Chapter 7
... orbits by a gravitational pull to the Sun and the other planets in the Solar System. • He went on to conclude that there is a mutual gravitational force between all particles of matter. • From that he saw that the attractive force was universal to all objects based on their mass and the distance the ...
... orbits by a gravitational pull to the Sun and the other planets in the Solar System. • He went on to conclude that there is a mutual gravitational force between all particles of matter. • From that he saw that the attractive force was universal to all objects based on their mass and the distance the ...
8th- Chapter 11 Review Game
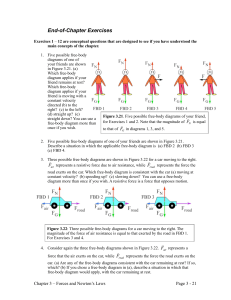
... A. less than the ship’s weight B. equal to the ship’s weight C. less than the ship’s speed D. greater than the ship’s speed ...
... A. less than the ship’s weight B. equal to the ship’s weight C. less than the ship’s speed D. greater than the ship’s speed ...
Chapter 7
... As mass increases, momentum increases. For example: getting hit by a tennis ball vs. getting hit by a bowling ball ...
... As mass increases, momentum increases. For example: getting hit by a tennis ball vs. getting hit by a bowling ball ...
Unit 4 – Chapter 7: Oscillatory Motion Requires a Set of Conditions
... A mass bobbing up and down on a spring executes "periodic motion" - motion that repeats over a specific "period" of time. ...
... A mass bobbing up and down on a spring executes "periodic motion" - motion that repeats over a specific "period" of time. ...
1 Fig. 1.1 shows the speed-time graph for the first 125 s of the
... (ii) The gas in the cylinder starts at a pressure of 1.0 105 Pa and has a volume of100 cm3. The volume of the gas decreases to 80 cm3. Calculate the final pressure of the gas. State the formula that you use. ...
... (ii) The gas in the cylinder starts at a pressure of 1.0 105 Pa and has a volume of100 cm3. The volume of the gas decreases to 80 cm3. Calculate the final pressure of the gas. State the formula that you use. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Equilibrium and Torque
... What affects the torque? 1. The distance from the axis rotation “r” that the force is applied 2. The component of force perpendicular to the r-vector ...
... What affects the torque? 1. The distance from the axis rotation “r” that the force is applied 2. The component of force perpendicular to the r-vector ...
Physics 51
... IDENTIFY: The electric field exerts a horizontal force away from the wall on the ball. When the ball hangs at rest, the forces on it (gravity, the tension in the string, and the electric force due to the field) add to zero. SET UP: The ball is in equilibrium, so for it Fx 0 and Fy 0. The for ...
... IDENTIFY: The electric field exerts a horizontal force away from the wall on the ball. When the ball hangs at rest, the forces on it (gravity, the tension in the string, and the electric force due to the field) add to zero. SET UP: The ball is in equilibrium, so for it Fx 0 and Fy 0. The for ...
inDinns
... The horizontal motion is uniform because there are no forces acting in that direction (ignoring friction). The vertical motion is accelerated due to the force of gravity. The projectile motion equations in this book do not hold when friction is taken into account. Projectile motion in both direction ...
... The horizontal motion is uniform because there are no forces acting in that direction (ignoring friction). The vertical motion is accelerated due to the force of gravity. The projectile motion equations in this book do not hold when friction is taken into account. Projectile motion in both direction ...
lesson plan
... 6. Which procedure do we follow to find the resultant force when forces with the same direction and sense come to scene? 7. And what about forces with the same direction and opposite sense? 8. Which procedure do we follow to find the resultant force when we have forces forming an angle with the dire ...
... 6. Which procedure do we follow to find the resultant force when forces with the same direction and sense come to scene? 7. And what about forces with the same direction and opposite sense? 8. Which procedure do we follow to find the resultant force when we have forces forming an angle with the dire ...
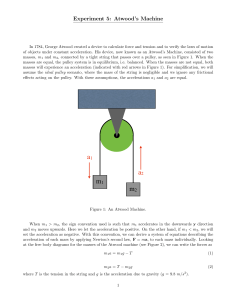
Experiment 5 - Atwood`s Machine
... • Devise an experimental procedure to measure the acceleration of the masses on the Atwood’s machine for 5 different mass combinations of m1 and m2 , but keeping the sum of the masses m1 +m2 constant. That is, if you decrease m1 by a set amount, increase the other mass (m2 ) so that the total mass ...
... • Devise an experimental procedure to measure the acceleration of the masses on the Atwood’s machine for 5 different mass combinations of m1 and m2 , but keeping the sum of the masses m1 +m2 constant. That is, if you decrease m1 by a set amount, increase the other mass (m2 ) so that the total mass ...
Chapter 15: Oscillations 15-23 THINK The maximum force that can
... THINK The maximum force that can be exerted by the surface must be less than the static frictional force or else the block will not follow the surface in its motion. EXPRESS The static frictional force is given by f s s FN , where µs is the coefficient of static friction and FN is the normal forc ...
... THINK The maximum force that can be exerted by the surface must be less than the static frictional force or else the block will not follow the surface in its motion. EXPRESS The static frictional force is given by f s s FN , where µs is the coefficient of static friction and FN is the normal forc ...