments are performed to obtain or test a relationship between two variables (manipulated and responding). Once the evidence is collected and analyzed, the relationship is expressed clearly and concisely using the concepts and language of mathematics. The math ...
2AngDyn - TuHS Physics
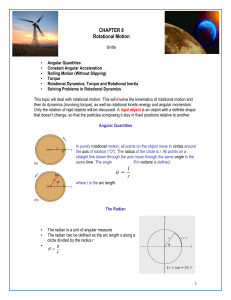
... Angular Mechanics – Torque and moment of inertia Now let’s put it all together, we can calculate torque and moment of inertia, so let’s relate ...
... Angular Mechanics – Torque and moment of inertia Now let’s put it all together, we can calculate torque and moment of inertia, so let’s relate ...
According to Newton`s ______ law, an object with no net force
... 0.0005 s. Calculate the speed of the golf ball immediately after it is hit. 47. (P3.4g)A 0.10 kg lump of clay is moving to the right at 15 m/s. It hits a wall and stops. The impact lasts for 0.003s. a. If the time of impact was increased, what would happen to the average force on the clay? b. If the ...
... 0.0005 s. Calculate the speed of the golf ball immediately after it is hit. 47. (P3.4g)A 0.10 kg lump of clay is moving to the right at 15 m/s. It hits a wall and stops. The impact lasts for 0.003s. a. If the time of impact was increased, what would happen to the average force on the clay? b. If the ...
Chapter 4 Exam Review
... A. For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. B. An object at rest tends to remain at rest while an object in motion tends to remain in motion at the same speed and in the same direction. C. An object in motion will stop easily and quickly if an opposite force is applied to it by ano ...
... A. For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. B. An object at rest tends to remain at rest while an object in motion tends to remain in motion at the same speed and in the same direction. C. An object in motion will stop easily and quickly if an opposite force is applied to it by ano ...
Slide 1
... Isaac Newton last words: "I don't know what I may seem to the world. But as to myself I seem to have been only like a boy playing on the seashore and diverting myself now and then finding a smoother pebble or a prettier shell than the ordinary, whilst the great ocean of truth lay all undiscovered ...
... Isaac Newton last words: "I don't know what I may seem to the world. But as to myself I seem to have been only like a boy playing on the seashore and diverting myself now and then finding a smoother pebble or a prettier shell than the ordinary, whilst the great ocean of truth lay all undiscovered ...
Circular Motion Web Quest:
... 16. A turn is only possible when there is a component of force directed towards the ______ of the circle about which the person is moving. 17. Any given physical situation can be analyzed in terms of the individual _____ which are acting upon an object; these individual forces must add up to the ___ ...
... 16. A turn is only possible when there is a component of force directed towards the ______ of the circle about which the person is moving. 17. Any given physical situation can be analyzed in terms of the individual _____ which are acting upon an object; these individual forces must add up to the ___ ...
IPC Review - Humble ISD
... of 20.0 meters per second. Which statement best describes the time required for the spheres to reach the ground and the horizontal distance they travel? (1) Both spheres hit the ground at the same time and at the same distance from the base of the tower. (2) Both spheres hit the ground at the same t ...
... of 20.0 meters per second. Which statement best describes the time required for the spheres to reach the ground and the horizontal distance they travel? (1) Both spheres hit the ground at the same time and at the same distance from the base of the tower. (2) Both spheres hit the ground at the same t ...
File
... on this equation, if balanced forces act on an object, which of the following outcomes can be expected? ...
... on this equation, if balanced forces act on an object, which of the following outcomes can be expected? ...
Newton`s Laws
... “For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.” Longer Version When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second exerts a force on the first that is equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction. ...
... “For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.” Longer Version When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second exerts a force on the first that is equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction. ...
Newton`s Laws
... “For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.” Longer Version When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second exerts a force on the first that is equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction. ...
... “For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.” Longer Version When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second exerts a force on the first that is equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction. ...
F = force, m = mass, a = acceleration
... baseball as hard as you can, why don't they have the same speed? • Because of their different masses • The acceleration of an object depends on the mass as well as the force applied to it • Force, Mass & Acceleration are all connected • Newton's 2nd Law of Motion describes this relationship ...
... baseball as hard as you can, why don't they have the same speed? • Because of their different masses • The acceleration of an object depends on the mass as well as the force applied to it • Force, Mass & Acceleration are all connected • Newton's 2nd Law of Motion describes this relationship ...