Collisions – Impulse and Momentum
... 4. At the bottom left of the screen click on Record to start collecting data, and let go of the dynamics cart, allowing it to be accelerated down the dynamics track till it collides with the force sensor, economy. About one second after the collision click on Stop to stop recording data. 5. Rescal ...
... 4. At the bottom left of the screen click on Record to start collecting data, and let go of the dynamics cart, allowing it to be accelerated down the dynamics track till it collides with the force sensor, economy. About one second after the collision click on Stop to stop recording data. 5. Rescal ...
ch 13 - Simple Harmonic Motion
... • The center of gravity of simple pendulum of mass m and length L is located at the position of the pendulum bob, a distance L from the pivot point. The center of gravity of a uniform rod of the same mass m and length 2L pivoted at one end is also a distance L from the pivot point. How does the peri ...
... • The center of gravity of simple pendulum of mass m and length L is located at the position of the pendulum bob, a distance L from the pivot point. The center of gravity of a uniform rod of the same mass m and length 2L pivoted at one end is also a distance L from the pivot point. How does the peri ...
Generation of Gravitational Force
... electron is dependent on force applied on it, and the resultant force is dependent on its position. The average value of resultant force Fe is not ZERO and is positive in all elements of matter. It was solved with certain assumptions for distance between atoms ( d ) ranging from 10-6 m to 107 m by a ...
... electron is dependent on force applied on it, and the resultant force is dependent on its position. The average value of resultant force Fe is not ZERO and is positive in all elements of matter. It was solved with certain assumptions for distance between atoms ( d ) ranging from 10-6 m to 107 m by a ...
Chapter 11
... Example: An automobile having a mass of 1000 kg is driven into a brick wall in a safety test. The bumper acts like a spring with a constant 5.00 x 106 N/m and is compressed 3.16 cm as the car is brought to rest. What was the speed of the car before impact, assuming that no energy is lost in the coll ...
... Example: An automobile having a mass of 1000 kg is driven into a brick wall in a safety test. The bumper acts like a spring with a constant 5.00 x 106 N/m and is compressed 3.16 cm as the car is brought to rest. What was the speed of the car before impact, assuming that no energy is lost in the coll ...
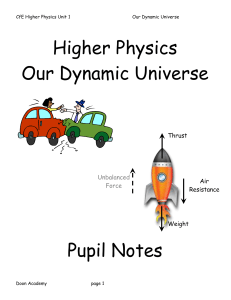
Our Dynamic Universe notes
... time it takes for the space craft to make one orbit will appear much longer than the time it actually takes to orbit. This is known as time dilation. Example: You leave earth and your twin to go on a space mission. You are in a spaceship travelling at 90% the speed of light and you go on a journey t ...
... time it takes for the space craft to make one orbit will appear much longer than the time it actually takes to orbit. This is known as time dilation. Example: You leave earth and your twin to go on a space mission. You are in a spaceship travelling at 90% the speed of light and you go on a journey t ...
Chapter 8
... A rigid body is an object or a system of particles in which the distances between particles are fixed (remain constant). In other words, a rigid body must be solid (but not all solid bodies are rigid). ...
... A rigid body is an object or a system of particles in which the distances between particles are fixed (remain constant). In other words, a rigid body must be solid (but not all solid bodies are rigid). ...
Momentum and Impulse
... – There are two kinds of momentum, linear and angular. A spinning object has angular momentum; an object traveling with a velocity has linear momentum. For now, and throughout chapter 7, we'll deal with linear momentum, and just refer to it as momentum, without the “linear”. – Things to know about m ...
... – There are two kinds of momentum, linear and angular. A spinning object has angular momentum; an object traveling with a velocity has linear momentum. For now, and throughout chapter 7, we'll deal with linear momentum, and just refer to it as momentum, without the “linear”. – Things to know about m ...
Practice Final
... 4) The fastest airplane is the Lockheed SR-71. If an SR-71 flies 10.0 miles in 15.3 sec, what is its average speed? A) 0.654 mph B) 39.2 mph C) 780 mph D) 1430 mph E) 2350 mph 5) How fast will a motorcycle starting at rest go after 5 seconds if its acceleration is 3 m/s2? A) 7 m/s B) 12 m/s C) 15 m/ ...
... 4) The fastest airplane is the Lockheed SR-71. If an SR-71 flies 10.0 miles in 15.3 sec, what is its average speed? A) 0.654 mph B) 39.2 mph C) 780 mph D) 1430 mph E) 2350 mph 5) How fast will a motorcycle starting at rest go after 5 seconds if its acceleration is 3 m/s2? A) 7 m/s B) 12 m/s C) 15 m/ ...
P3 Forces for Transport
... 1) Paddy likes playing golf. He strikes a golf ball with a force of 80N. If the ball has a mass of 200g and the club is in contact with it for 0.2s calculate a) the change in momentum of the golf ball, b) its speed. ...
... 1) Paddy likes playing golf. He strikes a golf ball with a force of 80N. If the ball has a mass of 200g and the club is in contact with it for 0.2s calculate a) the change in momentum of the golf ball, b) its speed. ...
Ch 16: Electric Charge and Electric Field
... Charge is measured in units of Coulombs, C, after the inventor of Coulomb’s Law. 1C is the amount of charge which, if placed on each of 2 point objects 1 m apart, will result in each object exerting a force of 9.0 x 109 N on the other. This would be enormous force (almost 1 trillion tons) so w ...
... Charge is measured in units of Coulombs, C, after the inventor of Coulomb’s Law. 1C is the amount of charge which, if placed on each of 2 point objects 1 m apart, will result in each object exerting a force of 9.0 x 109 N on the other. This would be enormous force (almost 1 trillion tons) so w ...
Mass on a plane with friction
... 2 attached masses on an inclined plane But how do you determine if acceleration will be up or down the plane? Compare the values of m1gsinθ and m2g to determine which is bigger. If m1gsinθ is bigger it will pull the mass down the plane. If m2g is bigger it will pull the mass up the plane. In genera ...
... 2 attached masses on an inclined plane But how do you determine if acceleration will be up or down the plane? Compare the values of m1gsinθ and m2g to determine which is bigger. If m1gsinθ is bigger it will pull the mass down the plane. If m2g is bigger it will pull the mass up the plane. In genera ...