1a - cloudfront.net
... 1a. On the earth, what is the ratio of an object’s weight to its mass? (Hint: The “ratio of x to y” = x/y.) b. A rock is dropped over the edge of a cliff. What is the rock’s acceleration? 2. Kyle is mad at Tu and pushes him to the right with a force of 500N. Tu’s body pushes back on Kyle with an equ ...
... 1a. On the earth, what is the ratio of an object’s weight to its mass? (Hint: The “ratio of x to y” = x/y.) b. A rock is dropped over the edge of a cliff. What is the rock’s acceleration? 2. Kyle is mad at Tu and pushes him to the right with a force of 500N. Tu’s body pushes back on Kyle with an equ ...
Dynamics
... motion will remain at rest or in uniform motion unless acted on by an external force. (AKA) an object at rest stays at rest Remember the table cloth demo? ...
... motion will remain at rest or in uniform motion unless acted on by an external force. (AKA) an object at rest stays at rest Remember the table cloth demo? ...
Dynamics Introduction to Forces Fundamental Forces
... surfaces will act differently with respect to friction. Every surface has a different amount of “grippeness”. This grippeness can be measured, and then for every pair of surfaces an associated value is given. This grippeness value is called the coefficient of friction. The symbol for the coefficient ...
... surfaces will act differently with respect to friction. Every surface has a different amount of “grippeness”. This grippeness can be measured, and then for every pair of surfaces an associated value is given. This grippeness value is called the coefficient of friction. The symbol for the coefficient ...
Chapter 4
... • Mutual force of attraction between any two objects • Expressed by Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation: – Every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proportional to the product of the masses of the particles and inversely proportional to the square ...
... • Mutual force of attraction between any two objects • Expressed by Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation: – Every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proportional to the product of the masses of the particles and inversely proportional to the square ...
Chapter 3 - Celina City Schools
... a) ____________ is a physical quantity that includes both size and direction B) ____________ the distance an object travels per unit time, is measured as ____________ per Second (m/s) in SI units 1) Calculation: speed = ____________ / time s=d/t 2) Speed ____________ as an object moves from one plac ...
... a) ____________ is a physical quantity that includes both size and direction B) ____________ the distance an object travels per unit time, is measured as ____________ per Second (m/s) in SI units 1) Calculation: speed = ____________ / time s=d/t 2) Speed ____________ as an object moves from one plac ...
Energy and Forces in Motion MS
... constant speed and in a straight line unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.” An unbalanced force doesn’t just mean someone stopping the object. Gravity, air resistance and friction are all unbalanced forces. ...
... constant speed and in a straight line unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.” An unbalanced force doesn’t just mean someone stopping the object. Gravity, air resistance and friction are all unbalanced forces. ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion Project
... A change in motion occurs only if a net force is exerted on an object. A net force changes the velocity of the object, and causes it to accelerate. If an object is acted upon by a net force, the change in velocity will be in the direction of the net force. The acceleration of an object depen ...
... A change in motion occurs only if a net force is exerted on an object. A net force changes the velocity of the object, and causes it to accelerate. If an object is acted upon by a net force, the change in velocity will be in the direction of the net force. The acceleration of an object depen ...
Applications of Newton`s first law of motion
... and the Normal Force An object at rest must have no net force on it. If it is sitting on a table, the force of gravity is still there; what other force is there? The force exerted perpendicular to a surface is called the normal force. It is exactly as large as needed to balance the force from the ob ...
... and the Normal Force An object at rest must have no net force on it. If it is sitting on a table, the force of gravity is still there; what other force is there? The force exerted perpendicular to a surface is called the normal force. It is exactly as large as needed to balance the force from the ob ...
Normal Reaction force
... The book is at rest, so, the resultant force on the book is zero. As a result N and mg are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. N and mg both act on the book and therefore cannot be action and reaction in the sense of Newton's 3 rd Law because action and reaction act on different bodies. In ...
... The book is at rest, so, the resultant force on the book is zero. As a result N and mg are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. N and mg both act on the book and therefore cannot be action and reaction in the sense of Newton's 3 rd Law because action and reaction act on different bodies. In ...
Work and Energy_ppt_RevW10
... • First Law: Objects continue their state of motion (rest or constant velocity) unless acted upon by a net external force. • Second Law: The action of a net external force on an object is to cause its momentum to change with time. For objects with a constant mass this can be written as F = ma. • Thi ...
... • First Law: Objects continue their state of motion (rest or constant velocity) unless acted upon by a net external force. • Second Law: The action of a net external force on an object is to cause its momentum to change with time. For objects with a constant mass this can be written as F = ma. • Thi ...
Y11-Doubles
... The rate of change in velocity of an object. Acceleration can be due to a change in speed, or a change in direction. The quantity of matter in an object. The force needed to stop a vehicle. The distance shortest distance a vehicle can stop in. It consists of both the thinking distance and the brakin ...
... The rate of change in velocity of an object. Acceleration can be due to a change in speed, or a change in direction. The quantity of matter in an object. The force needed to stop a vehicle. The distance shortest distance a vehicle can stop in. It consists of both the thinking distance and the brakin ...
Gravity
... Isaac Newton (1643-1727): English Discovered: three laws of motion, one law of universal gravitation. ...
... Isaac Newton (1643-1727): English Discovered: three laws of motion, one law of universal gravitation. ...
File
... •a change in velocity •a measurement of how quickly an object is changing speed, direction or both Velocity: The rate of change of a position along a straight line with respect to time Force: strength or energy ...
... •a change in velocity •a measurement of how quickly an object is changing speed, direction or both Velocity: The rate of change of a position along a straight line with respect to time Force: strength or energy ...
FREE Sample Here
... common for students to include both members of a pair of 3rd Law forces as though they were acting on the same object. Also, students may think that the net force is an extra force that must be added (this becomes particularly evident when discussing rotational dynamics), or that the individual forc ...
... common for students to include both members of a pair of 3rd Law forces as though they were acting on the same object. Also, students may think that the net force is an extra force that must be added (this becomes particularly evident when discussing rotational dynamics), or that the individual forc ...
* Work (W) done by a constant force F exerted on an object through
... no change in speed; centripetal force can not change the speed, only direction for example, gravitational force on the moon does not change speed of the moon ...
... no change in speed; centripetal force can not change the speed, only direction for example, gravitational force on the moon does not change speed of the moon ...
physics_11_review_be.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
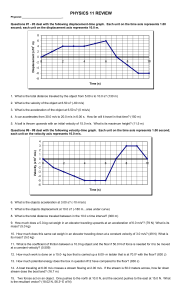
... 21. An object is thrown directly upwards with an initial velocity of 25 m/s. (A) What is the maximum height the object will travel? (32 m) (B) How long will it take to return to its starting point? (5.15 s) (C) What will its velocity be when it is 2.0 meters above its starting point as it travels do ...
... 21. An object is thrown directly upwards with an initial velocity of 25 m/s. (A) What is the maximum height the object will travel? (32 m) (B) How long will it take to return to its starting point? (5.15 s) (C) What will its velocity be when it is 2.0 meters above its starting point as it travels do ...