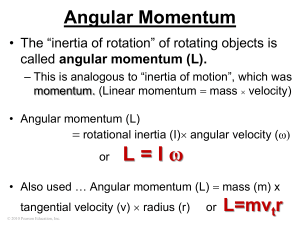
Chapter 8 – Momentum, Impulse, and Collisions
... Example: A 10 kg block traveling at constant velocity of 1.5 m/s breaks up into three pieces after a firecracker explodes in the block. A 5 kg piece continues in the original direction at 4 m/s. A 3 kg piece travels in a direction perpendicular to the original direction at 6 m/s. How fast and in wha ...
... Example: A 10 kg block traveling at constant velocity of 1.5 m/s breaks up into three pieces after a firecracker explodes in the block. A 5 kg piece continues in the original direction at 4 m/s. A 3 kg piece travels in a direction perpendicular to the original direction at 6 m/s. How fast and in wha ...
100 Lec11 06
... Forces pointing thru the axis (F1, F4) do not affect rotation Forces x, with lever arm ≠ 0, ( F2, F3), have maximal effect and the effect is proportional to the length of the ...
... Forces pointing thru the axis (F1, F4) do not affect rotation Forces x, with lever arm ≠ 0, ( F2, F3), have maximal effect and the effect is proportional to the length of the ...
Uniform Circular Motion
... 1. You will use the same value of M throughout this part. Your are varying the rotating mass. 2. Keep the same radius used in Part III. 3. Take data as above for two additional runs: first by changing the hooked mass by removing 50 g so that m is 150 g, and then by changing the hooked mass m to 100g ...
... 1. You will use the same value of M throughout this part. Your are varying the rotating mass. 2. Keep the same radius used in Part III. 3. Take data as above for two additional runs: first by changing the hooked mass by removing 50 g so that m is 150 g, and then by changing the hooked mass m to 100g ...
4.1 The Concepts of Force and Mass
... 6.5.1. Two balls of equal size are dropped from the same height from the roof of a building. One ball has twice the mass of the other. When the balls reach the ground, how do the kinetic energies of the two balls compare? a) The lighter one has one fourth as much kinetic energy as the other does. b ...
... 6.5.1. Two balls of equal size are dropped from the same height from the roof of a building. One ball has twice the mass of the other. When the balls reach the ground, how do the kinetic energies of the two balls compare? a) The lighter one has one fourth as much kinetic energy as the other does. b ...
Circular Motion Webquest Project Physics 12
... • “Well that is all very nice Cameron, but I still don’t know very much about The Widow Maker. I still don’t want you on that ride! Do you even know how fast its going? Will it break? I am just not convinced it is safe, I’m ...
... • “Well that is all very nice Cameron, but I still don’t know very much about The Widow Maker. I still don’t want you on that ride! Do you even know how fast its going? Will it break? I am just not convinced it is safe, I’m ...
Forces - Lincoln Park High School
... First law: The velocity of a body remains constant unless the body is acted upon by an unbalanced external force. Second law: The acceleration a of a body is parallel and directly proportional to the net force F and inversely proportional to the mass m, i.e., F = ma. Third law: The mutual forces of ...
... First law: The velocity of a body remains constant unless the body is acted upon by an unbalanced external force. Second law: The acceleration a of a body is parallel and directly proportional to the net force F and inversely proportional to the mass m, i.e., F = ma. Third law: The mutual forces of ...
rev1 - UConn Physics
... 1. Molar Mass = mass in grams of one mole of the substance. 2. Atomic Mass = mass in u (a.m.u.) of one atom of a substance, is approximately the number of protons and neutrons in one atom of that substance. Molar Mass and Atomic Mass are other units for density. ...
... 1. Molar Mass = mass in grams of one mole of the substance. 2. Atomic Mass = mass in u (a.m.u.) of one atom of a substance, is approximately the number of protons and neutrons in one atom of that substance. Molar Mass and Atomic Mass are other units for density. ...
Physics, Force, Motion - Region 11 Math and Science Teacher
... (Forces are like shoes - they come in pairs!) ...
... (Forces are like shoes - they come in pairs!) ...
Electrostatics - PRADEEP KSHETRAPAL PHYSICS
... (i) The position of centre of mass is independent of the co-ordinate system chosen. (ii) The position of centre of mass depends upon the shape of the body and distribution of mass. Example : The centre of mass of a circular disc is within the material of the body while that of a circular ring is out ...
... (i) The position of centre of mass is independent of the co-ordinate system chosen. (ii) The position of centre of mass depends upon the shape of the body and distribution of mass. Example : The centre of mass of a circular disc is within the material of the body while that of a circular ring is out ...
The Complete Group 1 Laboratory Manual
... 2. A work station and lab partners will be assigned to you in the first lab meeting. You will do experiments in a group but you are expected to bear your share of responsibility in doing the experiments. You must actively participate in obtaining the data and not merely watch your partners do it for ...
... 2. A work station and lab partners will be assigned to you in the first lab meeting. You will do experiments in a group but you are expected to bear your share of responsibility in doing the experiments. You must actively participate in obtaining the data and not merely watch your partners do it for ...
Potential Energy - McMaster Physics and Astronomy
... One useful result: for elastic collisions, the magnitude of the relative velocity is the same before and after the collision: |v1,i – v2,i | = |v1,f – v2,f | (This is true for elastic collisions in 2 and 3 dimensions as well). An important case is a particle directed at a stationary target (v2,i = ...
... One useful result: for elastic collisions, the magnitude of the relative velocity is the same before and after the collision: |v1,i – v2,i | = |v1,f – v2,f | (This is true for elastic collisions in 2 and 3 dimensions as well). An important case is a particle directed at a stationary target (v2,i = ...