Rotation Lecture Notes B
... There is a common misconception that an object moving in a circle has an outward force acting on it, a socalled centrifugal (center-fleeing) force. Consider for example a person swinging a ball on the end of a string. If you have ever done this yourself, you know that you feel a force pulling outwar ...
... There is a common misconception that an object moving in a circle has an outward force acting on it, a socalled centrifugal (center-fleeing) force. Consider for example a person swinging a ball on the end of a string. If you have ever done this yourself, you know that you feel a force pulling outwar ...
Limitations on Newton`s 2nd Law
... Newton's Second Law Newton's Second Law as stated below applies to a wide range of physical phenomena, but it is not a fundamental principle like the Conservation Laws. It is applicable only if the force is the net external force. It does not apply directly to situations where the mass is changing, ...
... Newton's Second Law Newton's Second Law as stated below applies to a wide range of physical phenomena, but it is not a fundamental principle like the Conservation Laws. It is applicable only if the force is the net external force. It does not apply directly to situations where the mass is changing, ...
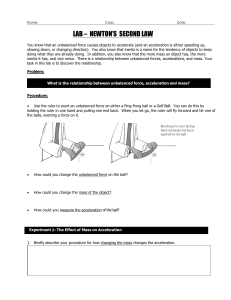
1. The apparent weight of an object increases in an elevator while
... have velocity and as the block is stopped in small time force is exerted by man in form of normal which is large as time is small. ...
... have velocity and as the block is stopped in small time force is exerted by man in form of normal which is large as time is small. ...
Circular
... experiment whirls a rubber bung attached to one end of a string which passes through a glass tube with smooth openings, and has a weight W hanging at its other end. The weight of the rubber bung is much smaller than W. The rubber bung is set into a horizontal uniform circular motion with angular spe ...
... experiment whirls a rubber bung attached to one end of a string which passes through a glass tube with smooth openings, and has a weight W hanging at its other end. The weight of the rubber bung is much smaller than W. The rubber bung is set into a horizontal uniform circular motion with angular spe ...
PS03H - willisworldbio
... falling object can be ignored, the object is said to be in ___ ____. • Close to Earth’s surface, the acceleration of a falling object in free fall is about _____. • This acceleration is given the symbol _ and is sometimes called the acceleration of gravity. • By Newton’s second law of motion, the fo ...
... falling object can be ignored, the object is said to be in ___ ____. • Close to Earth’s surface, the acceleration of a falling object in free fall is about _____. • This acceleration is given the symbol _ and is sometimes called the acceleration of gravity. • By Newton’s second law of motion, the fo ...
P1_Forces on a System of Objects
... A system of objects has a special location which is called the system’s center of mass (CM). A single object also has a center of mass, because a single object is actually a system of objects called “atoms”. If the system consists only of two objects, then the CM is on the line joining the two objec ...
... A system of objects has a special location which is called the system’s center of mass (CM). A single object also has a center of mass, because a single object is actually a system of objects called “atoms”. If the system consists only of two objects, then the CM is on the line joining the two objec ...
Conditions of Linear Motion
... Orthogonal forces – forces acting perpendicular to each other; they do not have an influence on each other fr ...
... Orthogonal forces – forces acting perpendicular to each other; they do not have an influence on each other fr ...
Chapter 4 Force Lecture Notes
... Also called the ‘Law of Inertia’ Inertia: Resistance to changes in motion. Stated: An object at rest will stay at rest and an object in motion will tend to stay in motion unless acted upon by some ‘net external force’. Net external force: the sum of all the vector forces acting on an object. ...
... Also called the ‘Law of Inertia’ Inertia: Resistance to changes in motion. Stated: An object at rest will stay at rest and an object in motion will tend to stay in motion unless acted upon by some ‘net external force’. Net external force: the sum of all the vector forces acting on an object. ...
Newton`s Laws presentation
... When a driver hits the gas, the wheels apply a force on the ground due to friction. This force accelerates the car forward. The brakes apply a force to the wheels, which in turn apply a frictional force to the ground, decelerating the car. So the gas pedal and the brakes are both accelerators, since ...
... When a driver hits the gas, the wheels apply a force on the ground due to friction. This force accelerates the car forward. The brakes apply a force to the wheels, which in turn apply a frictional force to the ground, decelerating the car. So the gas pedal and the brakes are both accelerators, since ...
Chapter 4 Lecture Notes Formulas: ΣF = ma FSF ≤ µSN Main Ideas
... more force to accelerate a spaceship of 11000 kg than to accelerate a man of 92 kg at the same rate. Now suppose an object is placed on a table. What are the forces acting on this object? Certainly gravity is acting on it. But if there was only gravity, then the object would accelerate down by Newto ...
... more force to accelerate a spaceship of 11000 kg than to accelerate a man of 92 kg at the same rate. Now suppose an object is placed on a table. What are the forces acting on this object? Certainly gravity is acting on it. But if there was only gravity, then the object would accelerate down by Newto ...
Mid Year Review
... 3. A car accelerates at 5.0 m/s2 from an initial velocity of 14 m/s. How long will it take to reach a velocity of 65 m/s? 10.2 s 4. A car accelerates form rest at 12.0 m/s2 for 14.0 s. a) How fast is it moving after 14.0 s? 168 m/s b) How far has it traveled in this time? 1176 m = 1180 m 5. A skier ...
... 3. A car accelerates at 5.0 m/s2 from an initial velocity of 14 m/s. How long will it take to reach a velocity of 65 m/s? 10.2 s 4. A car accelerates form rest at 12.0 m/s2 for 14.0 s. a) How fast is it moving after 14.0 s? 168 m/s b) How far has it traveled in this time? 1176 m = 1180 m 5. A skier ...