Chapter 9 PPT
... 3. Choose a convenient set of x, y axes and resolve all forces into components that lie along these axes. ...
... 3. Choose a convenient set of x, y axes and resolve all forces into components that lie along these axes. ...
external forces. - Mahidol University
... an inertial frame, and for our purposes we can consider the Earth as being such a frame. The Earth is not really an inertial frame because of its orbital motion around the Sun and its rotational motion about its own axis, both of which result in centripetal accelerations. However, these acceleration ...
... an inertial frame, and for our purposes we can consider the Earth as being such a frame. The Earth is not really an inertial frame because of its orbital motion around the Sun and its rotational motion about its own axis, both of which result in centripetal accelerations. However, these acceleration ...
First Diploma in Engineering Mathematics for Engineering
... a) The force required to move and accelerate a mass up an incline is given by the equation:F = mgsinθ + mgμcosθ + ma, where m is the mass, g is gravity, a is acceleration, μ is the coefficient of friction, and θ is the angle of the incline. If g = 9.8, m = 25kg, a = 3msˉ², μ = 0.4 and θ= 35°, calcul ...
... a) The force required to move and accelerate a mass up an incline is given by the equation:F = mgsinθ + mgμcosθ + ma, where m is the mass, g is gravity, a is acceleration, μ is the coefficient of friction, and θ is the angle of the incline. If g = 9.8, m = 25kg, a = 3msˉ², μ = 0.4 and θ= 35°, calcul ...
of Sliding and rolling: rolling ball physics
... Let us consider, for instance, a rigid sphere, solid and uniform, of mass M and radius r, which is thrown horizontally along a rigid horizontal surface with an initial velocity v,. To study the motion described by the sphere we must consider two phases which are dearly different. In the first phase ...
... Let us consider, for instance, a rigid sphere, solid and uniform, of mass M and radius r, which is thrown horizontally along a rigid horizontal surface with an initial velocity v,. To study the motion described by the sphere we must consider two phases which are dearly different. In the first phase ...
force
... • The less massive an object the greater the acceleration • The more massive an object the smaller the acceleration. • The less force applied the smaller the ...
... • The less massive an object the greater the acceleration • The more massive an object the smaller the acceleration. • The less force applied the smaller the ...
Lake Compounce General Info
... Earth Gravity and G - Forces Gravity refers to the force of attraction between objects. All objects exert a gravitational force. Any two objects with mass attract each other, and the strength of this force depends on the mass of the objects and the distance between them. The larger or more massive t ...
... Earth Gravity and G - Forces Gravity refers to the force of attraction between objects. All objects exert a gravitational force. Any two objects with mass attract each other, and the strength of this force depends on the mass of the objects and the distance between them. The larger or more massive t ...
Acceleration and Force
... The speed of the needle is a measure of your acceleration (in a straight line). ...
... The speed of the needle is a measure of your acceleration (in a straight line). ...
SPH4U: Lecture 15 Today’s Agenda
... Colliding carts problem Two dimensional collision problems (scattering) Solving elastic collision problems using COM and inertial reference frame transformations ...
... Colliding carts problem Two dimensional collision problems (scattering) Solving elastic collision problems using COM and inertial reference frame transformations ...
File - Phy 2048-0002
... • We know that if an object is in (translational) equilibrium then it does not accelerate. We can say that SF = 0 • An object in rotational equilibrium does not change its rotational speed. In this case we can say that there is no net torque or in other words that: ...
... • We know that if an object is in (translational) equilibrium then it does not accelerate. We can say that SF = 0 • An object in rotational equilibrium does not change its rotational speed. In this case we can say that there is no net torque or in other words that: ...
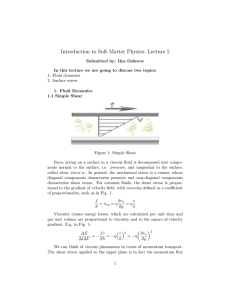
Introduction to Soft Matter Physics- Lecture 5
... is a typical relation from the theory of transport phenomena: velocity gradient leads to the associated flux of momentum. The momentum is getting transported from layer to layer by shear forces in between the layers, or, on the molecular level, by molecules jumping from one layer to another and tran ...
... is a typical relation from the theory of transport phenomena: velocity gradient leads to the associated flux of momentum. The momentum is getting transported from layer to layer by shear forces in between the layers, or, on the molecular level, by molecules jumping from one layer to another and tran ...
Exercises - PHYSICSMr. Bartholomew
... 37. Circle the letter of each factor that affects the amount of air resistance experienced by an object. a. time in contact with the air b. speed of object through the air c. surface area of object d. weight of object 38. Circle the letter that describes the forces that are in balance when an object ...
... 37. Circle the letter of each factor that affects the amount of air resistance experienced by an object. a. time in contact with the air b. speed of object through the air c. surface area of object d. weight of object 38. Circle the letter that describes the forces that are in balance when an object ...
NEWTON`S FIRST LAW CONCEPTUAL WORKSHEET
... A metal ball is put into the end of the tube indicated by the arrow. The ball is then shot out of the other end of the tube at high speed. Pick the path the ball will follow after it exits the tube. Note – you are looking down on these tubes, they are not vertical. ...
... A metal ball is put into the end of the tube indicated by the arrow. The ball is then shot out of the other end of the tube at high speed. Pick the path the ball will follow after it exits the tube. Note – you are looking down on these tubes, they are not vertical. ...