Chapter 4 Functional Groups
... 2. Carbon atoms are the most versatile building blocks of molecules • With a total of 6 electrons, a carbon atom has 2 in the first shell and 4 in the second shell. • Carbon has little tendency to form ionic bonds by loosing or gaining 4 electrons. • Instead, carbon usually completes its valence sh ...
... 2. Carbon atoms are the most versatile building blocks of molecules • With a total of 6 electrons, a carbon atom has 2 in the first shell and 4 in the second shell. • Carbon has little tendency to form ionic bonds by loosing or gaining 4 electrons. • Instead, carbon usually completes its valence sh ...
lewis acids and bases
... a diagram that shows the bonding between atoms and the lone pairs of electrons of a molecule * Writing Lewis structures 1.Determine # of valence electrons (neutral molecule, cation, anion) 2.Connect the atoms with only single bonds 3.Place a sufficient number of non-bonded electron pairs around each ...
... a diagram that shows the bonding between atoms and the lone pairs of electrons of a molecule * Writing Lewis structures 1.Determine # of valence electrons (neutral molecule, cation, anion) 2.Connect the atoms with only single bonds 3.Place a sufficient number of non-bonded electron pairs around each ...
Organic Chemistry
... Slow rates of reaction due to complexity of bonds (often catalyst needed) Breakdown/decompose at low temperature compared to other compounds ...
... Slow rates of reaction due to complexity of bonds (often catalyst needed) Breakdown/decompose at low temperature compared to other compounds ...
Chapter 2 Name___________________________________
... 6) Which of the following describes any reaction that has reached chemical equilibrium? A) Both the forward and the reverse reactions have stopped with no net effect on the concentration of the reactants and the products. B) The rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reacti ...
... 6) Which of the following describes any reaction that has reached chemical equilibrium? A) Both the forward and the reverse reactions have stopped with no net effect on the concentration of the reactants and the products. B) The rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reacti ...
CHM – 124 Principles of Chemistry
... Identify single, double, and triple covalent bonds. Describe the formation of a coordinate covalent bond. Provide examples of compounds that are exceptions to the octet rule. Describe the changes in electronegativity in (a) moving across a period and (b) moving down a group in the periodic table. De ...
... Identify single, double, and triple covalent bonds. Describe the formation of a coordinate covalent bond. Provide examples of compounds that are exceptions to the octet rule. Describe the changes in electronegativity in (a) moving across a period and (b) moving down a group in the periodic table. De ...
B.Sc. Physical Sciences - Department of Computer Science
... R, R2, R3 as vector spaces over R . Standard basis for each of them. Concept of Linear Independence and examples of different bases. Subspaces of R2, R3. Translation, Dilation, Rotation, Reflection in a point, line and plane. Matrix form of basic geometric transformations.Interpretation of eigenvalu ...
... R, R2, R3 as vector spaces over R . Standard basis for each of them. Concept of Linear Independence and examples of different bases. Subspaces of R2, R3. Translation, Dilation, Rotation, Reflection in a point, line and plane. Matrix form of basic geometric transformations.Interpretation of eigenvalu ...
Protecting Groups Introduction to Carbonyl
... Reagents; Oxidation and Reduction Protecting Groups Solving this problem requires a three-step strategy: [1] Convert the OH group into another functional group that does not interfere with the desired reaction. This new blocking group is called a protecting group, and the reaction that creates it is ...
... Reagents; Oxidation and Reduction Protecting Groups Solving this problem requires a three-step strategy: [1] Convert the OH group into another functional group that does not interfere with the desired reaction. This new blocking group is called a protecting group, and the reaction that creates it is ...
Aldehydes and Ketones-12c - TAMU
... Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones Structure Deduction using Classification Tests ...
... Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones Structure Deduction using Classification Tests ...
Chemistry - StudyTime NZ
... From this informa>on, we can tell that Magnesium has three electron shells, the last of which contains 2 electrons. We can assume that the first two electron shells are full with 2 electrons and 8 ...
... From this informa>on, we can tell that Magnesium has three electron shells, the last of which contains 2 electrons. We can assume that the first two electron shells are full with 2 electrons and 8 ...
Microsoft Word - Final Exam Study Guide
... A list of major topics (not all inclusive) Formal charge, resonance structures, hybridization, bond-line structures, acid/base equilibria, pKa’s, trends in acidity/basicity, functional groups, alkane nomenclature, conformational analysis, Newman projections, causes of strain, cyclohexane ring struct ...
