oscillations - Sakshieducation.com
... The physical quantity which gives the information about the position and direction of motion of particle in SHM at any instant from mean position is called phase. In general, the displacement of a particle in SHM can be written as Y = A sin(ωt ± φ ) , where (ωt ± φ ) is called phase, expressed in ra ...
... The physical quantity which gives the information about the position and direction of motion of particle in SHM at any instant from mean position is called phase. In general, the displacement of a particle in SHM can be written as Y = A sin(ωt ± φ ) , where (ωt ± φ ) is called phase, expressed in ra ...
Monday, Nov. 11, 2002
... Both internal and external forces can provide torque to individual particles. However, the internal forces do not generate net torque due to Newton’s third law. Let’s consider a two particle system where the two exert forces on each other. ...
... Both internal and external forces can provide torque to individual particles. However, the internal forces do not generate net torque due to Newton’s third law. Let’s consider a two particle system where the two exert forces on each other. ...
CHAPTER 27: Magnetism Responses to Questions
... moving in a straight line. Another possible situation is that there is an electric field with a magnitude and direction (perpendicular to the magnetic field) such that the electric and magnetic forces on the particle cancel each other out. The net force would be zero and the particle would continue ...
... moving in a straight line. Another possible situation is that there is an electric field with a magnitude and direction (perpendicular to the magnetic field) such that the electric and magnetic forces on the particle cancel each other out. The net force would be zero and the particle would continue ...
Bubbles in Magmas
... shallower in the vat (remember that P=rgh, where h is depth). The greater pressure at depth results in upward force on the object. ...
... shallower in the vat (remember that P=rgh, where h is depth). The greater pressure at depth results in upward force on the object. ...
Exam Review
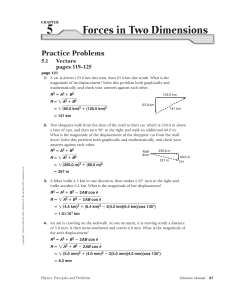
... 42. An object is pushed from rest across a sheet of ice, accelerating at 5.0 m/s2 over a distance of 80.0 cm. The object then slides with a constant speed for 4.0 s until it reaches a rough section which causes it to stop in 2.5 s. (a) What is the speed of the object when it reaches the rough sectio ...
... 42. An object is pushed from rest across a sheet of ice, accelerating at 5.0 m/s2 over a distance of 80.0 cm. The object then slides with a constant speed for 4.0 s until it reaches a rough section which causes it to stop in 2.5 s. (a) What is the speed of the object when it reaches the rough sectio ...