Chapter 2: Pressure Distribution in a Fluid
... Condition for static equilibrium: (1) ∑Fv=0 and (2) ∑M=0 Condition (2) is met only when C and G coincide, otherwise we can have either a righting moment (stable) or a heeling moment (unstable) when the body is heeled. Study: Floating Bodies For a floating body the situation is more complicated since ...
... Condition for static equilibrium: (1) ∑Fv=0 and (2) ∑M=0 Condition (2) is met only when C and G coincide, otherwise we can have either a righting moment (stable) or a heeling moment (unstable) when the body is heeled. Study: Floating Bodies For a floating body the situation is more complicated since ...
The Force! - Cobb Learning
... • A cannon ball is shot out of a cannon with an acceleration of 10 m/s2. If its mass is 100 kg, how much force does the cannon fire with? • What is the mass of a cart if a horse pulls it with a force of 500 N and accelerates it by 0.5 m/s2? ...
... • A cannon ball is shot out of a cannon with an acceleration of 10 m/s2. If its mass is 100 kg, how much force does the cannon fire with? • What is the mass of a cart if a horse pulls it with a force of 500 N and accelerates it by 0.5 m/s2? ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion, Reference Frames and Inertia
... publications and texts assertions along the lines of that “Any reference frame that moves with constant velocity relative to an inertial reference frame is also an inertial reference frame.” The literature is saturated with such claims, yet they are simply untrue. To see why, consider some reference ...
... publications and texts assertions along the lines of that “Any reference frame that moves with constant velocity relative to an inertial reference frame is also an inertial reference frame.” The literature is saturated with such claims, yet they are simply untrue. To see why, consider some reference ...
Kinetic Energy and Work
... In the figure (a) below a 2N force is applied to a 4kg block at a downward angle θ as the block moves right-ward through 1m across a frictionless floor. Find an expression for the speed vf at the end of that distance if the block’s initial velocity is: (a) 0 and (b) 1m/s to the right. (c) The situa ...
... In the figure (a) below a 2N force is applied to a 4kg block at a downward angle θ as the block moves right-ward through 1m across a frictionless floor. Find an expression for the speed vf at the end of that distance if the block’s initial velocity is: (a) 0 and (b) 1m/s to the right. (c) The situa ...
MasteringPhysics: Assignmen
... If there is a net force acting on a body, regardless of whether it is a constant force, the body accelerates. If the body is at rest and the net force acting on it is zero, then it will remain at rest. The net force could be zero either because there are no forces acting on the body at all or becaus ...
... If there is a net force acting on a body, regardless of whether it is a constant force, the body accelerates. If the body is at rest and the net force acting on it is zero, then it will remain at rest. The net force could be zero either because there are no forces acting on the body at all or becaus ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... Under the condition that an object is viewed from an inertial reference frame, an object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will remain in motion with a constant velocity (that is, with a constant speed in a straight line), unless the object is acted upon by an external force. The n ...
... Under the condition that an object is viewed from an inertial reference frame, an object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will remain in motion with a constant velocity (that is, with a constant speed in a straight line), unless the object is acted upon by an external force. The n ...
Acceleration - Solon City Schools
... We are looking for: Balanced forces result in zero net for and no acceleration. Unbalanced forces result in acceleration of the object in the direction of the greater force ...
... We are looking for: Balanced forces result in zero net for and no acceleration. Unbalanced forces result in acceleration of the object in the direction of the greater force ...
Dynamics What causes motion? What causes changes in motion? Mass
... downward. Then the frame related to the elevator is not inertial. The person is at rest with respect to the elevator: Gravity (-mg) + Reaction of scales (N) = Net force = -ma -mg+N=-ma, => N=mg-ma The scales show the magnitude of the pushing force (=mg-ma>mg) – weight is smaller than mg !! How muc ...
... downward. Then the frame related to the elevator is not inertial. The person is at rest with respect to the elevator: Gravity (-mg) + Reaction of scales (N) = Net force = -ma -mg+N=-ma, => N=mg-ma The scales show the magnitude of the pushing force (=mg-ma>mg) – weight is smaller than mg !! How muc ...
posted
... F T k mB g Use the first equation to replace T in the second: F k mA g k mB g. (a) F k (mA mB ) g (b) T k mA g EVALUATE: We can also consider both crates together as a single object of mass (mA mB ). Fx max for this combined object gives F f k k (mA mB ) g , in agreeme ...
... F T k mB g Use the first equation to replace T in the second: F k mA g k mB g. (a) F k (mA mB ) g (b) T k mA g EVALUATE: We can also consider both crates together as a single object of mass (mA mB ). Fx max for this combined object gives F f k k (mA mB ) g , in agreeme ...
Dynamics Homework
... springboard, as shown below. The board is attached to a hinge at the left end but simply rests on the right support. (a) Draw a force diagram for the board, making sure all forces are drawn to scale. (b) Using the left support as the axis of rotation, determine the magnitude and direction of the for ...
... springboard, as shown below. The board is attached to a hinge at the left end but simply rests on the right support. (a) Draw a force diagram for the board, making sure all forces are drawn to scale. (b) Using the left support as the axis of rotation, determine the magnitude and direction of the for ...
