Chapter 17 - Cengage Learning
... Increases in the temperature and concentration of reactants bring about more collisions, and the rate of reaction increases. The collision model explains many observations about reactions. Not all molecules that collide react. Colliding molecules must have a minimum amount of energy for a reaction t ...
... Increases in the temperature and concentration of reactants bring about more collisions, and the rate of reaction increases. The collision model explains many observations about reactions. Not all molecules that collide react. Colliding molecules must have a minimum amount of energy for a reaction t ...
Chapter 3 Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Equations
... • Elements combine together to make an almost limitless number of compounds compounds. ...
... • Elements combine together to make an almost limitless number of compounds compounds. ...
M - GZ @ Science Class Online
... Converting number of particles to amount, n If the actual number of particles is known (atoms, ions or molecules) then the amount, n, is easily calculated since ...
... Converting number of particles to amount, n If the actual number of particles is known (atoms, ions or molecules) then the amount, n, is easily calculated since ...
Stoichiometry - Mrs. Wiedeman
... (a) Caproic acid, responsible for the odor of dirty socks, is composed of C, H, and O atoms. Combustion of a 0.225-g sample of this compound produces 0.512 g CO2 and 0.209 g H2O.What is the empirical formula of caproic acid? (b) Caproic acid has a molar mass of 116 g/mol. What is its molecular formu ...
... (a) Caproic acid, responsible for the odor of dirty socks, is composed of C, H, and O atoms. Combustion of a 0.225-g sample of this compound produces 0.512 g CO2 and 0.209 g H2O.What is the empirical formula of caproic acid? (b) Caproic acid has a molar mass of 116 g/mol. What is its molecular formu ...
Material Equilibrium
... During a chemical reaction, the change Δn in the no. of moles of each substance is proportional to its stoichometric coefficient v, where the proportionality constant is the same for all species. This proportionality constant is called the extent of reaction For general chemical reaction undergoing ...
... During a chemical reaction, the change Δn in the no. of moles of each substance is proportional to its stoichometric coefficient v, where the proportionality constant is the same for all species. This proportionality constant is called the extent of reaction For general chemical reaction undergoing ...
Enthalpy Moles Notes - Chemistry Teaching Resources
... Ethanol can be burned in a spirit burner. The heat released (exothermic) must be absorbed by water placed in a beaker, or, if possible, a copper can, just above the flame. (Copper is an excellent conductor). Heatproof mats can be used to provide a draught shield around the apparatus; to keep the flame ...
... Ethanol can be burned in a spirit burner. The heat released (exothermic) must be absorbed by water placed in a beaker, or, if possible, a copper can, just above the flame. (Copper is an excellent conductor). Heatproof mats can be used to provide a draught shield around the apparatus; to keep the flame ...
Chapter 5HW_Ans
... One molecules of Al2(SO4)3 has 2 aluminum ions , 3 sulfur atoms, 12 oxygen atoms, and it has 3 sulfate ions. Therefore one mole of Al2(SO4)3 will have as 2 moles of aluminum ions, 3 moles of sulfur, 12 moles of oxygen, and 3 moles of SO42- ions. ...
... One molecules of Al2(SO4)3 has 2 aluminum ions , 3 sulfur atoms, 12 oxygen atoms, and it has 3 sulfate ions. Therefore one mole of Al2(SO4)3 will have as 2 moles of aluminum ions, 3 moles of sulfur, 12 moles of oxygen, and 3 moles of SO42- ions. ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and
... Avogadro’s number of those particles • One mole of molecules or formula units contains Avogadro’s number times the number of atoms or ions of each element in the compound Stoichiometry ...
... Avogadro’s number of those particles • One mole of molecules or formula units contains Avogadro’s number times the number of atoms or ions of each element in the compound Stoichiometry ...
Chapter 3 Molecules Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical
... relative numbers of reactant and product molecules that are required can be used to determine weights of reactants used and products that can be made ...
... relative numbers of reactant and product molecules that are required can be used to determine weights of reactants used and products that can be made ...
Downloaded - Maynooth University ePrints and eTheses Archive
... molecules contained within the lattice being hydrogen bonded to the pyridyl nitrogen atoms16 and with the methanol molecule enclathrated within the calix[4]arene cone-shaped cavity.17 As part of our continuing research, we have previously reported upper and lower rim functionalised calix[4]arenes, c ...
