Unit #7 Take Home Test
... a. Write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction, including the products formed. [1] b. Using the Solubility Guidelines on the Chemistry Reference Table, determine which of the products formed is the precipitate. [1] c. Write the net ionic equation for this reaction. [1] d. Identify the spe ...
... a. Write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction, including the products formed. [1] b. Using the Solubility Guidelines on the Chemistry Reference Table, determine which of the products formed is the precipitate. [1] c. Write the net ionic equation for this reaction. [1] d. Identify the spe ...
1.1 - cloudfront.net
... condensation reaction: A chemical reaction in which two molecules combine to form one single molecule, together with the loss of a small molecule, often water. disaccharide: A carbohydrate composed of two monosaccharides. glycogen: A carbohydrate used for long-term energy storage in animal cells; hu ...
... condensation reaction: A chemical reaction in which two molecules combine to form one single molecule, together with the loss of a small molecule, often water. disaccharide: A carbohydrate composed of two monosaccharides. glycogen: A carbohydrate used for long-term energy storage in animal cells; hu ...
chapter_2_2009
... The atoms sharing electrons sit close enough together so that their outer energy levels overlap. Single covalent bond-one pair of electrons is shared. ...
... The atoms sharing electrons sit close enough together so that their outer energy levels overlap. Single covalent bond-one pair of electrons is shared. ...
Benefits & Dangers of Radioisotopes
... C-14 used to date organic (previously living) materials Living organisms incorporate C-14 into their structure, along with C-12 ...
... C-14 used to date organic (previously living) materials Living organisms incorporate C-14 into their structure, along with C-12 ...
Preparatory School to the Winter Collegue on Optics: Optical
... • Energy scale for rotations << vibrations – Each vibrational level has rotational bands built on it • Selection rule δJ = ±1 ...
... • Energy scale for rotations << vibrations – Each vibrational level has rotational bands built on it • Selection rule δJ = ±1 ...
c - Batavia CSD
... aldehyde may be structural isomers with different properties, as is the case for acetone and propanal. ...
... aldehyde may be structural isomers with different properties, as is the case for acetone and propanal. ...
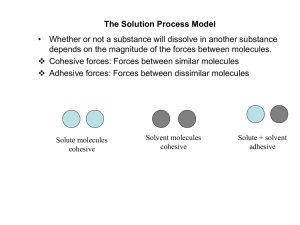
The Solution Process Model
... If Ct is very small (Ct >0.1 Cs), then dissolution rate is directly proportional to the saturation solubility (Cs). This assumes that S is constant which is only true at the very beginning of the experiment when only a small amount (>0.5%) of the solid drug has dissolved. When these two requirements ...
... If Ct is very small (Ct >0.1 Cs), then dissolution rate is directly proportional to the saturation solubility (Cs). This assumes that S is constant which is only true at the very beginning of the experiment when only a small amount (>0.5%) of the solid drug has dissolved. When these two requirements ...
exam3 answers - Moorpark College
... A. List all the intermolecular forces that need to be overcome for the compound A given below to boil? ...
... A. List all the intermolecular forces that need to be overcome for the compound A given below to boil? ...
Test
... assigned to an electron and a proton? (1) Both an electron and a proton are positive. (2) An electron is positive and a proton is negative. (3) An electron is negative and a proton is positive. (4) Both an electron and a proton are negative. ...
... assigned to an electron and a proton? (1) Both an electron and a proton are positive. (2) An electron is positive and a proton is negative. (3) An electron is negative and a proton is positive. (4) Both an electron and a proton are negative. ...
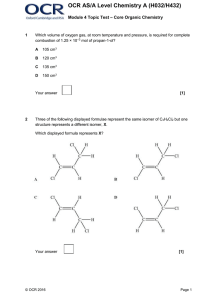
Topic 16 Test - A
... How many structural isomers, which are aldehydes, have the molecular formula C5H10O? A ...
... How many structural isomers, which are aldehydes, have the molecular formula C5H10O? A ...
Regular Evening08-11-2013Tuition
... Topics Solutions Electrochemistry Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers Section A ...
