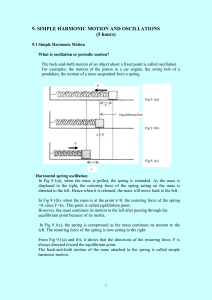
simple harmonic motion and oscilation
... extended by 2.00 cm. If the mass is oscillating in vertical plane, a) Prove that the mass is in simple harmonic motion, and b) Find i) the period of the motion. ii) the frequency of its oscillation. iii) the maximum velocity of the particle iv) the maximum kinetic energy of the particle. ...
... extended by 2.00 cm. If the mass is oscillating in vertical plane, a) Prove that the mass is in simple harmonic motion, and b) Find i) the period of the motion. ii) the frequency of its oscillation. iii) the maximum velocity of the particle iv) the maximum kinetic energy of the particle. ...
Lecture 12
... – The work done by the object (on something else) on a given path is equivalent to the work done by the something else on the object on its return trip. – This means that the net work done on the object over the closed loop is zero, which means, from the workenergy theorem, that the change in energy ...
... – The work done by the object (on something else) on a given path is equivalent to the work done by the something else on the object on its return trip. – This means that the net work done on the object over the closed loop is zero, which means, from the workenergy theorem, that the change in energy ...
FanCartPhysicsSE-1
... 4. Experiment: Select the BAR CHART tab and turn on Show numerical values. For each of the situations below, record the acceleration of the cart. ...
... 4. Experiment: Select the BAR CHART tab and turn on Show numerical values. For each of the situations below, record the acceleration of the cart. ...
"Video Input Driven Animation (VIDA)",
... It is difficult to tackle these problems in a unified, comprehensive way. Rather, it would appear that different approaches will be needed for different classes of phenomena. In this paper, we shall validate VIDA by studying the problem of inverse harmonic oscillation and use it to “reverse engineer ...
... It is difficult to tackle these problems in a unified, comprehensive way. Rather, it would appear that different approaches will be needed for different classes of phenomena. In this paper, we shall validate VIDA by studying the problem of inverse harmonic oscillation and use it to “reverse engineer ...
SEC - Warrenphysics
... incline? At what rate is the force of the rope doing work on the skier when the rope moves with a speed of (b) 1.0 m/s and (c) 2.0 m/s? 35P. A fully loaded, slow-moving freight elevator has a cab with a total mass of 1200 kg, which is required to travel upward 54 m in 3.0 min, starting and ending at ...
... incline? At what rate is the force of the rope doing work on the skier when the rope moves with a speed of (b) 1.0 m/s and (c) 2.0 m/s? 35P. A fully loaded, slow-moving freight elevator has a cab with a total mass of 1200 kg, which is required to travel upward 54 m in 3.0 min, starting and ending at ...
Motion - GEOCITIES.ws
... A. They are exactly the same. B. Speed tells how fast you are going, velocity only gives you the direction. C. They both tell you how fast you are going, but speed also gives the direction. D. They have nothing in common. E. They both tell you how fast you are going, but velocity also gives the dire ...
... A. They are exactly the same. B. Speed tells how fast you are going, velocity only gives you the direction. C. They both tell you how fast you are going, but speed also gives the direction. D. They have nothing in common. E. They both tell you how fast you are going, but velocity also gives the dire ...
Forces and Their Measurement
... This proportionality can be stated as an equality with the introduction of the body’s mass, resulting in the famous Newtonian equation F = ma. The International System unit for force is the newton (N), with 1 N being the force needed to cause a mass of 1 kg to accelerate by 1 m/s2. Simply put, an ap ...
... This proportionality can be stated as an equality with the introduction of the body’s mass, resulting in the famous Newtonian equation F = ma. The International System unit for force is the newton (N), with 1 N being the force needed to cause a mass of 1 kg to accelerate by 1 m/s2. Simply put, an ap ...