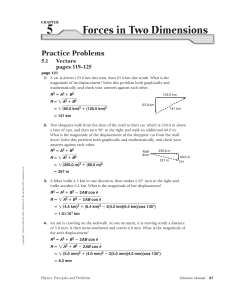
Final Exam Review
... a. To increase power, you can decrease the amount of work you do in a given amount of time, or you can do a given amount of work in less time. b. To increase power, you can decrease the amount of work you do in a given amount of time, or you can do a given amount of work in more time. c. To increase ...
... a. To increase power, you can decrease the amount of work you do in a given amount of time, or you can do a given amount of work in less time. b. To increase power, you can decrease the amount of work you do in a given amount of time, or you can do a given amount of work in more time. c. To increase ...
Using the Law of Universal Gravitation
... The Gravitational Field 20. What type of force is gravity? Gravity is a field force. Gravity acts over a distance. It acts between objects that are not touching or that are not close together, unlike other forces that are contact forces. For example, friction. In the 19th century, Michael Faraday de ...
... The Gravitational Field 20. What type of force is gravity? Gravity is a field force. Gravity acts over a distance. It acts between objects that are not touching or that are not close together, unlike other forces that are contact forces. For example, friction. In the 19th century, Michael Faraday de ...
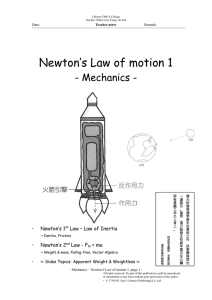
Newton`s Law of motion 1
... A helicopter has a mass of 1000 kg. The rotation of the rotor blades can produce a maximum upward force of 15000 N. (a) What upward force must be produced by the rotation of the rotor blades to keep the uploaded helicopter at a constant height? (b) What is the maximum upward acceleration of the heli ...
... A helicopter has a mass of 1000 kg. The rotation of the rotor blades can produce a maximum upward force of 15000 N. (a) What upward force must be produced by the rotation of the rotor blades to keep the uploaded helicopter at a constant height? (b) What is the maximum upward acceleration of the heli ...
Ch11 - Rolling, Torque, and Angular Momentum
... Answer: The maximum height reached by B is less than that reached by A. For A, all the kinetic energy becomes potential energy at h. Since the ramp is frictionless for B, all of the rotational K stays rotational, and only the translational kinetic energy becomes potential energy at its maximum ...
... Answer: The maximum height reached by B is less than that reached by A. For A, all the kinetic energy becomes potential energy at h. Since the ramp is frictionless for B, all of the rotational K stays rotational, and only the translational kinetic energy becomes potential energy at its maximum ...
nt2_Formal_Exercises - Glen Urquhart High School
... 14. Use free body diagrams to analyse the forces on an object. 15. State what is meant by the resultant of a number of forces. 16. Use a scale diagram, or otherwise, to find the magnitude and direction of the resultant of two forces acting at right angles to each other. 17. Carry out calculations us ...
... 14. Use free body diagrams to analyse the forces on an object. 15. State what is meant by the resultant of a number of forces. 16. Use a scale diagram, or otherwise, to find the magnitude and direction of the resultant of two forces acting at right angles to each other. 17. Carry out calculations us ...
Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh, Conceptual Integrated Science
... • Weight is the only force until air resistance acts. • As falling speed increases, air resistance on diver builds up, net force is reduced, and acceleration becomes less. • When air resistance equals the diver’s weight, net force is zero and acceleration terminates. ...
... • Weight is the only force until air resistance acts. • As falling speed increases, air resistance on diver builds up, net force is reduced, and acceleration becomes less. • When air resistance equals the diver’s weight, net force is zero and acceleration terminates. ...
PHYSICS 2325 EXAM 2 REVIEW
... 79. A thin plate of negligible mass is attached to the end of spring A, which has k 1380 N m . The end with the plate is pressed against an identical spring B fastened to a wall until the force exerted on the end of A is 225 N. By how much has spring B been compressed from its unstretched length? ...
... 79. A thin plate of negligible mass is attached to the end of spring A, which has k 1380 N m . The end with the plate is pressed against an identical spring B fastened to a wall until the force exerted on the end of A is 225 N. By how much has spring B been compressed from its unstretched length? ...