... molecules contained within the lattice being hydrogen bonded to the pyridyl nitrogen atoms16 and with the methanol molecule enclathrated within the calix[4]arene cone-shaped cavity.17 As part of our continuing research, we have previously reported upper and lower rim functionalised calix[4]arenes, c ...
Part One: Mass and Moles of Substance A. Molecular Mass and
... How many grams of MgO could be formed by the reaction of 30 g Mg with 16 g O2 in the following reaction? ...
... How many grams of MgO could be formed by the reaction of 30 g Mg with 16 g O2 in the following reaction? ...
IX Chemistry Chapter 02
... The mass of an atom depends upon the number of protons and neutrons present in it. As the atoms are extremely small particles, it is difficult to weigh them directly. For example the mass of single hydrogen (H) atom, is 1.6x10-24g (0.000 000 000 000 000 000 000 0016g). Clearly we cannot weigh a hydr ...
... The mass of an atom depends upon the number of protons and neutrons present in it. As the atoms are extremely small particles, it is difficult to weigh them directly. For example the mass of single hydrogen (H) atom, is 1.6x10-24g (0.000 000 000 000 000 000 000 0016g). Clearly we cannot weigh a hydr ...
03_Worked_Examples
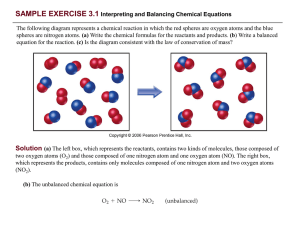
... (c) The reactants box contains four O2 and eight NO. Thus, the molecular ratio is one O2 for each two NO, as required by the balanced equation. The products box contains eight NO 2, which means the number of NO2 product molecules equals the number of NO reactant molecules, as the balanced equation r ...
... (c) The reactants box contains four O2 and eight NO. Thus, the molecular ratio is one O2 for each two NO, as required by the balanced equation. The products box contains eight NO 2, which means the number of NO2 product molecules equals the number of NO reactant molecules, as the balanced equation r ...
03_Worked_Examples
... (c) The reactants box contains four O2 and eight NO. Thus, the molecular ratio is one O2 for each two NO, as required by the balanced equation. The products box contains eight NO 2, which means the number of NO2 product molecules equals the number of NO reactant molecules, as the balanced equation r ...
... (c) The reactants box contains four O2 and eight NO. Thus, the molecular ratio is one O2 for each two NO, as required by the balanced equation. The products box contains eight NO 2, which means the number of NO2 product molecules equals the number of NO reactant molecules, as the balanced equation r ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... • A molar mass is the mass of 1 mol of a substance (i.e., g/mol). • The molar mass of an element is the atomic weight for the element from the periodic table. If it is diatomic, it is twice that atomic weight. • The formula weight (in amu’s) will be the same number as the molar mass (in g/mol). © 20 ...
... • A molar mass is the mass of 1 mol of a substance (i.e., g/mol). • The molar mass of an element is the atomic weight for the element from the periodic table. If it is diatomic, it is twice that atomic weight. • The formula weight (in amu’s) will be the same number as the molar mass (in g/mol). © 20 ...
Chemical Thermodynamics presentation 1
... Because ΔG° is positive, the reaction is not spontaneous under standard conditions at 298 K. Note: We had to convert the units of the T ΔS term to kJ sp that it could be added to the ΔH term whose units are kJ ...
... Because ΔG° is positive, the reaction is not spontaneous under standard conditions at 298 K. Note: We had to convert the units of the T ΔS term to kJ sp that it could be added to the ΔH term whose units are kJ ...
Ionic Strength and Electrostatic Effects in
... small λ the limiting case of simple charged molecules (DebyeHückel or Tanford equations), and for large λ the limiting case of polyelectrolyte behavior (Gouy-Chapman or Donnan models) are approximated. The model showed good agreement with the experimental data of these authors. The advantage of thi ...
... small λ the limiting case of simple charged molecules (DebyeHückel or Tanford equations), and for large λ the limiting case of polyelectrolyte behavior (Gouy-Chapman or Donnan models) are approximated. The model showed good agreement with the experimental data of these authors. The advantage of thi ...
