Chapter 8 notepacket
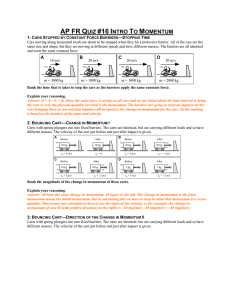
... Chapter 8 Momentum The BIG IDEA Momentum is _____________________ for all collisions as long as _________________ forces don’t interfere. Objectives • Define momentum • Define impulse and describe how it affects changes in momentum • State the Law of Conservation of Momentum • Describe how conserv ...
... Chapter 8 Momentum The BIG IDEA Momentum is _____________________ for all collisions as long as _________________ forces don’t interfere. Objectives • Define momentum • Define impulse and describe how it affects changes in momentum • State the Law of Conservation of Momentum • Describe how conserv ...
Chapter 15 - KFUPM Faculty List
... Q13 A particle (m = 0.2 kg) is attached to a spring. The motion of the particle is described by x = 0.10 cos (10*t +PI/3) where x is m and t is in s. What is the mechanical energy of the particle? A1 0.1 J Q14 The frequency of small oscillations of a simple pendulum of length (L) on the surface of E ...
... Q13 A particle (m = 0.2 kg) is attached to a spring. The motion of the particle is described by x = 0.10 cos (10*t +PI/3) where x is m and t is in s. What is the mechanical energy of the particle? A1 0.1 J Q14 The frequency of small oscillations of a simple pendulum of length (L) on the surface of E ...
Two-Photon Direct Frequency Comb Spectroscopy of Rubidium
... In terms of the positions of the peaks, the calculated spectra had good qualitative agreement with the experimental spectra. However, detailed features of the measured spectra, such as linewidth and relative amplitudes of the spectral peaks, do not agree with calculations. These features are still u ...
... In terms of the positions of the peaks, the calculated spectra had good qualitative agreement with the experimental spectra. However, detailed features of the measured spectra, such as linewidth and relative amplitudes of the spectral peaks, do not agree with calculations. These features are still u ...
Color Strings
... A. Bialas, Phys. Lett. B 466 (1999) 301. 2. Percolation of color sources and critical temperature J. Dias de Deus and C. Pajares, Phys.Lett B 642 (2006) 455 ...
... A. Bialas, Phys. Lett. B 466 (1999) 301. 2. Percolation of color sources and critical temperature J. Dias de Deus and C. Pajares, Phys.Lett B 642 (2006) 455 ...
Q QUANTUM COHERENCE PROGRESS
... the appropriate degrees of freedom that might be entangled. The subsystems are technically known as modes, and the possibly entangled degrees of freedom are called observables. Most formally, entanglement is the degree of correlation between observables pertaining to different modes that exceeds any ...
... the appropriate degrees of freedom that might be entangled. The subsystems are technically known as modes, and the possibly entangled degrees of freedom are called observables. Most formally, entanglement is the degree of correlation between observables pertaining to different modes that exceeds any ...
Rotational motion
... Collisions: two objects strike each other Explosions: one object separates into two There is a third common case for conservation of angular momentum: Collisions: a child runs and jumps on a merry-go-round Explosions: throwing a ball off-center A spinning object changes its moment of inertia This la ...
... Collisions: two objects strike each other Explosions: one object separates into two There is a third common case for conservation of angular momentum: Collisions: a child runs and jumps on a merry-go-round Explosions: throwing a ball off-center A spinning object changes its moment of inertia This la ...
The Classical Electromagnetism of Particle Detection
... in medium 2 do not satisfy the EM boundary conditions at the surface. To do this a free wave is emitted from the interface. This is TR. The Cherenkov Radiation (CR) emitted in medium 1 and/or medium 2 is diffracted at the surface ie the CR emission stops/starts there, causing diffraction in the sa ...
... in medium 2 do not satisfy the EM boundary conditions at the surface. To do this a free wave is emitted from the interface. This is TR. The Cherenkov Radiation (CR) emitted in medium 1 and/or medium 2 is diffracted at the surface ie the CR emission stops/starts there, causing diffraction in the sa ...
Welcome to Physics I !!!
... • Cross products are messy…why would we ever use them, instead of the simpler L I RF • Because the cross product allows us to determine the angular momentum of, or torque on, objects which are not necessarily moving with constant, or even circular motion! ...
... • Cross products are messy…why would we ever use them, instead of the simpler L I RF • Because the cross product allows us to determine the angular momentum of, or torque on, objects which are not necessarily moving with constant, or even circular motion! ...