Questions - TTU Physics
... with equations, but keep these to a minimum and explain what the symbols mean!! a. State Newton’s 2nd Law for Rotational Motion. Explain the meaning of any symbols! (Note: The answer ∑F = ma will receive ZERO credit!) b. State the conditions for static equilibrium. Explain the meaning of any symbols ...
... with equations, but keep these to a minimum and explain what the symbols mean!! a. State Newton’s 2nd Law for Rotational Motion. Explain the meaning of any symbols! (Note: The answer ∑F = ma will receive ZERO credit!) b. State the conditions for static equilibrium. Explain the meaning of any symbols ...
to Ms. D`s Power Point Presentation on Chap 6-1
... The north pole of the magnet in your hand repelling the north pole of the hanging magnet. ...
... The north pole of the magnet in your hand repelling the north pole of the hanging magnet. ...
Force - Mona Shores Blogs
... Newton’s Third Law • If two objects interact, the magnitude of the force exerted on object 1 by object 2 is equal to the magnitude of the force simultaneously exerted on object 2 by object 1, and these two forces are opposite in direction. • We will shrink that tongue twister down to for every acti ...
... Newton’s Third Law • If two objects interact, the magnitude of the force exerted on object 1 by object 2 is equal to the magnitude of the force simultaneously exerted on object 2 by object 1, and these two forces are opposite in direction. • We will shrink that tongue twister down to for every acti ...
Kreutter: Dynamics 9 Lesson 9: Applying Newton`s Second Law
... Simplify and Diagram: • Consider the system as a particle. • Decide if you can ignore any interactions of the environment with the system object. • Draw a force diagram for the system. Label the forces with two subscripts. Make sure the diagram is consistent with the acceleration of the system objec ...
... Simplify and Diagram: • Consider the system as a particle. • Decide if you can ignore any interactions of the environment with the system object. • Draw a force diagram for the system. Label the forces with two subscripts. Make sure the diagram is consistent with the acceleration of the system objec ...
Chapter 3 Review - tylerparkerphysicalscience
... Law of conservation of momentum-states that as long as interacting objects are not influenced by outside forces (like friction), their momentum before the interaction will equal their momentum after the interaction. Newton’s first law of motion-states any object at rest will remain at rest unless ac ...
... Law of conservation of momentum-states that as long as interacting objects are not influenced by outside forces (like friction), their momentum before the interaction will equal their momentum after the interaction. Newton’s first law of motion-states any object at rest will remain at rest unless ac ...
IGCSE-13-Forces&Movement
... Calculate the acceleration that is produced by a force of 600N acting on a mass of 120kg. (a) What is weight? (b) Calculate the weight of a person of mass 90kg on the surface of (i) the Earth and (ii) the Moon. (a) Give two factors in each case that would increase the (i) braking distance (ii) think ...
... Calculate the acceleration that is produced by a force of 600N acting on a mass of 120kg. (a) What is weight? (b) Calculate the weight of a person of mass 90kg on the surface of (i) the Earth and (ii) the Moon. (a) Give two factors in each case that would increase the (i) braking distance (ii) think ...
AHSGE Review
... The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed. It can only change forms. Complicated calculations have been completed to prove this law. The conservation of energy depends on whether or not a system is open (energy flowing in and out easily) or closed (energ ...
... The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed. It can only change forms. Complicated calculations have been completed to prove this law. The conservation of energy depends on whether or not a system is open (energy flowing in and out easily) or closed (energ ...
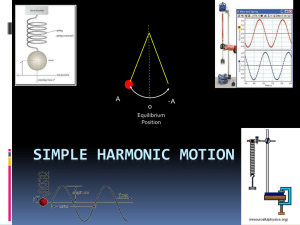
Simple Harmonic motion
... forth replicating the SHM of the mass attached to a spring seen earlier. ...
... forth replicating the SHM of the mass attached to a spring seen earlier. ...
Chapter 2
... depends on the force applied to an object but it also depends on the mass of the object. ...
... depends on the force applied to an object but it also depends on the mass of the object. ...
uniform circular motion
... Velocity can be constant in magnitude, and we still have acceleration because the direction changes. • Direction: towards the center of the circle ...
... Velocity can be constant in magnitude, and we still have acceleration because the direction changes. • Direction: towards the center of the circle ...
Unit 6 Notes NEWTON`S 1 st LAW OF MOTION
... Newton’s third law describes what happens when one object exerts a force on another object. According to Newton’s third law of motion, forces always act in equal but opposite pairs. Newton’s Third Law: For every action, there is an equal but opposite reaction. Newton’s Third Law is also know as the ...
... Newton’s third law describes what happens when one object exerts a force on another object. According to Newton’s third law of motion, forces always act in equal but opposite pairs. Newton’s Third Law: For every action, there is an equal but opposite reaction. Newton’s Third Law is also know as the ...
8th 2014 midterm
... d) A change in the velocity during a time interval divided by the time interval during which the velocity changes. Acceleration e) The speed and the direction of a moving object. Velocity f) The total distance traveled divided by the total time taken to travel that distance. Average speed g) The pro ...
... d) A change in the velocity during a time interval divided by the time interval during which the velocity changes. Acceleration e) The speed and the direction of a moving object. Velocity f) The total distance traveled divided by the total time taken to travel that distance. Average speed g) The pro ...
Week 4
... 17. A jar-opening tool grabs onto a jar’s lid and then provides a long handle for you to turn. Why does this handle’s length help you to open the jar? E.17 By pushing far from the pivot, you exert more torque on the lid. 18. When you climb out on a thin tree limb, there’s a chance that the limb will ...
... 17. A jar-opening tool grabs onto a jar’s lid and then provides a long handle for you to turn. Why does this handle’s length help you to open the jar? E.17 By pushing far from the pivot, you exert more torque on the lid. 18. When you climb out on a thin tree limb, there’s a chance that the limb will ...
PPT - SBEL - University of Wisconsin–Madison
... Sometimes the approach might seem to be an overkill, but it’s general, and remember, it’s the computer that does the work and not you In other words, we hit it with a heavy hammer that takes care of all jobs, although at times it seems like killing a mosquito with a cannon… ...
... Sometimes the approach might seem to be an overkill, but it’s general, and remember, it’s the computer that does the work and not you In other words, we hit it with a heavy hammer that takes care of all jobs, although at times it seems like killing a mosquito with a cannon… ...
Document
... If we know the moment of inertia through the centre of mass, the moment of inertia along a parallel axis d is; ...
... If we know the moment of inertia through the centre of mass, the moment of inertia along a parallel axis d is; ...
Forces And Motion
... the acceleration will be in comparison to an object with a larger mass. • Force= mass x acceleration ...
... the acceleration will be in comparison to an object with a larger mass. • Force= mass x acceleration ...
Potoourii of Interia Demos - Otterbein Neutrino Research Group
... The bicycle wheel, you, and the chair comprise a system that obeys the principle of conservation of angular momentum. This means that any change in angular momentum within the system must be accompanied by an equal and opposite change, so the net effect is zero. Suppose you are now sitting on the st ...
... The bicycle wheel, you, and the chair comprise a system that obeys the principle of conservation of angular momentum. This means that any change in angular momentum within the system must be accompanied by an equal and opposite change, so the net effect is zero. Suppose you are now sitting on the st ...
Chapter 6 – Force and Motion II
... -Terminal speed: vt - Reached when the acceleration of an object that experiences a vertical movement through the air becomes zero Fg=D ...
... -Terminal speed: vt - Reached when the acceleration of an object that experiences a vertical movement through the air becomes zero Fg=D ...