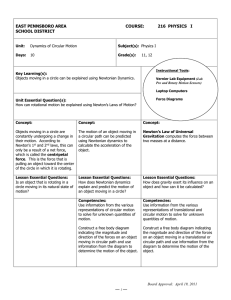
Knowledge Check (Answer Key)
... Mass: Mass is the amount of material present in an object. This dimension describes how much material makes up an object. Often, mass and weight are confused as being the same because the units used to describe them are similar. Weight is a derived unit, not a fundamental unit, and is a measurement ...
... Mass: Mass is the amount of material present in an object. This dimension describes how much material makes up an object. Often, mass and weight are confused as being the same because the units used to describe them are similar. Weight is a derived unit, not a fundamental unit, and is a measurement ...
Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh, Conceptual Integrated Science
... • Read the directions on the handout that I give you and perform the activities described. • Keep track of your data and add it to the class data on the board. • After you complete the activity we will discuss the class results. © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • Read the directions on the handout that I give you and perform the activities described. • Keep track of your data and add it to the class data on the board. • After you complete the activity we will discuss the class results. © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
CHAPTER 4
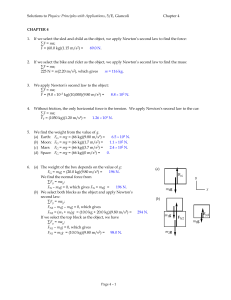
... We write ∑F = ma from the force diagram for the elevator: y-component: FTmax – mg = ma, or FTmax = m(a + g) = (1200 kg)(0.0600 + 1)(9.80 m/s2) = 5.04104 N. The minimum tension will be exerted by the motor when the elevator is accelerating downward. We write ∑F = ma from the force diagram for the ...
... We write ∑F = ma from the force diagram for the elevator: y-component: FTmax – mg = ma, or FTmax = m(a + g) = (1200 kg)(0.0600 + 1)(9.80 m/s2) = 5.04104 N. The minimum tension will be exerted by the motor when the elevator is accelerating downward. We write ∑F = ma from the force diagram for the ...
PPT
... • Wed: Recitation on Chap 15, Lab • Thurs: Lecture on Chap 15, Part 2 Week after that (4/21) • Monday: Chapter 15 & 16 due in WebCT • Tues: Reading for Chapter 18 • Tues: Lecture on Chapter 18 • Wed: Recitation on Chapter 18, Lab ...
... • Wed: Recitation on Chap 15, Lab • Thurs: Lecture on Chap 15, Part 2 Week after that (4/21) • Monday: Chapter 15 & 16 due in WebCT • Tues: Reading for Chapter 18 • Tues: Lecture on Chapter 18 • Wed: Recitation on Chapter 18, Lab ...
FORCE AND MOTION - University of Puget Sound
... factor 1 oz = weight of 0.02835 kg = (9.81 m/s2)(0.02835 kg) = 0.2778 N (Appendix C). Recall that 340 g = 0.340 kg. EVALUATE (a) The actual weight (equal to the gravitational force on the object at the surface of the Earth) is ...
... factor 1 oz = weight of 0.02835 kg = (9.81 m/s2)(0.02835 kg) = 0.2778 N (Appendix C). Recall that 340 g = 0.340 kg. EVALUATE (a) The actual weight (equal to the gravitational force on the object at the surface of the Earth) is ...
Ch 5 Solutions Glencoe 2013
... Not necessarily. For example, you could walk around the block (one km per side). Your displacement would be zero, but the distance that you walk would be 4 kilometers. 17. Critical Thinking You move a box through one displacement and then through a second displacement. The magnitudes of the two disp ...
... Not necessarily. For example, you could walk around the block (one km per side). Your displacement would be zero, but the distance that you walk would be 4 kilometers. 17. Critical Thinking You move a box through one displacement and then through a second displacement. The magnitudes of the two disp ...
2 Spacetime and General - Farmingdale State College
... (d)2, (ds)2 is equal to zero. In this case, (dx) = d = (cdt). Hence, dx = cdt, or dx/dt = c. But dx/dt is a velocity. For it to equal c, it must be the world line of something moving at the speed of light. Thus (ds)2 = 0 represents a light ray and the world line is called lightlike. Lightlike worl ...
... (d)2, (ds)2 is equal to zero. In this case, (dx) = d = (cdt). Hence, dx = cdt, or dx/dt = c. But dx/dt is a velocity. For it to equal c, it must be the world line of something moving at the speed of light. Thus (ds)2 = 0 represents a light ray and the world line is called lightlike. Lightlike worl ...
Momentum - USU Physics
... An impulse acting on an object causes a change in its momentum. • The change in momentum is equal in magnitude and direction to the applied impulse. impulse Δv m • Impulse = m. Δv F. Δt • A new way of looking at Newton’s 2nd law! Example: A 50kg rock is hurled by a giant catapult with a force of 4 ...
... An impulse acting on an object causes a change in its momentum. • The change in momentum is equal in magnitude and direction to the applied impulse. impulse Δv m • Impulse = m. Δv F. Δt • A new way of looking at Newton’s 2nd law! Example: A 50kg rock is hurled by a giant catapult with a force of 4 ...
Final Momentum NRG Review
... which is moving in the same direction with a speed of 0.40 m/s. If the faster ball slows down to a speed of 0.65 m/s, then what is the speed of the second ball? PSYW 56. A 0.050-kg billiard ball moving at 1.5 m/s strikes a second 0.050-kg billiard ball which is at rest on the table. If the first bal ...
... which is moving in the same direction with a speed of 0.40 m/s. If the faster ball slows down to a speed of 0.65 m/s, then what is the speed of the second ball? PSYW 56. A 0.050-kg billiard ball moving at 1.5 m/s strikes a second 0.050-kg billiard ball which is at rest on the table. If the first bal ...
I = m • Δ v - CUSDPhysics
... Momentum is a conserved quantity in physics. This means that if you have several objects in a system, perhaps interacting with each other, but not being influenced by forces from outside of the system, then the total momentum of the system does not change over time. However, the separate momenta of ...
... Momentum is a conserved quantity in physics. This means that if you have several objects in a system, perhaps interacting with each other, but not being influenced by forces from outside of the system, then the total momentum of the system does not change over time. However, the separate momenta of ...
Angular Momentum Solutions
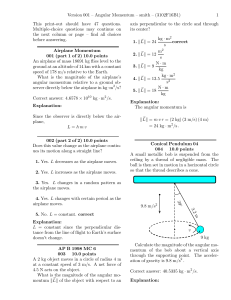
... Gravity is the only force acting on the particle. The change in angular momentum is negative (going from zero to negative values) because the torque of the gravity force is negative (−k̂ direction) as you can see from the ~ ×F ...
... Gravity is the only force acting on the particle. The change in angular momentum is negative (going from zero to negative values) because the torque of the gravity force is negative (−k̂ direction) as you can see from the ~ ×F ...