AP Physics – The Physics Little AP Test Review Helper
... Galaxy.) Draw a picture. Visualize what is happening. Write down all the things that are given using proper symbols. Ask yourself these questions: What is going on in the problem? What do you have to find out? What kind of problem is it? Is it an electric problem? Is it a projectile motion problem? ...
... Galaxy.) Draw a picture. Visualize what is happening. Write down all the things that are given using proper symbols. Ask yourself these questions: What is going on in the problem? What do you have to find out? What kind of problem is it? Is it an electric problem? Is it a projectile motion problem? ...
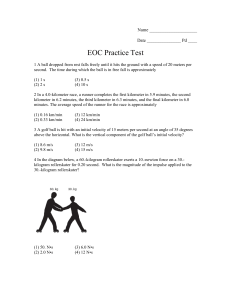
1 - Net Start Class
... 1/6-th that of Earth's? ________ Explain or show your work. 5. How much net force is required to keep a 5-kg object moving rightward with a constant velocity of 2 m/s? ________ Explain or show your work. 6. TRUE or FALSE: For an object resting upon a non-accelerating surface, the normal force is equ ...
... 1/6-th that of Earth's? ________ Explain or show your work. 5. How much net force is required to keep a 5-kg object moving rightward with a constant velocity of 2 m/s? ________ Explain or show your work. 6. TRUE or FALSE: For an object resting upon a non-accelerating surface, the normal force is equ ...
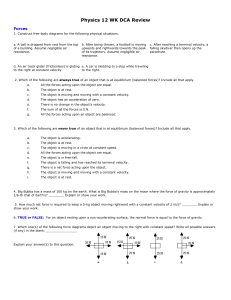
04 Forces WS08 [v6.0]
... Write an equation € that relates g, M1 , θ , T (the tension in the rope joining the masses) and a (the magnitude of the acceleration of the masses). Take the direction down the incline (the direction M1 moves) as positive. (Answer: M1gSin θ − T = M1 a ) € g, a, T and M . Take upward (the direction M ...
... Write an equation € that relates g, M1 , θ , T (the tension in the rope joining the masses) and a (the magnitude of the acceleration of the masses). Take the direction down the incline (the direction M1 moves) as positive. (Answer: M1gSin θ − T = M1 a ) € g, a, T and M . Take upward (the direction M ...
Centripetal Force
... The Spinning Penny demonstrates forces in motion. A force is a push or pull. To understand how and why it works, you have to look at the forces that are acting on the penny. The shape of the balloon makes the penny move in a circular path - otherwise the penny would want to continue to move in a str ...
... The Spinning Penny demonstrates forces in motion. A force is a push or pull. To understand how and why it works, you have to look at the forces that are acting on the penny. The shape of the balloon makes the penny move in a circular path - otherwise the penny would want to continue to move in a str ...
Dynamics Powerpoint - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... The bus is initially at rest, as is the package. In the absence of any force, the natural state of the package is to remain at rest. When the bus pulls forward, the package remains at rest because of its inertia (until the back of the seat applies a forward force to make it move with the bus). From ...
... The bus is initially at rest, as is the package. In the absence of any force, the natural state of the package is to remain at rest. When the bus pulls forward, the package remains at rest because of its inertia (until the back of the seat applies a forward force to make it move with the bus). From ...
Document
... • When the block is moving it experiences a smaller friction force called the kinetic friction force • It is a common experience that it takes more force to get something moving than to keep it moving. ...
... • When the block is moving it experiences a smaller friction force called the kinetic friction force • It is a common experience that it takes more force to get something moving than to keep it moving. ...
How? Newton`s second law of motion
... • To solve for the net force, multiply both sides of the equation by the mass: • The mass, m, on the left side cancels, giving the equation: ...
... • To solve for the net force, multiply both sides of the equation by the mass: • The mass, m, on the left side cancels, giving the equation: ...
CHAPTER 4 NEWTON`S LAWS • Little bit of history • Forces
... A force is best described as an action or influence that when acting on an object, will change its motion. There are two main types of forces: • contact forces (push, pull, friction, etc.) ⇒ direct force • non-contact (or field) forces (gravity, magnetic, electric, etc.) ⇒ “action” at a distance and ...