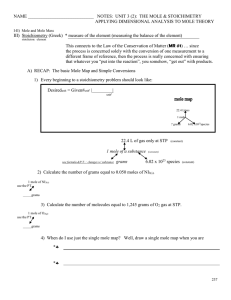
Unit 3 2 Basic Mole Conversions and Mole Maps
... Meaning: For every 2 mol of ethane, 7 mol of dioxygen molecules are consumed in the combustion (a ratio of 2 to 7) This produces 4 moles of carbon dioxide, 6 moles of water and releases 3,170 kJ of energy from the bonding chemicals to the environment. This set of relationships can indicate, at a gla ...
... Meaning: For every 2 mol of ethane, 7 mol of dioxygen molecules are consumed in the combustion (a ratio of 2 to 7) This produces 4 moles of carbon dioxide, 6 moles of water and releases 3,170 kJ of energy from the bonding chemicals to the environment. This set of relationships can indicate, at a gla ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and
... Avogadro’s number of those particles • One mole of molecules or formula units contains Avogadro’s number times the number of atoms or ions of each element in the compound Stoichiometry ...
... Avogadro’s number of those particles • One mole of molecules or formula units contains Avogadro’s number times the number of atoms or ions of each element in the compound Stoichiometry ...
PRACTICE EXERCISE - Needham.K12.ma.us
... (c) The left box (reactants) contains four O2 molecules and eight NO molecules. Thus, the molecular ratio is one O2 for each two NO as required by the balanced equation. The right box (products) contains eight NO 2 molecules. The number of NO2 molecules on the right equals the number of NO molecules ...
... (c) The left box (reactants) contains four O2 molecules and eight NO molecules. Thus, the molecular ratio is one O2 for each two NO as required by the balanced equation. The right box (products) contains eight NO 2 molecules. The number of NO2 molecules on the right equals the number of NO molecules ...
Rotational−Vibrational Levels of Diatomic Molecules Represented
... where ωe, ωexe, Be, and De are the usual spectroscopic constants, and J and V are the molecular rotational and vibrational quantum numbers, respectively. Expression 2 is a truncated series expansion solution of the Schrödinger equation for the rotating Morse oscillator.3 Even though more accurate ( ...
... where ωe, ωexe, Be, and De are the usual spectroscopic constants, and J and V are the molecular rotational and vibrational quantum numbers, respectively. Expression 2 is a truncated series expansion solution of the Schrödinger equation for the rotating Morse oscillator.3 Even though more accurate ( ...
Equilibrium - District 196
... At equilibrium, the color of a beaker containing this system would be violet (light purple) What would you see if the following possible stressors were Introduced according to LeChatlier? •Addition of Co(H2O)6+2 •Removal of Cl-(aq) •Removal of H2O(l) •Addition of CoCl4-2(aq) •Addition of ∆H •Removal ...
... At equilibrium, the color of a beaker containing this system would be violet (light purple) What would you see if the following possible stressors were Introduced according to LeChatlier? •Addition of Co(H2O)6+2 •Removal of Cl-(aq) •Removal of H2O(l) •Addition of CoCl4-2(aq) •Addition of ∆H •Removal ...
Molecular-Fluorescence Enhancement via Blue
... (PMT) (H7422PA-40, Hamamatsu) in non-descanned detection scheme. Before reaching the photon-counting board (SPC150, Becker and Hickl GmbH), the output current of the PMT is amplified via a preamplifier (HFAC-26, Becker and Hickl GmbH). The detailed information for FLIM setup can be found in a previous ...
... (PMT) (H7422PA-40, Hamamatsu) in non-descanned detection scheme. Before reaching the photon-counting board (SPC150, Becker and Hickl GmbH), the output current of the PMT is amplified via a preamplifier (HFAC-26, Becker and Hickl GmbH). The detailed information for FLIM setup can be found in a previous ...
Host–guest chemistry

In supramolecular chemistry, host–guest chemistry describes complexes that are composed of two or more molecules or ions that are held together in unique structural relationships by forces other than those of full covalent bonds. Host–guest chemistry encompasses the idea of molecular recognition and interactions through noncovalent bonding. Noncovalent bonding is critical in maintaining the 3D structure of large molecules, such as proteins and is involved in many biological processes in which large molecules bind specifically but transiently to one another. There are four commonly mentioned types of non-covalent interactions: hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, van der Waals forces, and hydrophobic interactions.