Second Law teacher power point
... acceleration a, and the applied force F is F = ma. Acceleration and force are vectors (as indicated by their symbols being displayed in slant bold font); in this law the direction of the force vector is the same as the direction of the acceleration vector. Newton's Third Law of Motion: III. For ever ...
... acceleration a, and the applied force F is F = ma. Acceleration and force are vectors (as indicated by their symbols being displayed in slant bold font); in this law the direction of the force vector is the same as the direction of the acceleration vector. Newton's Third Law of Motion: III. For ever ...
Newton`s Laws Gravity & Falling Objects Energy, Work
... An object resists change in motion – an object in motion will stay on motion or an object at rest will stay at rest unless acted upon by an outside force. ...
... An object resists change in motion – an object in motion will stay on motion or an object at rest will stay at rest unless acted upon by an outside force. ...
The Nature of Force
... means they take up the same amount of space. The difference is the amount of mass each one has. Mass is the amount of matter in an object. ...
... means they take up the same amount of space. The difference is the amount of mass each one has. Mass is the amount of matter in an object. ...
5.7 Newtons Laws of motion
... The acceleration produced by a net force on an object is directly proportional to the net force, is in the same direction as the net force, and is inversely proportional to the mass of the object. ...
... The acceleration produced by a net force on an object is directly proportional to the net force, is in the same direction as the net force, and is inversely proportional to the mass of the object. ...
P2.3 Rev
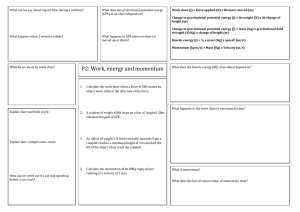
... Work done (j) = force applied (N) x Distance moved (m) Change in gravitational potential energy (j) = its weight (N) x its change of height (m) Change in gravitational potential energy (j) = mass (Kg) x gravitational field strength (N/Kg) x change of height (m) ...
... Work done (j) = force applied (N) x Distance moved (m) Change in gravitational potential energy (j) = its weight (N) x its change of height (m) Change in gravitational potential energy (j) = mass (Kg) x gravitational field strength (N/Kg) x change of height (m) ...
Survey about us Survey about us How do we describe motion?
... How do gravity and energy together ...
... How do gravity and energy together ...
hw4,5
... 2) A block is dragged without acceleration in a straight-line path across a level surface by a force of 6 N. What is the force of friction between the block and the surface? A) less than 6 N B) more than 6 N C) 6 N D) need more information to say ...
... 2) A block is dragged without acceleration in a straight-line path across a level surface by a force of 6 N. What is the force of friction between the block and the surface? A) less than 6 N B) more than 6 N C) 6 N D) need more information to say ...
Pre-lab on forces
... 1. How does the mass of the car affect the force at which it hits the wall? 2. Do you see any relationship between the mass of the car and its velocity? (If mass increases, does velocity increase?) 3. If a semi-truck and a Honda Civic were to hit a block wall going at the same velocity, which would ...
... 1. How does the mass of the car affect the force at which it hits the wall? 2. Do you see any relationship between the mass of the car and its velocity? (If mass increases, does velocity increase?) 3. If a semi-truck and a Honda Civic were to hit a block wall going at the same velocity, which would ...
CONForces
... STRAIGHT LINE unless acted upon by an outside force. ◦ Simply put…objects like to keep doing what they’re doing. ...
... STRAIGHT LINE unless acted upon by an outside force. ◦ Simply put…objects like to keep doing what they’re doing. ...
33333.3 N How much force is needed to keep a 1000 g ball moving
... This is the law that explains why, when riding a skateboard, if you hit a pebble stopping the board, you continue to move forward. ...
... This is the law that explains why, when riding a skateboard, if you hit a pebble stopping the board, you continue to move forward. ...
Chapter 6 Guided Questions
... 4. What is the formula for the Velocity of a Falling Object? 5. In the formula, what is G equal to? 6. What force opposes the motion of objects through air? 7. What does air resistance depend upon? 8. What is Terminal Velocity? Explain how terminal velocity is reached. 9. What is free fall? 10. Wher ...
... 4. What is the formula for the Velocity of a Falling Object? 5. In the formula, what is G equal to? 6. What force opposes the motion of objects through air? 7. What does air resistance depend upon? 8. What is Terminal Velocity? Explain how terminal velocity is reached. 9. What is free fall? 10. Wher ...
Forces
... change because it’s location has changed. – Weight is a vector measurement of the force gravity exerts on an object. If you take an object from the surface of the earth to the surface of the moon, it’s weight will change, but it’s mass will not. ...
... change because it’s location has changed. – Weight is a vector measurement of the force gravity exerts on an object. If you take an object from the surface of the earth to the surface of the moon, it’s weight will change, but it’s mass will not. ...
Chapter 2 Study Guide
... Be able to calculate the speed of an object: 20. What is the formula for speed: ______________________________________________________ Be able to calculate average speed: 21. What is average speed? _____________________________________________________________ 22. What is the formula for average spee ...
... Be able to calculate the speed of an object: 20. What is the formula for speed: ______________________________________________________ Be able to calculate average speed: 21. What is average speed? _____________________________________________________________ 22. What is the formula for average spee ...