... A force is best described as an action or influence that when acting on an object, will change its motion. There are two main types of forces: • contact forces (push, pull, friction, etc.) ⇒ direct force • non-contact (or field) forces (gravity, magnetic, electric, etc.) ⇒ “action” at a distance and ...
Lecture 7 - Purdue Physics
... Tension with “Ideal Cord” • “Ideal cord”: a cord that has zero mass and thus zero weight • In an ideal cord, (a) the tension has the same value at all points along the cord, and (b) the tension is equal to the force that the cord exerts on the objects attached to its ends (as long as there is no ex ...
... Tension with “Ideal Cord” • “Ideal cord”: a cord that has zero mass and thus zero weight • In an ideal cord, (a) the tension has the same value at all points along the cord, and (b) the tension is equal to the force that the cord exerts on the objects attached to its ends (as long as there is no ex ...
TB_chapter15 - AppServ Open Project 2.4.9
... c. move away from each other. d. move towards each other. e. remain in an equilibrium state. ANS: d 7. As a submarine dives, the pressure on its hull a. increases. b. decreases. c. remains constant. d. depends on the thickness of the walls of the submarine. e. depends on the decrease in volume of th ...
... c. move away from each other. d. move towards each other. e. remain in an equilibrium state. ANS: d 7. As a submarine dives, the pressure on its hull a. increases. b. decreases. c. remains constant. d. depends on the thickness of the walls of the submarine. e. depends on the decrease in volume of th ...
What is motion? (cont.) - Riverdale Middle School
... How can you identify forces on an object? • Many forces can be acting on an object at the same time. These forces can also act in different ...
... How can you identify forces on an object? • Many forces can be acting on an object at the same time. These forces can also act in different ...
Derived copy of Further Applications of Newton`s
... A ea jumps by exerting a force of 1.20 × 10 N straight down on the ground. A breeze blowing on the ea parallel to the ground exerts a force of 0.500 × 10 N on the ea. Find the direction and magnitude of the acceleration of the ea if its mass is 6.00 × 10 kg. Do not neglect the gravitational forc ...
... A ea jumps by exerting a force of 1.20 × 10 N straight down on the ground. A breeze blowing on the ea parallel to the ground exerts a force of 0.500 × 10 N on the ea. Find the direction and magnitude of the acceleration of the ea if its mass is 6.00 × 10 kg. Do not neglect the gravitational forc ...
Physics 231 Topic 9: Solids & Fluids Wade Fisher
... A block of weight w is placed in water and found to stay submerged as shown in the picture. The liquid is then replaced by another liquid of lower density. What will happen if the block is placed in the liquid of lower density? the block will float on the surface of the liquid the block will be part ...
... A block of weight w is placed in water and found to stay submerged as shown in the picture. The liquid is then replaced by another liquid of lower density. What will happen if the block is placed in the liquid of lower density? the block will float on the surface of the liquid the block will be part ...
Momentum - SCHOOLinSITES
... and are zooming along in a 100kg amusement park bumper car at 10m/s. They bump Melinda’s car, which is sitting still. Melinda has a mass of 25kg. After the elastic collision, the twins continue ahead with a speed of 4.12m/s. How fast is Melinda’s car bumped across the ...
... and are zooming along in a 100kg amusement park bumper car at 10m/s. They bump Melinda’s car, which is sitting still. Melinda has a mass of 25kg. After the elastic collision, the twins continue ahead with a speed of 4.12m/s. How fast is Melinda’s car bumped across the ...
Pull It, Push It
... won’t move. The tendency for objects to stay at rest or to keep moving is called inertia. Throw a ball and it soars to the basket. Your push overcomes the ball’s inertia so the ball moves. Objects need a push or pull to stop moving, too. The ball’s inertia would keep it moving. When you catch a ball ...
... won’t move. The tendency for objects to stay at rest or to keep moving is called inertia. Throw a ball and it soars to the basket. Your push overcomes the ball’s inertia so the ball moves. Objects need a push or pull to stop moving, too. The ball’s inertia would keep it moving. When you catch a ball ...
press the brake to apply a force in the opposite direction, so that the
... Newton’s Third Law For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. When the cannon fires, the chemical energy of the gunpowder is converted into the kinetic energy of the cannonball. The cannon applies a force to the cannonball, causing a sudden increase in velocity. ...
