Document
... How do you determine the acceleration of an object that is NOT changing its speed, but is changing its direction? ...
... How do you determine the acceleration of an object that is NOT changing its speed, but is changing its direction? ...
Student Review Sheet Physics Semester A Examination
... given the forces acting on an object and the mass of the object, determine the magnitude of the net force. given the forces acting on an object and the mass of the object, determine the acceleration. given a vector diagram of an object’s velocity, determine the magnitude of its components. i ...
... given the forces acting on an object and the mass of the object, determine the magnitude of the net force. given the forces acting on an object and the mass of the object, determine the acceleration. given a vector diagram of an object’s velocity, determine the magnitude of its components. i ...
Monday, Sept. 29, 2008
... Independent of the object’s surroundings: The same no matter where you go. Independent of the method of measurement: The same no matter how you measure it. ...
... Independent of the object’s surroundings: The same no matter where you go. Independent of the method of measurement: The same no matter how you measure it. ...
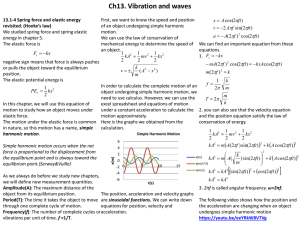
13.1-4 Spring force and elastic energy revisited. (Hooke’s law)
... Calculate the total energy of the system and A wave traveling in the positive x-direction is the maximum speed of the object if the pictured in Figure below. Find the amplitude of the motion is 0.0300m.(b) amplitude, wave length, speed and period What is the velocity of the object when the of the wa ...
... Calculate the total energy of the system and A wave traveling in the positive x-direction is the maximum speed of the object if the pictured in Figure below. Find the amplitude of the motion is 0.0300m.(b) amplitude, wave length, speed and period What is the velocity of the object when the of the wa ...
Force Diagrams
... direction the force is being exerted, and label it by (a) the type of force, (b) the object exerting the force, and (c) the object receiving the force (which will be you object of interest). 5. If the object is stationary or is moving at a constant velocity, the vectors should graphically add up to ...
... direction the force is being exerted, and label it by (a) the type of force, (b) the object exerting the force, and (c) the object receiving the force (which will be you object of interest). 5. If the object is stationary or is moving at a constant velocity, the vectors should graphically add up to ...
9-4,5,6,7
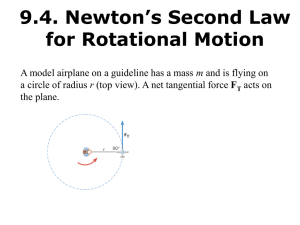
... dumbbell in each hand. In this position the total moment of inertia of the rotating system (platform, woman, and dumbbells) is 5.40 kg·m2. By pulling in her arms, she reduces the moment of inertia to 3.80 kg·m2. Find her new angular speed. ...
... dumbbell in each hand. In this position the total moment of inertia of the rotating system (platform, woman, and dumbbells) is 5.40 kg·m2. By pulling in her arms, she reduces the moment of inertia to 3.80 kg·m2. Find her new angular speed. ...
Honor`s Physics Chapter 5 Notes
... The direction of this force is toward the center of the circle and is therefore constant changing direction. The centripetal force is the external force required to make a body follow a curved path. Hence centripetal force is a kinematic force requirement, not a particular kind of force like gravit ...
... The direction of this force is toward the center of the circle and is therefore constant changing direction. The centripetal force is the external force required to make a body follow a curved path. Hence centripetal force is a kinematic force requirement, not a particular kind of force like gravit ...