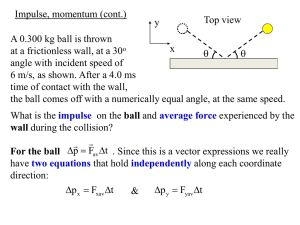
Perturbation Method in the Analysis of Manipulator Inertial
... mechanical vibrations can be induced during motion. Simultaneously, the accuracy with which the gripping device follows the given motion trajectory belongs to basic characteristics of its quantitative evaluation [6, 10, 12]. Errors in following the motion trajectory by the gripping device depend on ...
... mechanical vibrations can be induced during motion. Simultaneously, the accuracy with which the gripping device follows the given motion trajectory belongs to basic characteristics of its quantitative evaluation [6, 10, 12]. Errors in following the motion trajectory by the gripping device depend on ...
Physics Beyond 2000
... • Whirl the bob in a horizontal circle with string. • The other end of the string is tied to some hanging weight. • Maintain the hanging weight in equilibrium. hollow plastic tube ...
... • Whirl the bob in a horizontal circle with string. • The other end of the string is tied to some hanging weight. • Maintain the hanging weight in equilibrium. hollow plastic tube ...
Velocity and Acceleration
... the car got from one position to the other. It might have moved at a steady rate or it might have speeded up and then slowed down before it got to its second position. It might also have been moving when you first noticed it and might still have been moving at its second location. The car may have m ...
... the car got from one position to the other. It might have moved at a steady rate or it might have speeded up and then slowed down before it got to its second position. It might also have been moving when you first noticed it and might still have been moving at its second location. The car may have m ...
Chapter 6 Work and Kinetic Energy
... True or false: (a) If the net or total work done on a particle was not zero, then its speed must have changed. (b) If the net or total work done on a particle was not zero, then its velocity must have changed. (c) If the net or total work done on a particle was not zero, then its direction of motion ...
... True or false: (a) If the net or total work done on a particle was not zero, then its speed must have changed. (b) If the net or total work done on a particle was not zero, then its velocity must have changed. (c) If the net or total work done on a particle was not zero, then its direction of motion ...
KEY - NNHS Tigerscience
... 1. Motion and Forces Central Concept: Newton’s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion of most objects. 1.1 Compare and contrast vector quantities (e.g., displacement, velocity, acceleration force, linear momentum) and scalar quantities (e.g., distance, speed, energy, mass, wo ...
... 1. Motion and Forces Central Concept: Newton’s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion of most objects. 1.1 Compare and contrast vector quantities (e.g., displacement, velocity, acceleration force, linear momentum) and scalar quantities (e.g., distance, speed, energy, mass, wo ...
Lab Manual 2005
... → in the Position box that appears click on “rot” to turn it off. This measurement is not required since our object has no rotation. → We are now able to run the simulation and track the path taken. → click RUN (note: the RUN button will change to a STOP button once started) → after approximately 2. ...
... → in the Position box that appears click on “rot” to turn it off. This measurement is not required since our object has no rotation. → We are now able to run the simulation and track the path taken. → click RUN (note: the RUN button will change to a STOP button once started) → after approximately 2. ...
- Physics Knowledge
... position. The force acting on the body at an instant is directed towards equilibrium position and is proportional to the displacement of the body form equilibrium position i.e. F = − ky A simple harmonic motion is represented by a single harmonic function (i.e. sine or cosine function) and of consta ...
... position. The force acting on the body at an instant is directed towards equilibrium position and is proportional to the displacement of the body form equilibrium position i.e. F = − ky A simple harmonic motion is represented by a single harmonic function (i.e. sine or cosine function) and of consta ...
Rotational motion
... Tension did positive rotational work (it made the Yo-Yo spin faster) Tension did negative translational work (it made the Yo-Yo move more slowly) ... the net work done by tension was zero. This happened because the string was stationary, and thus enforced a = ±αr. This is also true in rolling motion ...
... Tension did positive rotational work (it made the Yo-Yo spin faster) Tension did negative translational work (it made the Yo-Yo move more slowly) ... the net work done by tension was zero. This happened because the string was stationary, and thus enforced a = ±αr. This is also true in rolling motion ...
Physics I - Rose
... Solve: Only spring 2 touches the mass, so the net force on the mass is Fm F2 on m. Newton’s third law tells us that F2 on m Fm on 2 and that F2 on 1 F1 on 2. From Fnet ma, the net force on a massless spring is zero. Thus Fw on 1 F2 on 1 k1x1 and Fm on 2 F1 on 2 k2x2. Combining thes ...
... Solve: Only spring 2 touches the mass, so the net force on the mass is Fm F2 on m. Newton’s third law tells us that F2 on m Fm on 2 and that F2 on 1 F1 on 2. From Fnet ma, the net force on a massless spring is zero. Thus Fw on 1 F2 on 1 k1x1 and Fm on 2 F1 on 2 k2x2. Combining thes ...
PHYS101
... 7. The mass is passing through the equilibrium position again, in the opposite direction, so it has a positive velocity. There is no net force, so the acceleration is zero. 8. The mass continues moving upward. The velocity is positive but its magnitude is decreasing, so the acceleration is ne ...
... 7. The mass is passing through the equilibrium position again, in the opposite direction, so it has a positive velocity. There is no net force, so the acceleration is zero. 8. The mass continues moving upward. The velocity is positive but its magnitude is decreasing, so the acceleration is ne ...
simple harmonic motion
... Description of Simple Harmonic Motion Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) occurs when an elastic force, described by Hooke’s Law, is present. If the force F on an object is proportional to the objects’ displacement x from a point O and is directed towards that point then the particle will move with SHM. F ...
... Description of Simple Harmonic Motion Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) occurs when an elastic force, described by Hooke’s Law, is present. If the force F on an object is proportional to the objects’ displacement x from a point O and is directed towards that point then the particle will move with SHM. F ...
Brownian motion

Brownian motion or pedesis (from Greek: πήδησις /pˈɪːdiːsis/ ""leaping"") is the random motion of particles suspended in a fluid (a liquid or a gas) resulting from their collision with the quick atoms or molecules in the gas or liquid. Wiener Process refers to the mathematical model used to describe such Brownian Motion, which is often called a particle theoryThis transport phenomenon is named after the botanist Robert Brown. In 1827, while looking through a microscope at particles trapped in cavities inside pollen grains in water, he noted that the particles moved through the water but was not able to determine the mechanisms that caused this motion. Atoms and molecules had long been theorized as the constituents of matter, and many decades later, Albert Einstein published a paper in 1905 that explained in precise detail how the motion that Brown had observed was a result of the pollen being moved by individual water molecules. This explanation of Brownian motion served as definitive confirmation that atoms and molecules actually exist, and was further verified experimentally by Jean Perrin in 1908. Perrin was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1926 ""for his work on the discontinuous structure of matter"" (Einstein had received the award five years earlier ""for his services to theoretical physics"" with specific citation of different research). The direction of the force of atomic bombardment is constantly changing, and at different times the particle is hit more on one side than another, leading to the seemingly random nature of the motion.The mathematical model of Brownian motion has numerous real-world applications. For instance, Stock market fluctuations are often cited, although Benoit Mandelbrot rejected its applicability to stock price movements in part because these are discontinuous.Brownian motion is among the simplest of the continuous-time stochastic (or probabilistic) processes, and it is a limit of both simpler and more complicated stochastic processes (see random walk and Donsker's theorem). This universality is closely related to the universality of the normal distribution. In both cases, it is often mathematical convenience, rather than the accuracy of the models, that motivates their use.