Newton`s 1st Law of Motion
... Galileo supported Copernicus and did not believe Aristotle’s theory of motion. Galileo believed a moving object did NOT need a force to remain in motion. He argued that a force was needed to keep an object moving only when friction was present. ...
... Galileo supported Copernicus and did not believe Aristotle’s theory of motion. Galileo believed a moving object did NOT need a force to remain in motion. He argued that a force was needed to keep an object moving only when friction was present. ...
2004_11_03ImpulseMomentum
... Hailstones Versus Raindrops Unlike rain, hail usually does not come to rest after striking a surface. Instead, the hailstones bounce off the roof of the car. If hail fell instead of rain, would the force on the roof be smaller than, equal to, or greater? ...
... Hailstones Versus Raindrops Unlike rain, hail usually does not come to rest after striking a surface. Instead, the hailstones bounce off the roof of the car. If hail fell instead of rain, would the force on the roof be smaller than, equal to, or greater? ...
Circular Motion and the Law of Gravity
... mvt or Fc = r 2. Force that maintain circular motion = mass x distance to axis x (angular speed)2 or ...
... mvt or Fc = r 2. Force that maintain circular motion = mass x distance to axis x (angular speed)2 or ...
here
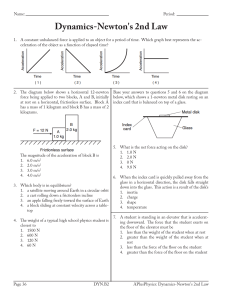
... 42. A force is applied to stop a moving shopping cart. Increasing the time interval over which the force is applied 43. An object is in equilibrium when 44. A baseball is released at rest from the top of the Washington Monument. It hits the ground after falling for 6.00 s. What was the height from w ...
... 42. A force is applied to stop a moving shopping cart. Increasing the time interval over which the force is applied 43. An object is in equilibrium when 44. A baseball is released at rest from the top of the Washington Monument. It hits the ground after falling for 6.00 s. What was the height from w ...
12.3 Newton`s 3rd Law of Motion
... has to push the bug forward. Identify this force. How does the bug produce it? (Hint: think back to how a swimmer moves through the water.) Air pushes the bug forward. The bug produces this force by pushing backward on the air with its wings, and the reaction force is that the air pushes forward on ...
... has to push the bug forward. Identify this force. How does the bug produce it? (Hint: think back to how a swimmer moves through the water.) Air pushes the bug forward. The bug produces this force by pushing backward on the air with its wings, and the reaction force is that the air pushes forward on ...
Circular Motion Notes
... Critical velocity – The maximum speed a car can safely round a curve. vc = (rg) Where: r = radius = coefficient of friction g –acceleration due to gravity The number of g’s an object experiences. #g’s = acceleration/ 9.8 ...
... Critical velocity – The maximum speed a car can safely round a curve. vc = (rg) Where: r = radius = coefficient of friction g –acceleration due to gravity The number of g’s an object experiences. #g’s = acceleration/ 9.8 ...
Document
... fields. • 6.3.2 Draw magnetic field patterns due to currents. • 6.3.3Determine the direction of the force on a currentcarrying conductor in a magnetic field. • 6.3.4 Determine the direction of the force on a charge moving in a magnetic field. • 6.3.5 Define the magnitude and direction of a magnetic ...
... fields. • 6.3.2 Draw magnetic field patterns due to currents. • 6.3.3Determine the direction of the force on a currentcarrying conductor in a magnetic field. • 6.3.4 Determine the direction of the force on a charge moving in a magnetic field. • 6.3.5 Define the magnitude and direction of a magnetic ...
The Two Body Problem
... earth’s moon is considered. The force on the moon due to the sun has a greater magnitude than that on the moon due to the earth. The moon basically orbits the sun while the earth perturbs its motion to speed up and slow down and to weave inside of and outside of the earth’s orbit. None-the-less, the ...
... earth’s moon is considered. The force on the moon due to the sun has a greater magnitude than that on the moon due to the earth. The moon basically orbits the sun while the earth perturbs its motion to speed up and slow down and to weave inside of and outside of the earth’s orbit. None-the-less, the ...