Chapter 4 Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion continued
... Newton’s 3rd law: Whatever magnitude of force the bat applies to the ball, the ball applies the same magnitude of force back (opposite direction) onto the bat. The bat is slowed by the force of the ball on the bat, and the ball is accelerated by the force of the bat A gun firing a bullet Newton’s 3r ...
... Newton’s 3rd law: Whatever magnitude of force the bat applies to the ball, the ball applies the same magnitude of force back (opposite direction) onto the bat. The bat is slowed by the force of the ball on the bat, and the ball is accelerated by the force of the bat A gun firing a bullet Newton’s 3r ...
Slide 1
... – Your mass is the same in both locations. – The acceleration due to gravity on Earth is 9.8 m/s2, and the moon’s acceleration due to gravity is 1/6th that on Earth. ...
... – Your mass is the same in both locations. – The acceleration due to gravity on Earth is 9.8 m/s2, and the moon’s acceleration due to gravity is 1/6th that on Earth. ...
Newton`s Second Law: Acceleration
... • The combination of all forces acting on an object is called the net force. • Acceleration depends on the net force. • To increase the acceleration of an object, you must increase the net force acting on it. • An object’s acceleration is directly proportional to the net force acting on it: ...
... • The combination of all forces acting on an object is called the net force. • Acceleration depends on the net force. • To increase the acceleration of an object, you must increase the net force acting on it. • An object’s acceleration is directly proportional to the net force acting on it: ...
CURRICULUM SUMMARY – September to October 2008
... Forces acting on bodies balanced & unbalanced (possible poster) Class exercise terminal velocity sky-diver.. working through stages of initial jump, acceleration to terminal velocity, effect of opening parachute and ground landing ...
... Forces acting on bodies balanced & unbalanced (possible poster) Class exercise terminal velocity sky-diver.. working through stages of initial jump, acceleration to terminal velocity, effect of opening parachute and ground landing ...
N 1 - EngineeringDuniya.com
... When different forces act on a system such that it is in motion with an acceleration in a particular direction, the vectorial sum of all the forces acting on the system including the inertia force (‘ma’ taken in the opposite direction to the direction of the acceleration) is zero. ...
... When different forces act on a system such that it is in motion with an acceleration in a particular direction, the vectorial sum of all the forces acting on the system including the inertia force (‘ma’ taken in the opposite direction to the direction of the acceleration) is zero. ...
StudyGuideForcesAP2016
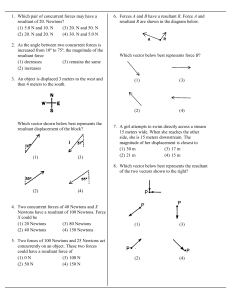
... 10. A 5 kg mass is pulled upward (off the ground) from rest by a rope exerting 80 N of force. What is the velocity of the mass after 5 seconds? 11. A 50 kg woman is standing on a scale moving downwards and speeding up at a rate of 3 m/s each second. What value does the scale read? 12. A woman pulls ...
... 10. A 5 kg mass is pulled upward (off the ground) from rest by a rope exerting 80 N of force. What is the velocity of the mass after 5 seconds? 11. A 50 kg woman is standing on a scale moving downwards and speeding up at a rate of 3 m/s each second. What value does the scale read? 12. A woman pulls ...
Newton`s First Law of Motion Friction and Newton`s First Law
... between an object and the surface it is moving over is an example of an unbalanced force that stops motion. • Inertia and Newton’s First Law Newton’s first law is sometimes called the law of inertia. Inertia is the tendency of all objects to resist any change in motion. ...
... between an object and the surface it is moving over is an example of an unbalanced force that stops motion. • Inertia and Newton’s First Law Newton’s first law is sometimes called the law of inertia. Inertia is the tendency of all objects to resist any change in motion. ...
Slide 1
... • The thing to do would be to take one of the tools from your tool belt and throw it is hard as you can directly away from the shuttle. Then, with the help of Newton's second and third laws, you will accelerate back towards the shuttle. As you throw the tool, you push against it, causing it to accel ...
... • The thing to do would be to take one of the tools from your tool belt and throw it is hard as you can directly away from the shuttle. Then, with the help of Newton's second and third laws, you will accelerate back towards the shuttle. As you throw the tool, you push against it, causing it to accel ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... • The thing to do would be to take one of the tools from your tool belt and throw it is hard as you can directly away from the shuttle. Then, with the help of Newton's second and third laws, you will accelerate back towards the shuttle. As you throw the tool, you push against it, causing it to accel ...
... • The thing to do would be to take one of the tools from your tool belt and throw it is hard as you can directly away from the shuttle. Then, with the help of Newton's second and third laws, you will accelerate back towards the shuttle. As you throw the tool, you push against it, causing it to accel ...
Newton - Swampscott Middle School
... • The thing to do would be to take one of the tools from your tool belt and throw it is hard as you can directly away from the shuttle. Then, with the help of Newton's second and third laws, you will accelerate back towards the shuttle. As you throw the tool, you push against it, causing it to accel ...
... • The thing to do would be to take one of the tools from your tool belt and throw it is hard as you can directly away from the shuttle. Then, with the help of Newton's second and third laws, you will accelerate back towards the shuttle. As you throw the tool, you push against it, causing it to accel ...
The Nature of Force and Motion
... 26. Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion – If one object exerts a force on another object, then the 2nd object exerts a force of equal strength in the opposite direction on the 1st object. 27. Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion - For every action force there is an equal in strength and opposite in direction reaction ...
... 26. Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion – If one object exerts a force on another object, then the 2nd object exerts a force of equal strength in the opposite direction on the 1st object. 27. Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion - For every action force there is an equal in strength and opposite in direction reaction ...
Force and Motion PPT
... • It would take more force to move an elephant than it would to move a mouse ...
... • It would take more force to move an elephant than it would to move a mouse ...
UNIT 7 Lab
... a. Tie a small object to one end of a string, put the other end of the string through a straw and then tie about 200g of mass to the other end. Holding the straw, twirl the object around in a circle (Try to make the circle as horizontal as possible.) b. Draw a force diagram for the object and for th ...
... a. Tie a small object to one end of a string, put the other end of the string through a straw and then tie about 200g of mass to the other end. Holding the straw, twirl the object around in a circle (Try to make the circle as horizontal as possible.) b. Draw a force diagram for the object and for th ...
Newton`s laws of motion
... Newton's third law does not mean that forces always cancel out so that nothing can ever move. If these two figure skaters, initially at rest, push against each other, they will both move. ...
... Newton's third law does not mean that forces always cancel out so that nothing can ever move. If these two figure skaters, initially at rest, push against each other, they will both move. ...
Acceleration - Sikeston R-6
... Teacher Page •IV. Force, motion and mechanical energy •A. Relative Motion •7th grade assessment •Science standards 3.1; 3.3; 4.1 •Students should be able to explain how an object’s acceleration is affected by outside forces and its mass. •View lesson before using with students. Click mouse to view s ...
... Teacher Page •IV. Force, motion and mechanical energy •A. Relative Motion •7th grade assessment •Science standards 3.1; 3.3; 4.1 •Students should be able to explain how an object’s acceleration is affected by outside forces and its mass. •View lesson before using with students. Click mouse to view s ...