Packet 4 - Momentum
... 1999M1 In a laboratory experiment, you wish to determine the initial speed of a dart just after it leaves a dart gun. The dart, of mass m, is fired with the gun very close to a wooden block of mass M 0 which hangs from a cord of length l and negligible mass, as shown above. Assume the size of the b ...
... 1999M1 In a laboratory experiment, you wish to determine the initial speed of a dart just after it leaves a dart gun. The dart, of mass m, is fired with the gun very close to a wooden block of mass M 0 which hangs from a cord of length l and negligible mass, as shown above. Assume the size of the b ...
Solution
... Total mechanical energy would be conserved and both blocks started with the same potential energy U = mgh and no kinetic energy. With friction present the energy lost due to friction is given by the work done by friction on the blocks Wnon-conservatice = −fk L = −(µk N) L = −(µk mg cosθ) h/sinθ = −( ...
... Total mechanical energy would be conserved and both blocks started with the same potential energy U = mgh and no kinetic energy. With friction present the energy lost due to friction is given by the work done by friction on the blocks Wnon-conservatice = −fk L = −(µk N) L = −(µk mg cosθ) h/sinθ = −( ...
Definitions of Physical Quantities
... The density of water is, for practical purposes, 1000 kg/m3 or 1 kg/l. (The litre (l) is 10-3 m3.) • The density of solids and liquids are usually stated in g/cm3, while gases are usually in kg/m3. Relative density or specific gravity • relative density of the substance = (mass of a substance / mass ...
... The density of water is, for practical purposes, 1000 kg/m3 or 1 kg/l. (The litre (l) is 10-3 m3.) • The density of solids and liquids are usually stated in g/cm3, while gases are usually in kg/m3. Relative density or specific gravity • relative density of the substance = (mass of a substance / mass ...
Physics Toolkit - Effingham County Schools
... Change in angular velocity depends on magnitude of force, distance from axis to point where force exerted, and direction of force ...
... Change in angular velocity depends on magnitude of force, distance from axis to point where force exerted, and direction of force ...
Lecture05-09
... A 71-kg parent and a 19-kg child meet at the center of an ice rink. They place their hands together and push. (a) Is the force experienced by the child more than, less than, or the same as the force experienced by the parent? (b) Is the acceleration of the child more than, less than, or the same as ...
... A 71-kg parent and a 19-kg child meet at the center of an ice rink. They place their hands together and push. (a) Is the force experienced by the child more than, less than, or the same as the force experienced by the parent? (b) Is the acceleration of the child more than, less than, or the same as ...
Motion & Forces
... You don't always need to see something move to know that motion has taken place. A reference point is needed to determine the position of an object. Motion occurs when an object changes its position relative to a reference point. The motion of an object depends on the reference point that is chosen. ...
... You don't always need to see something move to know that motion has taken place. A reference point is needed to determine the position of an object. Motion occurs when an object changes its position relative to a reference point. The motion of an object depends on the reference point that is chosen. ...
Wizard Test Maker - Physics 12
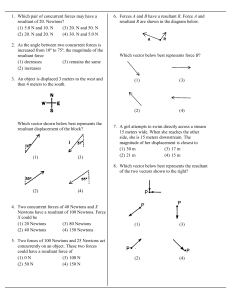
... 1. Which pair of concurrent forces may have a resultant of 20. Newtons? (1) 5.0 N and 10. N (3) 20. N and 50. N (2) 20. N and 20. N (4) 30. N and 5.0 N 2. As the angle between two concurrent forces is increased from 10º to 75º, the magnitude of the resultant force (1) decreases (3) remains the same ...
... 1. Which pair of concurrent forces may have a resultant of 20. Newtons? (1) 5.0 N and 10. N (3) 20. N and 50. N (2) 20. N and 20. N (4) 30. N and 5.0 N 2. As the angle between two concurrent forces is increased from 10º to 75º, the magnitude of the resultant force (1) decreases (3) remains the same ...
Newton`s Second Law I
... Inertia is a term used to measure the ability of an object to resist a change in its state of motion. An object with a lot of inertia takes a lot of force to start or stop; an object with a small amount of inertia requires a small amount of force to start or stop. The word “inertia” comes from the L ...
... Inertia is a term used to measure the ability of an object to resist a change in its state of motion. An object with a lot of inertia takes a lot of force to start or stop; an object with a small amount of inertia requires a small amount of force to start or stop. The word “inertia” comes from the L ...
Important Instructions for the School Principal
... respective velocity after collision become V1 and V2. A hammer of mass 500g moving at 50 ms-1 strikes a nail. The nail stops the hammer in a small time interval of 0.01/s. What is the change in momentum suffered by the hammer ? Also calculate the force of the hammer on the nail. What will be the for ...
... respective velocity after collision become V1 and V2. A hammer of mass 500g moving at 50 ms-1 strikes a nail. The nail stops the hammer in a small time interval of 0.01/s. What is the change in momentum suffered by the hammer ? Also calculate the force of the hammer on the nail. What will be the for ...
- St. Aidan School
... or object used for comparison to determine if something is moving. SI units - scientists use the International System of Units to describe the distance an object moves. Section 2 Calculating Speed Speed = Distance/Time ...
... or object used for comparison to determine if something is moving. SI units - scientists use the International System of Units to describe the distance an object moves. Section 2 Calculating Speed Speed = Distance/Time ...
08 lecture ppt
... The above system of equations can be solved for v at the bottom of the ramp. The result is the same as when using energy methods. (See text example 8.13.) It is static friction that makes an object roll. ...
... The above system of equations can be solved for v at the bottom of the ramp. The result is the same as when using energy methods. (See text example 8.13.) It is static friction that makes an object roll. ...
Physics HSC - Kotara High School
... perform a first-hand investigation, gather information and analyse data to calculate initial and final velocity, maximum height reached, range and time of flight of a projectile for a range of situations by using simulations, data loggers and computer analysis ...
... perform a first-hand investigation, gather information and analyse data to calculate initial and final velocity, maximum height reached, range and time of flight of a projectile for a range of situations by using simulations, data loggers and computer analysis ...
SC81 Physics Curriculum Map 2010/2011 Revised 7/29/2010
... 2. Calculate the magnitude of centripetal force and centripetal acceleration for an object in circular motion. S5 C2 PO 11 1. Predict how the force will change between two masses when the distance between them increases or decreases. Predict how the force will change between two masses when the mass ...
... 2. Calculate the magnitude of centripetal force and centripetal acceleration for an object in circular motion. S5 C2 PO 11 1. Predict how the force will change between two masses when the distance between them increases or decreases. Predict how the force will change between two masses when the mass ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... A heavy moving object has a greater amount of motion than a light object. The amount of motion/mass of a body is defined as momentum. Momentum is taken as the product of mass & velocity of a body. The unit of momentum is therefore kilograms x metres per second kg ms-1 or kg m/s For the same given fo ...
... A heavy moving object has a greater amount of motion than a light object. The amount of motion/mass of a body is defined as momentum. Momentum is taken as the product of mass & velocity of a body. The unit of momentum is therefore kilograms x metres per second kg ms-1 or kg m/s For the same given fo ...