Paper Reference(s)
... Full marks may be obtained for answers to ALL questions. This paper has seven questions. Advice to Candidates You must ensure that your answers to parts of questions are clearly labelled. You must show sufficient working to make your methods clear to the Examiner. Answers without working may gain no ...
... Full marks may be obtained for answers to ALL questions. This paper has seven questions. Advice to Candidates You must ensure that your answers to parts of questions are clearly labelled. You must show sufficient working to make your methods clear to the Examiner. Answers without working may gain no ...
Circular_Motion
... of friction, Ff, between the wheel and the road. If the force of friction is not strong enough, the vehicle will skid. ...
... of friction, Ff, between the wheel and the road. If the force of friction is not strong enough, the vehicle will skid. ...
Monday, April 27, 2009
... If you grab onto a pole while running, your body will rotate about the pole, gaining angular momentum. We’ve used the linear momentum to solve physical problems with linear motions, the angular momentum will do the same for rotational motions. Let’s consider a point-like object ( particle) with mass ...
... If you grab onto a pole while running, your body will rotate about the pole, gaining angular momentum. We’ve used the linear momentum to solve physical problems with linear motions, the angular momentum will do the same for rotational motions. Let’s consider a point-like object ( particle) with mass ...
Chapter 7: Circular Motion and Gravitation
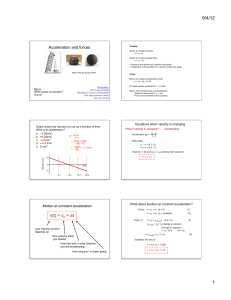
... the car enters the turn, your inertia makes to tend to move along the original straightline path. This movement is in accordance with Newton’s first law, which states that the natural tendency of a body is to continue moving in a straight line. ...
... the car enters the turn, your inertia makes to tend to move along the original straightline path. This movement is in accordance with Newton’s first law, which states that the natural tendency of a body is to continue moving in a straight line. ...
ce-phy ii
... 1 What physical quantity does the area of the shaded region represent? A. B. C. D. ...
... 1 What physical quantity does the area of the shaded region represent? A. B. C. D. ...
PHYS 1443 – Section 501 Lecture #1
... If you grab onto a pole while running, your body will rotate about the pole, gaining angular momentum. We’ve used the linear momentum to solve physical problems with linear motions, the angular momentum will do the same for rotational motions. Let’s consider a point-like object ( particle) with mass ...
... If you grab onto a pole while running, your body will rotate about the pole, gaining angular momentum. We’ve used the linear momentum to solve physical problems with linear motions, the angular momentum will do the same for rotational motions. Let’s consider a point-like object ( particle) with mass ...
document
... Work Demo Revisited. Have a student walk across the front of the room, carrying the 10 kg brick, at a constant speed. How much work did they do? What is the equation for the change in PE of the brick? Change in PE = PE2 – PE1 = (mgh2 – mgh1) But h2 = h1, so no PE is added or change in PE = 0. So no ...
... Work Demo Revisited. Have a student walk across the front of the room, carrying the 10 kg brick, at a constant speed. How much work did they do? What is the equation for the change in PE of the brick? Change in PE = PE2 – PE1 = (mgh2 – mgh1) But h2 = h1, so no PE is added or change in PE = 0. So no ...
Circular Motion Lab
... the time it takes to swing the stopper in 10 complete circles at a constant radius (this will be divided by 10 to obtain the period T of the swing) the length (in meters) of the string for each particular swing. You will measure the length from the center of the stopper to the top of the tube. 2 ...
... the time it takes to swing the stopper in 10 complete circles at a constant radius (this will be divided by 10 to obtain the period T of the swing) the length (in meters) of the string for each particular swing. You will measure the length from the center of the stopper to the top of the tube. 2 ...
2, 4, 6, 7, 12 / 3, 9, 15, 20, 26, 37, 41, 44, 47, 53, 60
... slowly, it is possible that the product 12 mv is greater for the car than it is for the faster-moving motorcycle. ...
... slowly, it is possible that the product 12 mv is greater for the car than it is for the faster-moving motorcycle. ...
Lesson 2: Coulomb`s Law
... and the proton’s charge is +1.60 x 10-19 C. Calculate the electrostatic force of attraction acting on the two charges. [8.22 x 10-8 N [attraction]] 2. The electric force between two charged objects is 5.2 x 10-4 N when the objects are 3.11 x 10-1 m apart. What is the electric force between the same ...
... and the proton’s charge is +1.60 x 10-19 C. Calculate the electrostatic force of attraction acting on the two charges. [8.22 x 10-8 N [attraction]] 2. The electric force between two charged objects is 5.2 x 10-4 N when the objects are 3.11 x 10-1 m apart. What is the electric force between the same ...
chapter FORCES AND NEWTON’S LAWS OF MOTION
... Which one of the following terms is used to indicate the natural tendency of an object to remain at rest or in motion at a constant speed along a straight line? (a) velocity (c) acceleration (e) inertia (b) force (d) equilibrium ...
... Which one of the following terms is used to indicate the natural tendency of an object to remain at rest or in motion at a constant speed along a straight line? (a) velocity (c) acceleration (e) inertia (b) force (d) equilibrium ...
Acutus Mens first term 2010-2011
... (rounding to nearest .01) Precision – ability to replicate - following the directions exactly as they are written every time. 4. A controlled experiment is one where one variable remains the same (called the control). This is like a point of reference for the experiment. Other variables may be chang ...
... (rounding to nearest .01) Precision – ability to replicate - following the directions exactly as they are written every time. 4. A controlled experiment is one where one variable remains the same (called the control). This is like a point of reference for the experiment. Other variables may be chang ...