Module P7.6 Mechanical properties of matter
... A wooden block with a mass of 5.001kg is resting on a horizontal table top. (a) What is the magnitude and direction of the normal reaction force exerted by the table on the block? (b) If a horizontal force of 2.001N now acts on the block and moves the block a distance of 3.501m along the surface, ca ...
... A wooden block with a mass of 5.001kg is resting on a horizontal table top. (a) What is the magnitude and direction of the normal reaction force exerted by the table on the block? (b) If a horizontal force of 2.001N now acts on the block and moves the block a distance of 3.501m along the surface, ca ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... same velocity as the less massive rock. The law of inertia also applies to objects in motion. An object in motion will continue moving at a constant velocity until it is acted upon by an unbalanced force. For example, if a bowling ball rolled across a completely frictionless surface with no other ob ...
... same velocity as the less massive rock. The law of inertia also applies to objects in motion. An object in motion will continue moving at a constant velocity until it is acted upon by an unbalanced force. For example, if a bowling ball rolled across a completely frictionless surface with no other ob ...
People`s Physics Book Ch 5-1 The Big Idea Acceleration is caused
... right now? Measuring acceleration is comparatively easy — you can feel accelerations. Here’s a clever way to determine your acceleration. As you accelerate your car on a flat stretch, you notice that the fuzzy dice hanging from your rearview mirror are no longer hanging straight up and down. In fact ...
... right now? Measuring acceleration is comparatively easy — you can feel accelerations. Here’s a clever way to determine your acceleration. As you accelerate your car on a flat stretch, you notice that the fuzzy dice hanging from your rearview mirror are no longer hanging straight up and down. In fact ...
Force - E
... to stop moving, to accelerate or decelerate. When two objects interact with each other, they exert a force on each other, the forces are equal in size but opposite in direction. The forces acting on an object can be replaced with a single force that causes the object to behave in the same way as all ...
... to stop moving, to accelerate or decelerate. When two objects interact with each other, they exert a force on each other, the forces are equal in size but opposite in direction. The forces acting on an object can be replaced with a single force that causes the object to behave in the same way as all ...
Physics Lesson Plan #06 - Forces
... What is weight? What does a bathroom scale measure? Weight is defined as Fg = mg so Fg changes with g g varies with your distance from the center of the Earth, but for all practical purposes it is constant at the Earth’s surface at 9.80 m/s2 Standing on a scale, there is one contact force – the scal ...
... What is weight? What does a bathroom scale measure? Weight is defined as Fg = mg so Fg changes with g g varies with your distance from the center of the Earth, but for all practical purposes it is constant at the Earth’s surface at 9.80 m/s2 Standing on a scale, there is one contact force – the scal ...
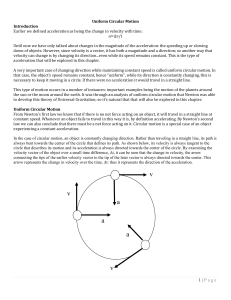
Acceleration Characteristics for Circular Motion
... Multiple forces and circular motion Often more than one force is acting on an object...including an object traveling in uniform circular motion. In that case, you treat this case the same way you did in any dynamics problem, the sum of the forces matters...not any one force. So for instance, if we ...
... Multiple forces and circular motion Often more than one force is acting on an object...including an object traveling in uniform circular motion. In that case, you treat this case the same way you did in any dynamics problem, the sum of the forces matters...not any one force. So for instance, if we ...
posted
... IDENTIFY: The reaction forces in Newton’s third law are always between a pair of objects. In Newton’s second law all the forces act on a single object. SET UP: Let y be downward. m w/g. EXECUTE: The reaction to the upward normal force on the passenger is the downward normal force, also of magnit ...
... IDENTIFY: The reaction forces in Newton’s third law are always between a pair of objects. In Newton’s second law all the forces act on a single object. SET UP: Let y be downward. m w/g. EXECUTE: The reaction to the upward normal force on the passenger is the downward normal force, also of magnit ...
Buoyancy
In science, buoyancy (pronunciation: /ˈbɔɪ.ənᵗsi/ or /ˈbuːjənᵗsi/; also known as upthrust) is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of an immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the pressure at the bottom of a column of fluid is greater than at the top of the column. Similarly, the pressure at the bottom of an object submerged in a fluid is greater than at the top of the object. This pressure difference results in a net upwards force on the object. The magnitude of that force exerted is proportional to that pressure difference, and (as explained by Archimedes' principle) is equivalent to the weight of the fluid that would otherwise occupy the volume of the object, i.e. the displaced fluid.For this reason, an object whose density is greater than that of the fluid in which it is submerged tends to sink. If the object is either less dense than the liquid or is shaped appropriately (as in a boat), the force can keep the object afloat. This can occur only in a reference frame which either has a gravitational field or is accelerating due to a force other than gravity defining a ""downward"" direction (that is, a non-inertial reference frame). In a situation of fluid statics, the net upward buoyancy force is equal to the magnitude of the weight of fluid displaced by the body.The center of buoyancy of an object is the centroid of the displaced volume of fluid.