Physics 111 Problem Set 8, Chapter 9
... dropped from the same point at t = 100 ms. (a) How far below the release point is the center of mass of the two stones at t = 300 ms? (Neither stone has yet reached the ground.) (b) How fast is the center of mass of the two-stone system moving at that time? ...
... dropped from the same point at t = 100 ms. (a) How far below the release point is the center of mass of the two stones at t = 300 ms? (Neither stone has yet reached the ground.) (b) How fast is the center of mass of the two-stone system moving at that time? ...
Chapter 8:
... and weight 80.0 N. A cable, inclined at a 35 angle with the boom, is attached at a distance of 2.38 m from the hinge at the wall. The weight of the sign is 120.0 N. ...
... and weight 80.0 N. A cable, inclined at a 35 angle with the boom, is attached at a distance of 2.38 m from the hinge at the wall. The weight of the sign is 120.0 N. ...
AM #1-35 - Edublogs
... 5. How is friction involved in unbalanced forces? 6. What 2 factors affect friction? AM #26 1. What are the 2 kinds of friction? 2. State one way that friction can be helpful and one way that friction can be harmful. 3. What is gravity? What unit do we use to measure gravity? 4. What do you have to ...
... 5. How is friction involved in unbalanced forces? 6. What 2 factors affect friction? AM #26 1. What are the 2 kinds of friction? 2. State one way that friction can be helpful and one way that friction can be harmful. 3. What is gravity? What unit do we use to measure gravity? 4. What do you have to ...
What is a Force?
... You are going down the road on your inline skates. Suddenly you look to your right and see a car accelerating fast coming right for you! You look for an escape to your left… Oh no! There’s a rock at the edge of neatly manicured lawn. Which will you choose... ...
... You are going down the road on your inline skates. Suddenly you look to your right and see a car accelerating fast coming right for you! You look for an escape to your left… Oh no! There’s a rock at the edge of neatly manicured lawn. Which will you choose... ...
Mechanics
... by a force F that is greater in magnitude than the rock's weight W. The change in kinetic energy of the rock during this time is equal to the (A) work done by the net force (F - W) (B) work done by F alone (C) work done by W alone (D) difference in the momentum of the rock before and after this time ...
... by a force F that is greater in magnitude than the rock's weight W. The change in kinetic energy of the rock during this time is equal to the (A) work done by the net force (F - W) (B) work done by F alone (C) work done by W alone (D) difference in the momentum of the rock before and after this time ...
17 M3 January 2006
... A booklet ‘Mathematical Formulae and Statistical Tables’ is provided. Full marks may be obtained for answers to ALL questions. The marks for individual questions and the parts of questions are shown in round brackets: e.g. (2). There are 7 questions on this paper. The total mark for this paper is 75 ...
... A booklet ‘Mathematical Formulae and Statistical Tables’ is provided. Full marks may be obtained for answers to ALL questions. The marks for individual questions and the parts of questions are shown in round brackets: e.g. (2). There are 7 questions on this paper. The total mark for this paper is 75 ...
chapter 2 - temsscience7
... required to overcome the force of gravity and part of it is required to give the desired acceleration. Compare this problem to problem 2 where the motion is in a horizontal direction and the force of gravity was perpendicular to the motion. ...
... required to overcome the force of gravity and part of it is required to give the desired acceleration. Compare this problem to problem 2 where the motion is in a horizontal direction and the force of gravity was perpendicular to the motion. ...
Unit A: Kinematics Exam
... “k” is know as a spring/elastic constant, this k value is unique for every spring. The value of this constant tells us how hard we must push/pull on a spring in order for it to expand/ contract. The “x” is the distance away from equilibrium x=0. ...
... “k” is know as a spring/elastic constant, this k value is unique for every spring. The value of this constant tells us how hard we must push/pull on a spring in order for it to expand/ contract. The “x” is the distance away from equilibrium x=0. ...
Monday, June 21, 2004 - UTA High Energy Physics page.
... People have been very curious about the stars in the sky, making observations for a long time. But the data people collected have not been explained until Newton has discovered the law of gravitation. Every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proporti ...
... People have been very curious about the stars in the sky, making observations for a long time. But the data people collected have not been explained until Newton has discovered the law of gravitation. Every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proporti ...
Angular Momentum about Center of Mass
... A gyroscope wheel is at one end of an axle of length d . The oth er end of the axle is suspended from a string of length s . The wheel is set into motion so that it executes uniform precession in the horizontal plane. The string makes an angle with the vertical. The wheel has mass M and moment of ...
... A gyroscope wheel is at one end of an axle of length d . The oth er end of the axle is suspended from a string of length s . The wheel is set into motion so that it executes uniform precession in the horizontal plane. The string makes an angle with the vertical. The wheel has mass M and moment of ...
1 PHYSICS 231 Lecture 9: More on forces
... First Law: If the net force exerted on an object is zero the object continues in its original state of motion; if it was at rest, it remains at rest. If it was moving with a certain velocity, it will keep on moving with the same velocity. Second Law: The acceleration of an object is proportional ...
... First Law: If the net force exerted on an object is zero the object continues in its original state of motion; if it was at rest, it remains at rest. If it was moving with a certain velocity, it will keep on moving with the same velocity. Second Law: The acceleration of an object is proportional ...
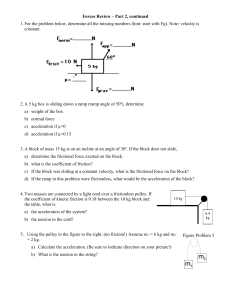
Review Forces Part 2
... a) What is the acceleration of the block? b) What is the distance covered in 10 s, if the initial velocity is 1.5 m/s? 7. A boy on a sled (total mass = 80 kg) is sliding down a snow-covered hill. The slope is at an angle of 15 to the horizontal. Find the boy’s a) acceleration if there is no frictio ...
... a) What is the acceleration of the block? b) What is the distance covered in 10 s, if the initial velocity is 1.5 m/s? 7. A boy on a sled (total mass = 80 kg) is sliding down a snow-covered hill. The slope is at an angle of 15 to the horizontal. Find the boy’s a) acceleration if there is no frictio ...
REGULATION 2013 ACADEMIC YEAR 2014
... 10. Write the mathematical expression for velocity. 11. Write short notes on speed vs velocity. 12. Write the equation of initial, final velocity formula. 13. What is average velocity? 14. Define instantaneous velocity? 15. Write the formula to find out the instantaneous velocity? 16. Find the Insta ...
... 10. Write the mathematical expression for velocity. 11. Write short notes on speed vs velocity. 12. Write the equation of initial, final velocity formula. 13. What is average velocity? 14. Define instantaneous velocity? 15. Write the formula to find out the instantaneous velocity? 16. Find the Insta ...