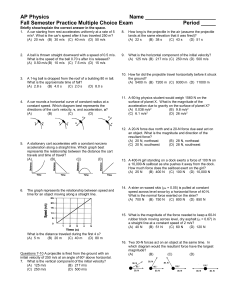
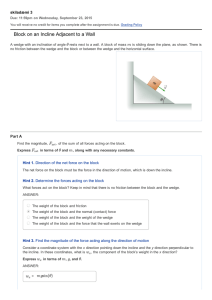
NEWTON`S LAWS OF MOTION
... NEWTON’S LAWS OF MOTION (Section 13.1) The motion of a particle is governed by Newton’s three laws of motion. First Law: A particle originally at rest, or moving in a straight line at constant velocity, will remain in this state if the resultant force acting on the particle is zero. Second Law: If ...
... NEWTON’S LAWS OF MOTION (Section 13.1) The motion of a particle is governed by Newton’s three laws of motion. First Law: A particle originally at rest, or moving in a straight line at constant velocity, will remain in this state if the resultant force acting on the particle is zero. Second Law: If ...
Centripetal Force / Gravity (very good practice)
... 5. The acceleration of gravity on the moon is one-sixth what it is on Earth. The radius of the moon is one-fourth that of the Earth. Determine the moon’s mass. 6. Two objects, with masses m1 and m2, are originally a distance r apart. The magnitude of the force between them is F. If the masses are ch ...
... 5. The acceleration of gravity on the moon is one-sixth what it is on Earth. The radius of the moon is one-fourth that of the Earth. Determine the moon’s mass. 6. Two objects, with masses m1 and m2, are originally a distance r apart. The magnitude of the force between them is F. If the masses are ch ...
Torque - rcasao
... As we have seen over and over again, a force is a push or a pull, and an unbalanced force causes an object to move (to accelerate). All the motion we have dealt with so far has moved objects from one point in space to another. This type of motion involving a displacement is called translational moti ...
... As we have seen over and over again, a force is a push or a pull, and an unbalanced force causes an object to move (to accelerate). All the motion we have dealt with so far has moved objects from one point in space to another. This type of motion involving a displacement is called translational moti ...
b. 4 m/s 2
... A heavy person and a light person parachute together and wear the same size parachutes. Assuming they open their parachutes at the same time, which person reaches the ground first? a. the light person b. the heavy person c. Neither -- they both reach the ground together. ...
... A heavy person and a light person parachute together and wear the same size parachutes. Assuming they open their parachutes at the same time, which person reaches the ground first? a. the light person b. the heavy person c. Neither -- they both reach the ground together. ...
Chapter 6 - MrCrabtreesScience
... Stopping Time and Force • A change in motion over a longer time, requires less force. • For example a car dashboard stops a person over a period of 0.026sec applies a significantly greater force than an airbag that stops a person over a period of .75 seconds. • How much more force? ...
... Stopping Time and Force • A change in motion over a longer time, requires less force. • For example a car dashboard stops a person over a period of 0.026sec applies a significantly greater force than an airbag that stops a person over a period of .75 seconds. • How much more force? ...
Higher Mechanics Notes
... Newton’s 1st Law of Motion Newton’s 1st law of Motion states that an object will remain at rest or travel with a constant speed in a straight line (constant velocity) unless acted on by an unbalanced force. Newton’s 2nd Law Newton’s 2nd law of motion states that the acceleration of an object: vari ...
... Newton’s 1st Law of Motion Newton’s 1st law of Motion states that an object will remain at rest or travel with a constant speed in a straight line (constant velocity) unless acted on by an unbalanced force. Newton’s 2nd Law Newton’s 2nd law of motion states that the acceleration of an object: vari ...
Honors/CP Physics
... It rises to a maximum height, H. If air resistance is negligible, which of the following must be true for the object when it is at a height ½H? (A) Its speed is half of its initial speed. (B) Its kinetic energy is hall of its initial kinetic energy (C) Its potential energy is half of its initial pot ...
... It rises to a maximum height, H. If air resistance is negligible, which of the following must be true for the object when it is at a height ½H? (A) Its speed is half of its initial speed. (B) Its kinetic energy is hall of its initial kinetic energy (C) Its potential energy is half of its initial pot ...
What Is Motion?
... Velocity ends with the sound at the beginning of east. Your velocity may be one meter per second east. If you are going in the opposite direction, your velocity may be one meter per second west. ...
... Velocity ends with the sound at the beginning of east. Your velocity may be one meter per second east. If you are going in the opposite direction, your velocity may be one meter per second west. ...
Here is the solution of Exam 1.
... 7. A positively charged particle of mass m = 6.0 × 10−8 kg is travelling due east with a speed of v = 90 m/s and enters a uniform magnetic field whose magnitude is B = 0.30 T . The particle moves through one-quarter of a circle in a time of t = 2.0 × 10−3 s, at which time it leaves the field headin ...
... 7. A positively charged particle of mass m = 6.0 × 10−8 kg is travelling due east with a speed of v = 90 m/s and enters a uniform magnetic field whose magnitude is B = 0.30 T . The particle moves through one-quarter of a circle in a time of t = 2.0 × 10−3 s, at which time it leaves the field headin ...