Review
... An object acted on by three forces moves with constant velocity. One force acting on the object is in the positive x direction and has a magnitude of 6.5 N; a second force has a magnitude of 4.4 N and points in the negative y direction. Find the direction and magnitude of the third force acting on t ...
... An object acted on by three forces moves with constant velocity. One force acting on the object is in the positive x direction and has a magnitude of 6.5 N; a second force has a magnitude of 4.4 N and points in the negative y direction. Find the direction and magnitude of the third force acting on t ...
Document
... How would the previous problem change if the boy threw the ball at an upward angle? In this type of problem yi ≠ 0. Therefore, we must account for the fact that gravity (g) first has to bring the upward velocity to a stop and then change the direction to downward. So the path of the object is a pa ...
... How would the previous problem change if the boy threw the ball at an upward angle? In this type of problem yi ≠ 0. Therefore, we must account for the fact that gravity (g) first has to bring the upward velocity to a stop and then change the direction to downward. So the path of the object is a pa ...
File
... An object of mass m is initially at rest and free to move without friction in any direction in the xy-plane. A constant net force of magnitude F directed in the +x direction acts on the object for 1 s. Immediately thereafter a constant net force of the same magnitude F directed in the +y direction a ...
... An object of mass m is initially at rest and free to move without friction in any direction in the xy-plane. A constant net force of magnitude F directed in the +x direction acts on the object for 1 s. Immediately thereafter a constant net force of the same magnitude F directed in the +y direction a ...
PowerPoint Lecture Chapter 6
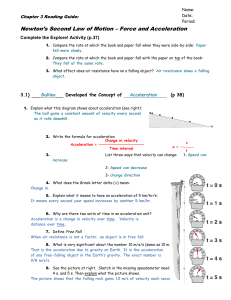
... Arrange Newton’s second law to read: force = mass × acceleration F = ma = (30,000 kg)(1.5 m/s2) = 45,000 kg•m/s2 = 45,000 N ...
... Arrange Newton’s second law to read: force = mass × acceleration F = ma = (30,000 kg)(1.5 m/s2) = 45,000 kg•m/s2 = 45,000 N ...
Physics 112 Course Review #1 Due Friday, Dec. 5 1. Describe what
... 10. A 45 kg diver steps off a 13 m high platform (initial velocity is zero). The swimmer comes to a stop 2.8 m below the surface of the water. Calculate the net stopping force exerted by the water. (F = 2050 N) ...
... 10. A 45 kg diver steps off a 13 m high platform (initial velocity is zero). The swimmer comes to a stop 2.8 m below the surface of the water. Calculate the net stopping force exerted by the water. (F = 2050 N) ...
U2_Physics - Orange Public Schools
... Connections to other DCIs in this grade-band: HS.PS3.A (HS-PS2-4),(HS-PS2-5); HS.PS3.C (HS-PS2-1); HS.PS4.B (HS-PS2-5); HS.ESS1.A (HS-PS2-1),(HS-PS2-2),(HS-PS2-4); HS.ESS1.B (HS-PS2-4); HS.ESS1.C(HSPS2-1),(HS-PS2-2),(HS-PS2-4); HS.ESS2.A (HS-PS2-5); HS.ESS2.C (HS-PS2-1),(HS-PS2-4); HS.ESS3.A (HS-PS2 ...
... Connections to other DCIs in this grade-band: HS.PS3.A (HS-PS2-4),(HS-PS2-5); HS.PS3.C (HS-PS2-1); HS.PS4.B (HS-PS2-5); HS.ESS1.A (HS-PS2-1),(HS-PS2-2),(HS-PS2-4); HS.ESS1.B (HS-PS2-4); HS.ESS1.C(HSPS2-1),(HS-PS2-2),(HS-PS2-4); HS.ESS2.A (HS-PS2-5); HS.ESS2.C (HS-PS2-1),(HS-PS2-4); HS.ESS3.A (HS-PS2 ...
Test Review Slides - University of Mount Union
... Draw picture/sketch of what is going on (object, ropes, surfaces) Draw free-body diagrams using all the forces (contact & long-range) acting on object at a common point, then identify the net force. Choose direction of axis (tilted for ramp problems) Decompose vectors into components (magnitude and ...
... Draw picture/sketch of what is going on (object, ropes, surfaces) Draw free-body diagrams using all the forces (contact & long-range) acting on object at a common point, then identify the net force. Choose direction of axis (tilted for ramp problems) Decompose vectors into components (magnitude and ...
Exam II Difficult Problems
... • For the mass in the problem above, what is the magnitude of the normal force exerted on the block by the hoop when the block reaches the bottom of the hoop? F⊥ supports weight and provides centripetal force for circular motion. ...
... • For the mass in the problem above, what is the magnitude of the normal force exerted on the block by the hoop when the block reaches the bottom of the hoop? F⊥ supports weight and provides centripetal force for circular motion. ...