Personality in the Workplace
... Believe their own abilities and efforts control the things that happen to them Are independent, like to participate in decisions, are involved in work, adjust to work and handle job stress well, like to influence others, are future rather than present oriented, are achievement oriented Ressources Ac ...
... Believe their own abilities and efforts control the things that happen to them Are independent, like to participate in decisions, are involved in work, adjust to work and handle job stress well, like to influence others, are future rather than present oriented, are achievement oriented Ressources Ac ...
1. The concept of “personality” most clearly embodies the notion of
... A) the part of human personality that lacks a sense of right and wrong. B) the thoughts, wishes, feelings, and memories, of which we are largely unaware. C) a set of universal concepts acquired by all humans from our common past. D) a reservoir of deeply repressed memories that does not affect behav ...
... A) the part of human personality that lacks a sense of right and wrong. B) the thoughts, wishes, feelings, and memories, of which we are largely unaware. C) a set of universal concepts acquired by all humans from our common past. D) a reservoir of deeply repressed memories that does not affect behav ...
Social Cognition and Crime
... the expectancy that one cannot escape aversive events & the motivational & learning deficits that result from the belief. ...
... the expectancy that one cannot escape aversive events & the motivational & learning deficits that result from the belief. ...
FAML 430 Week 11 - I
... orientation, refers to motivation to achieve mastery of challenging tasks. 2. Achievement motivation is often correlated with actual achievement behavior. 3. Parenting practices affect achievement motivation. 4. Achievement motivation is a relatively stable characteristic of personality. 5. Individu ...
... orientation, refers to motivation to achieve mastery of challenging tasks. 2. Achievement motivation is often correlated with actual achievement behavior. 3. Parenting practices affect achievement motivation. 4. Achievement motivation is a relatively stable characteristic of personality. 5. Individu ...
Influences on health behaviour
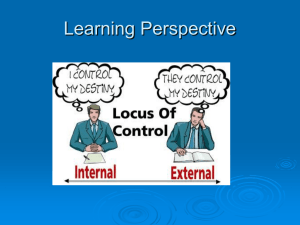
... ◦ Another commonly investigated aspect of personality is an individual’s locus of control. ◦ In general people are considered to have either an internal or external orientation. ◦ Internal locus of control – personal responsibility for actions and outcomes ◦ External locus of control – responsibilit ...
... ◦ Another commonly investigated aspect of personality is an individual’s locus of control. ◦ In general people are considered to have either an internal or external orientation. ◦ Internal locus of control – personal responsibility for actions and outcomes ◦ External locus of control – responsibilit ...
Locus of control
... can happen as a result of having an extreme external locus of control. 1. Learned helplessness: repeatedly faced with traumatic events over which a person has no control, he/she come to feel helpless, hopeless, and depressed. ...
... can happen as a result of having an extreme external locus of control. 1. Learned helplessness: repeatedly faced with traumatic events over which a person has no control, he/she come to feel helpless, hopeless, and depressed. ...