Uniform Circular Motion
... the average the angular speed (or angular velocity) of the system. Record any other information you will need to analyze the force on the spring, such as the radius and the total force (determined while the system was stationary). Make sure you have a column for the speed of the rotating object, whi ...
... the average the angular speed (or angular velocity) of the system. Record any other information you will need to analyze the force on the spring, such as the radius and the total force (determined while the system was stationary). Make sure you have a column for the speed of the rotating object, whi ...
Stacey Carpenter
... Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion Whenever one body exerts a force on a second body, the second body exerts an equal and opposite force on the first. This is often stated: For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. In Newton's 1st Law, we looked at the sum of forces on a single object, whic ...
... Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion Whenever one body exerts a force on a second body, the second body exerts an equal and opposite force on the first. This is often stated: For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. In Newton's 1st Law, we looked at the sum of forces on a single object, whic ...
Aim: How do we explain Newton`s 3rd Law?
... upon a shelf are: μs = 0.50 and μk = 0.40. Suppose the book has weight 14.5 N and a horizontal force is applied to it. (a) Determine the maximum force that can be applied without moving the book. (b) Determine the force required to keep the book moving at a constant speed across the shelf. (c) If th ...
... upon a shelf are: μs = 0.50 and μk = 0.40. Suppose the book has weight 14.5 N and a horizontal force is applied to it. (a) Determine the maximum force that can be applied without moving the book. (b) Determine the force required to keep the book moving at a constant speed across the shelf. (c) If th ...
Chapter 13 Periodic Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Amplitude
... As it moves toward the equilibrium position, force and acceleration decrease, but velocity increases At x = 0, F =0 and a = 0, but v = max The object’s momentum causes it to overshoot the equilibrium position As it moves away from the equilibrium position, force and acceleration increase, an ...
... As it moves toward the equilibrium position, force and acceleration decrease, but velocity increases At x = 0, F =0 and a = 0, but v = max The object’s momentum causes it to overshoot the equilibrium position As it moves away from the equilibrium position, force and acceleration increase, an ...
Example: A motorcyclist is trying to leap across the canyon by... horizontally off a cliff 38.0 m/s. Ignoring air resistance,...
... From the work-energy theorem, doing work results in a change in energy for the system, so alternatively: ...
... From the work-energy theorem, doing work results in a change in energy for the system, so alternatively: ...
PHYS2330 Intermediate Mechanics Quiz 14 Sept 2009
... The coordinate x measures the downward position of m1 as shown. The Lagrangian is A. L = 12 (m1 + m2 )ẋ2 − (m1 + m2 )gx B. L = 21 (m1 + m2 )ẋ2 + (m1 + m2 )gx C. L = 21 (m1 + m2 )ẋ2 + (m1 − m2 )gx D. L = 12 (m1 − m2 )ẋ2 − (m1 + m2 )gx E. L = 21 (m1 − m2 )ẋ2 − (m1 − m2 )gx 2. Given a Lagrangian L ...
... The coordinate x measures the downward position of m1 as shown. The Lagrangian is A. L = 12 (m1 + m2 )ẋ2 − (m1 + m2 )gx B. L = 21 (m1 + m2 )ẋ2 + (m1 + m2 )gx C. L = 21 (m1 + m2 )ẋ2 + (m1 − m2 )gx D. L = 12 (m1 − m2 )ẋ2 − (m1 + m2 )gx E. L = 21 (m1 − m2 )ẋ2 − (m1 − m2 )gx 2. Given a Lagrangian L ...
powerpoint jeopardy
... • B. is related to the amount of mass of the objects unless the mass is too small • C. is related to the amount of mass of the objects but ...
... • B. is related to the amount of mass of the objects unless the mass is too small • C. is related to the amount of mass of the objects but ...
1994 AAPT/Metrologic Physics Bowl Exam
... 32. In Young’s double slit experiment, second and higher order bright bands can overlap. Which third order band would occur at the same location as a second order band of wavelength 660 nm? A. 1320 nm B. 990 nm C. 495 nm D. 440 nm E. 330 nm 33. An air track car with mass m and velocity v to the righ ...
... 32. In Young’s double slit experiment, second and higher order bright bands can overlap. Which third order band would occur at the same location as a second order band of wavelength 660 nm? A. 1320 nm B. 990 nm C. 495 nm D. 440 nm E. 330 nm 33. An air track car with mass m and velocity v to the righ ...
Circular Motion
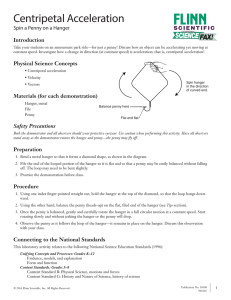
... turntable does the penny require the largest centripetal force to remain in place? 1) at the edge of the turntable 2) at the center of the turntable 3) it is the same everywhere on the turntable Q18) A car of mass m, traveling at constant speed, rides over the top of a hill. ...
... turntable does the penny require the largest centripetal force to remain in place? 1) at the edge of the turntable 2) at the center of the turntable 3) it is the same everywhere on the turntable Q18) A car of mass m, traveling at constant speed, rides over the top of a hill. ...