... Topics Solutions Electrochemistry Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers Section A ...
lecture 13
... Balancing chemical equations is an application of both the Modern Atomic Theory and the Law of Conservation of Mass. BALANCING EQUATIONS: The same number of each type of element must occur on the left (BEFORE the reaction) and on the right (AFTER the reaction) ...
... Balancing chemical equations is an application of both the Modern Atomic Theory and the Law of Conservation of Mass. BALANCING EQUATIONS: The same number of each type of element must occur on the left (BEFORE the reaction) and on the right (AFTER the reaction) ...
chemical reaction
... Chemical vs Physical Change • Physical change – a change in substance that does not change its chemical composition; ex: phase changes, size changes • Chemical change – a change in substance that results in entirely new substance with different chemical composition and properties; ex: burning, tar ...
... Chemical vs Physical Change • Physical change – a change in substance that does not change its chemical composition; ex: phase changes, size changes • Chemical change – a change in substance that results in entirely new substance with different chemical composition and properties; ex: burning, tar ...
Chapter 8 - TeacherWeb
... WATER AND OTHER POLAR MOLECULES In a covalent bond, one atom can attract the other atom more strongly For example, in water the Oxygen attracts the Hydrogen more The Oxygen is more negative and has a partial negative charge The Hydrogen has a partial positive charge A molecule that has a pa ...
... WATER AND OTHER POLAR MOLECULES In a covalent bond, one atom can attract the other atom more strongly For example, in water the Oxygen attracts the Hydrogen more The Oxygen is more negative and has a partial negative charge The Hydrogen has a partial positive charge A molecule that has a pa ...
Chemistry Midterm Review
... C. The following data was collected by a group of students who were trying to determine the density of a metal bar. What is the density of the metal? length = 10.0 cm Mass of bar = 480.00 g width = 4.00 cm height = 3.00 cm Chapter 4: Atomic Structure The idea of an indivisible particle in all matter ...
... C. The following data was collected by a group of students who were trying to determine the density of a metal bar. What is the density of the metal? length = 10.0 cm Mass of bar = 480.00 g width = 4.00 cm height = 3.00 cm Chapter 4: Atomic Structure The idea of an indivisible particle in all matter ...
AP Biology
... a variety of organic compounds that play key roles in living cells were synthesized in Miller’s apparatus ...
... a variety of organic compounds that play key roles in living cells were synthesized in Miller’s apparatus ...
Chemical Reactions
... that the NO3- does not change. Since the nitrate ion and the sodium ion appear on both sides of the equation and they do not seem to do anything in this reaction, they are called a spectator ions. We will actually not even show them in the reaction. ...
... that the NO3- does not change. Since the nitrate ion and the sodium ion appear on both sides of the equation and they do not seem to do anything in this reaction, they are called a spectator ions. We will actually not even show them in the reaction. ...
macromolecules
... • The hydrocarbon tails of the fatty acids are hydrophobic • the phosphate group end of the molecule is hydrophilic because of the oxygens with all of their pairs of unshared ...
... • The hydrocarbon tails of the fatty acids are hydrophobic • the phosphate group end of the molecule is hydrophilic because of the oxygens with all of their pairs of unshared ...
The origin and status of the Arrhenius equation
... rate constant could he correlated by one simple equation (3). I t still hears his name and is widely regarded as one of the most important equations in physical chemistry. Svante August Arrhenius, horn in 1859, was initially a student at Uppsala in Sweden. In Stockholm, he began in 1882 the series o ...
... rate constant could he correlated by one simple equation (3). I t still hears his name and is widely regarded as one of the most important equations in physical chemistry. Svante August Arrhenius, horn in 1859, was initially a student at Uppsala in Sweden. In Stockholm, he began in 1882 the series o ...
Section 7.1 Describing Reactions
... 1. Is the following sentence true or false? The new substances formed as a result of a chemical reaction are called products. 2. Circle the letter of each sentence that is a correct interpretation of the chemical equation C ⫹ O2 h CO2. a. Carbon and oxygen react and form carbon monoxide. b. Carbon a ...
... 1. Is the following sentence true or false? The new substances formed as a result of a chemical reaction are called products. 2. Circle the letter of each sentence that is a correct interpretation of the chemical equation C ⫹ O2 h CO2. a. Carbon and oxygen react and form carbon monoxide. b. Carbon a ...