8-3 Perfectly Inelastic Collisions
... and kinetic energy • The relative velocity of the colliding objects changes sign but does not change magnitude. ...
... and kinetic energy • The relative velocity of the colliding objects changes sign but does not change magnitude. ...
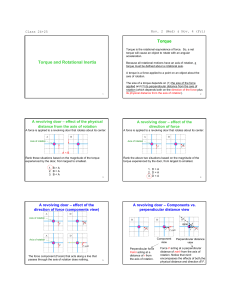
Centripetal Acceleration and Centripetal Force
... Centripetal Acceleration • Centripetal means center-seeking. • Centripetal acceleration is always directed toward the center of the circle of motion. • It is this centripetal acceleration that is responsible for the change in the direction of the velocity; the magnitude of the velocity remains cons ...
... Centripetal Acceleration • Centripetal means center-seeking. • Centripetal acceleration is always directed toward the center of the circle of motion. • It is this centripetal acceleration that is responsible for the change in the direction of the velocity; the magnitude of the velocity remains cons ...
Physics 8 — Wednesday, October 19, 2011
... Troublesome HW4 questions 16. I push on a refrigerator (horizontally), but it does not move. Explain how this can be. (A) the downward force of gravity on the fridge is larger than the force that I can exert on the fridge. (B) the frictional force of the floor on the fridge exactly cancels the forc ...
... Troublesome HW4 questions 16. I push on a refrigerator (horizontally), but it does not move. Explain how this can be. (A) the downward force of gravity on the fridge is larger than the force that I can exert on the fridge. (B) the frictional force of the floor on the fridge exactly cancels the forc ...
Name - Manhasset Public Schools
... 2. As shown in the diagram, a neutral pith ball suspended on a string is attracted to a positively charged rod. During contact with the rod, the pith ball 1. become negatively charged by gaining electrons 2. become negatively charged by losing protons 3. become positively charged by gaining protons ...
... 2. As shown in the diagram, a neutral pith ball suspended on a string is attracted to a positively charged rod. During contact with the rod, the pith ball 1. become negatively charged by gaining electrons 2. become negatively charged by losing protons 3. become positively charged by gaining protons ...
Physics I - Rose
... 13.23. Model: A circular plastic disk rotating on an axle through its center is a rigid body. Assume axis is perpendicular to the disk. Solve: To determine the torque () needed to take the plastic disk from i 0 rad/s to f 1800 rpm (1800)(2)/ 60 rad/s 60 rad/s in tf – ti 4.0 s, we nee ...
... 13.23. Model: A circular plastic disk rotating on an axle through its center is a rigid body. Assume axis is perpendicular to the disk. Solve: To determine the torque () needed to take the plastic disk from i 0 rad/s to f 1800 rpm (1800)(2)/ 60 rad/s 60 rad/s in tf – ti 4.0 s, we nee ...
Newton`s Second Law
... a is acceleration, Fnet is net force, and m is mass. Applying Newton’s Second Law to the static setup used in this activity for an object accelerated by the weight of a hanging mass, neglecting friction, the acceleration of the object and hanging mass can be written as: ...
... a is acceleration, Fnet is net force, and m is mass. Applying Newton’s Second Law to the static setup used in this activity for an object accelerated by the weight of a hanging mass, neglecting friction, the acceleration of the object and hanging mass can be written as: ...
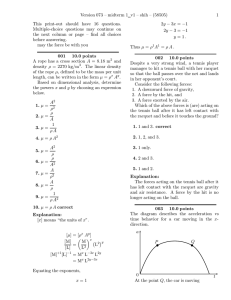
Version 073 – midterm 1 v1 – shih – (58505) 1
... Despite a very strong wind, a tennis player manages to hit a tennis ball with her racquet so that the ball passes over the net and lands in her opponent’s court. Consider the following forces: 1. A downward force of gravity, 2. A force by the hit, and 3. A force exerted by the air. Which of the abov ...
... Despite a very strong wind, a tennis player manages to hit a tennis ball with her racquet so that the ball passes over the net and lands in her opponent’s court. Consider the following forces: 1. A downward force of gravity, 2. A force by the hit, and 3. A force exerted by the air. Which of the abov ...
Biomechanics - study
... uniform straight line motion, unless acted upon by a force to change that state of rest or motion”. e.g.. Daniel Carter kicking a penalty; the ball will remain at rest until Dan applies a force with his foot. The ball would travel in a straight line into the sky, but is acted upon by gravity and air ...
... uniform straight line motion, unless acted upon by a force to change that state of rest or motion”. e.g.. Daniel Carter kicking a penalty; the ball will remain at rest until Dan applies a force with his foot. The ball would travel in a straight line into the sky, but is acted upon by gravity and air ...