... Newton’s Third Law For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. When the cannon fires, the chemical energy of the gunpowder is converted into the kinetic energy of the cannonball. The cannon applies a force to the cannonball, causing a sudden increase in velocity. ...
Secondary Robot
... Motion states that the acceleration of an object is produced by a net force in the same direction as the acceleration, is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. This means that the acceleration (a) of an object is dependant on a ...
... Motion states that the acceleration of an object is produced by a net force in the same direction as the acceleration, is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. This means that the acceleration (a) of an object is dependant on a ...
Newton`s Third Law - Center Grove Schools
... reaction force pairs don’t cancel because they act on different objects. Forces can cancel only if they act on the same object. For example, imagine you’re driving a bumper car and are about to bump a friend in another car, as shown in Figure 14. When the two cars collide, your car pushes on the oth ...
... reaction force pairs don’t cancel because they act on different objects. Forces can cancel only if they act on the same object. For example, imagine you’re driving a bumper car and are about to bump a friend in another car, as shown in Figure 14. When the two cars collide, your car pushes on the oth ...
04_Force and Motion
... approximation; the actual phenomenon is very complicated. The coefficient of friction may vary somewhat with speed; there may be some dependence on the surface area of the objects. Also, remember that these equations are for the magnitude of the frictional force—it is always perpendicular to the nor ...
... approximation; the actual phenomenon is very complicated. The coefficient of friction may vary somewhat with speed; there may be some dependence on the surface area of the objects. Also, remember that these equations are for the magnitude of the frictional force—it is always perpendicular to the nor ...
Revision
... (1) The object is accelerating in the first 5 seconds. (2) The maximum speed of the object is less than ...
... (1) The object is accelerating in the first 5 seconds. (2) The maximum speed of the object is less than ...
P3: Forces for Transport
... If an object is stationary and has NO resultant force on it the object will… If an object is stationary and a resultant force acts on it the object will… If an object is already moving and NO resultant force acts on it the object will… If an object is already moving and a resultant force acts on it ...
... If an object is stationary and has NO resultant force on it the object will… If an object is stationary and a resultant force acts on it the object will… If an object is already moving and NO resultant force acts on it the object will… If an object is already moving and a resultant force acts on it ...
Practice Exam
... 28 A balloon is rubbed against a student’s hair and then touched to a wall. The balloon “sticks” to the wall due to (1) electrostatic forces between the particles of the balloon (2) magnetic forces between the particles of the wall (3) electrostatic forces between the particles of the balloon and th ...
... 28 A balloon is rubbed against a student’s hair and then touched to a wall. The balloon “sticks” to the wall due to (1) electrostatic forces between the particles of the balloon (2) magnetic forces between the particles of the wall (3) electrostatic forces between the particles of the balloon and th ...
Buoyancy
In science, buoyancy (pronunciation: /ˈbɔɪ.ənᵗsi/ or /ˈbuːjənᵗsi/; also known as upthrust) is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of an immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the pressure at the bottom of a column of fluid is greater than at the top of the column. Similarly, the pressure at the bottom of an object submerged in a fluid is greater than at the top of the object. This pressure difference results in a net upwards force on the object. The magnitude of that force exerted is proportional to that pressure difference, and (as explained by Archimedes' principle) is equivalent to the weight of the fluid that would otherwise occupy the volume of the object, i.e. the displaced fluid.For this reason, an object whose density is greater than that of the fluid in which it is submerged tends to sink. If the object is either less dense than the liquid or is shaped appropriately (as in a boat), the force can keep the object afloat. This can occur only in a reference frame which either has a gravitational field or is accelerating due to a force other than gravity defining a ""downward"" direction (that is, a non-inertial reference frame). In a situation of fluid statics, the net upward buoyancy force is equal to the magnitude of the weight of fluid displaced by the body.The center of buoyancy of an object is the centroid of the displaced volume of fluid.
![04 Forces WS08 [v6.0]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017538421_1-2d2da7feadc016eec54eb7cdf19da8aa-300x300.png)