Chapter 6 Forces in Motion
... Acceleration Stops at the Terminal Velocity • As an object falls, air resistance continues to increase until it exactly matches the downward force of gravity. The object has then reached its terminal velocity…or a net force of zero ...
... Acceleration Stops at the Terminal Velocity • As an object falls, air resistance continues to increase until it exactly matches the downward force of gravity. The object has then reached its terminal velocity…or a net force of zero ...
ppt - SBEL
... … then, we can conclude that the solution is unique, and not only at tk, but in a small interval about time tk. Additionally, in this small time interval, there is an explicit functional dependency of q on t, that is, there is a function f(t) such that: ...
... … then, we can conclude that the solution is unique, and not only at tk, but in a small interval about time tk. Additionally, in this small time interval, there is an explicit functional dependency of q on t, that is, there is a function f(t) such that: ...
Honors Physics Unit 5 Notes
... The relative locations of all particles making up the object remain constant All real objects are deformable to some extent, but the rigid object model is very useful in many situations where the deformation is negligible ...
... The relative locations of all particles making up the object remain constant All real objects are deformable to some extent, but the rigid object model is very useful in many situations where the deformation is negligible ...
THREE DlMENSIONAL KlNEMATICS AND KINETICS OF THE
... 3) A motor-drive treadmill (250 Kg in mass) was fixed upon a set up of two force plates (kistler, 60x40 cm). Head and tail parts of the treadmill were supported by each force plate respectively. The sum of outputs from both plates showed the external force acting upon the C/G, because both plates co ...
... 3) A motor-drive treadmill (250 Kg in mass) was fixed upon a set up of two force plates (kistler, 60x40 cm). Head and tail parts of the treadmill were supported by each force plate respectively. The sum of outputs from both plates showed the external force acting upon the C/G, because both plates co ...
Force
... 4. You travel to and from RHHS, which is located 5 mi to the west of your house. What is your distance & displacement? ...
... 4. You travel to and from RHHS, which is located 5 mi to the west of your house. What is your distance & displacement? ...
Document
... A particle falls under the force of gravity in a medium that exerts a resisting force proportional to the velocity of the particle. Develop equations for the velocity and displacement of the particle. The velocity and displacement of the particle are zero at ...
... A particle falls under the force of gravity in a medium that exerts a resisting force proportional to the velocity of the particle. Develop equations for the velocity and displacement of the particle. The velocity and displacement of the particle are zero at ...
(the terminal velocity is smaller for larger cross
... Galileo: If no force is applied to a moving object, it will continue to move with constant speed in a straight line Inertial reference frames Galilean principle of relativity: Laws of physics (and everything in the Universe) look the same for all observers who move with a constant velocity with res ...
... Galileo: If no force is applied to a moving object, it will continue to move with constant speed in a straight line Inertial reference frames Galilean principle of relativity: Laws of physics (and everything in the Universe) look the same for all observers who move with a constant velocity with res ...
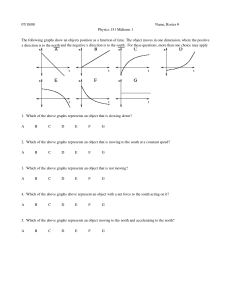
Final Exam
... 3. The torque exerted on the disk about an axis passing by the center is (see figure) a. − FRiˆ ...
... 3. The torque exerted on the disk about an axis passing by the center is (see figure) a. − FRiˆ ...
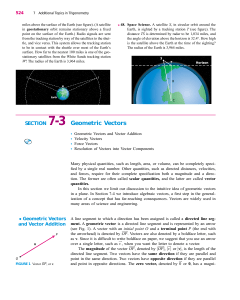
SECTION 7-3 Geometric Vectors
... directions are exact. 25. Navigation. An airplane is flying with a compass heading of 285° and an airspeed of 230 miles per hour. A steady wind of 35 miles per hour is blowing in the direction of 260°. What is the plane’s actual velocity; that is, what is its speed and direction relative to the grou ...
... directions are exact. 25. Navigation. An airplane is flying with a compass heading of 285° and an airspeed of 230 miles per hour. A steady wind of 35 miles per hour is blowing in the direction of 260°. What is the plane’s actual velocity; that is, what is its speed and direction relative to the grou ...
y 1
... with a velocity of magnitude Vm. What is magnitude of the velocity when the bullet returns to the ground? Hits the target at height H above the ground? How high it will go? ...
... with a velocity of magnitude Vm. What is magnitude of the velocity when the bullet returns to the ground? Hits the target at height H above the ground? How high it will go? ...