... A list of major topics (not all inclusive) Formal charge, resonance structures, hybridization, bond-line structures, acid/base equilibria, pKa’s, trends in acidity/basicity, functional groups, alkane nomenclature, conformational analysis, Newman projections, causes of strain, cyclohexane ring struct ...
ch 1: organic chemistry
... structure similar to water H-O-H and alcohols R-O-H only in ethers, structure is R-O-R (where R=alkyl groups) alkyl groups may be identical or different there are no OH bonds in ethers so they do not form hydrogen bonds C-O bonds are polar and the v-shape of the C-O-C group make ether molecu ...
... structure similar to water H-O-H and alcohols R-O-H only in ethers, structure is R-O-R (where R=alkyl groups) alkyl groups may be identical or different there are no OH bonds in ethers so they do not form hydrogen bonds C-O bonds are polar and the v-shape of the C-O-C group make ether molecu ...
2.10 Assessed Homework Task - A
... Give one advantage and one disadvantage of manufacturing ethanol by fermentation rather than by hydration. Do not include energy consumption or cost. Advantage .................................................................................................... ...
... Give one advantage and one disadvantage of manufacturing ethanol by fermentation rather than by hydration. Do not include energy consumption or cost. Advantage .................................................................................................... ...
Review
... Nucleophiles (in their free base and anionic forms) SN2 Reactions (stereochemical outcomes) When site of attack is a chiral center When site of attack is not a chiral center Leaving Group abilities SN1 Reactions (stereochemical outcomes) Carbocations; factors which determine carbocation stability Ha ...
... Nucleophiles (in their free base and anionic forms) SN2 Reactions (stereochemical outcomes) When site of attack is a chiral center When site of attack is not a chiral center Leaving Group abilities SN1 Reactions (stereochemical outcomes) Carbocations; factors which determine carbocation stability Ha ...
North Carolina Test of Chemistry RELEASED
... 2 – Structures & Properties of Matter 2 – Structures & Properties of Matter 2 – Structures & Properties of Matter 2 – Structures & Properties of Matter 2 – Structures & Properties of Matter 2 – Structures & Properties of Matter 2 – Structures & Properties of Matter 3 – Regularities in Chemistry 3 – ...
... 2 – Structures & Properties of Matter 2 – Structures & Properties of Matter 2 – Structures & Properties of Matter 2 – Structures & Properties of Matter 2 – Structures & Properties of Matter 2 – Structures & Properties of Matter 2 – Structures & Properties of Matter 3 – Regularities in Chemistry 3 – ...
Chapter 6
... 2. Zinc Metal, used as a coating in galvanized iron, also reacts with air to form a coating that resists further corrosion. zinc+ oxygen → ___________________ 3. When aluminum foil is placed in a solution of copper (II) chloride, copper metal and another solution are formed: aluminum + copper (II) c ...
... 2. Zinc Metal, used as a coating in galvanized iron, also reacts with air to form a coating that resists further corrosion. zinc+ oxygen → ___________________ 3. When aluminum foil is placed in a solution of copper (II) chloride, copper metal and another solution are formed: aluminum + copper (II) c ...
B.Sc. Physical Sciences - Educational Multimedia Research Centre
... R, R2, R3 as vector spaces over R . Standard basis for each of them. Concept of Linear Independence and examples of different bases. Subspaces of R2, R3. Translation, Dilation, Rotation, Reflection in a point, line and plane. Matrix form of basic geometric transformations.Interpretation of eigenvalu ...
... R, R2, R3 as vector spaces over R . Standard basis for each of them. Concept of Linear Independence and examples of different bases. Subspaces of R2, R3. Translation, Dilation, Rotation, Reflection in a point, line and plane. Matrix form of basic geometric transformations.Interpretation of eigenvalu ...
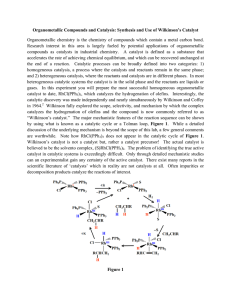
Organometallic Compounds and Catalysis: Synthesis
... compounds as catalysts in industrial chemistry. A catalyst is defined as a substance that accelerates the rate of achieving chemical equilibrium, and which can be recovered unchanged at the end of a reaction. Catalytic processes can be broadly defined into two categories: 1) homogeneous catalysis, a ...
... compounds as catalysts in industrial chemistry. A catalyst is defined as a substance that accelerates the rate of achieving chemical equilibrium, and which can be recovered unchanged at the end of a reaction. Catalytic processes can be broadly defined into two categories: 1) homogeneous catalysis, a ...