Document
... The two nucleic acid chains are held together by _____________________. When a cell divides, the double helix of the DNA molecule ____________ by breaking down the hydrogen bonds. A ________________________ chain is formed adjacent to each of the original chain by the formation of new hydrogen ...
... The two nucleic acid chains are held together by _____________________. When a cell divides, the double helix of the DNA molecule ____________ by breaking down the hydrogen bonds. A ________________________ chain is formed adjacent to each of the original chain by the formation of new hydrogen ...
Heat of reaction
... to make informed decisions. • For several reactions a direct measurement can be done with a calorimeter. • Many times this is impossible or it is a time consuming task which makes it very hard. • Hess’s law allows us to manipulate equations for calculating ΔH for a given reaction. • If a reaction is ...
... to make informed decisions. • For several reactions a direct measurement can be done with a calorimeter. • Many times this is impossible or it is a time consuming task which makes it very hard. • Hess’s law allows us to manipulate equations for calculating ΔH for a given reaction. • If a reaction is ...
Section 01 Introduction to Analytical Chemistry ( powerpoint )
... Training of Chemical Analysts (Analytical Chemists) • Training focuses on principles and techniques for solving measurement problems … but… • Chemical analysts interface multiple disciplines to the solution of chemical measurement problems – Physical-, organic-, inorganic-, bio-chem-, physics, mat ...
... Training of Chemical Analysts (Analytical Chemists) • Training focuses on principles and techniques for solving measurement problems … but… • Chemical analysts interface multiple disciplines to the solution of chemical measurement problems – Physical-, organic-, inorganic-, bio-chem-, physics, mat ...
AP Chemistry
... C) Single Displacement (Redox) An element reacts with a compound totake the place of one of the elements of that compound. A new element is formed along with a new compound. a) Metal and Acid hydrogen + salt H2SO4(aq) + Fe(s) → FeSO4(aq) + H2(g) b) Metal and Water hydrogen + metal hydroxide OR me ...
... C) Single Displacement (Redox) An element reacts with a compound totake the place of one of the elements of that compound. A new element is formed along with a new compound. a) Metal and Acid hydrogen + salt H2SO4(aq) + Fe(s) → FeSO4(aq) + H2(g) b) Metal and Water hydrogen + metal hydroxide OR me ...
Symbol
... Determine the percent composition of CaCl2. A chemist combines 1.26g iron with 0.56g oxygen to form rust. What is the percent composition of this new compound? Cerium (III) iodide (CeI3) occurs as a hydrate with the composition 76.3% CeI3 and 23.7% H2O. Calculate the formula of the hydrate. Name the ...
... Determine the percent composition of CaCl2. A chemist combines 1.26g iron with 0.56g oxygen to form rust. What is the percent composition of this new compound? Cerium (III) iodide (CeI3) occurs as a hydrate with the composition 76.3% CeI3 and 23.7% H2O. Calculate the formula of the hydrate. Name the ...
Chemistry Unit Summaries - Oak Park Unified School District
... and arrangement of electrons around the atom. Much of what is so the molar mass of H2O is 18.0 g. known about the electronic structure of atoms was obtained by In the dimensional analysis technique, we keep track of units observing atomic spectra, which is the radiant energy emitted or as we carry m ...
... and arrangement of electrons around the atom. Much of what is so the molar mass of H2O is 18.0 g. known about the electronic structure of atoms was obtained by In the dimensional analysis technique, we keep track of units observing atomic spectra, which is the radiant energy emitted or as we carry m ...
Chapter 2
... • In the formula you put a dot and then write the number of molecules. • Calcium chloride dihydrate = CaCl22O • Chromium (III) nitrate hexahydrate = Cr(NO3)3 6H2O ...
... • In the formula you put a dot and then write the number of molecules. • Calcium chloride dihydrate = CaCl22O • Chromium (III) nitrate hexahydrate = Cr(NO3)3 6H2O ...
ppt
... total mass of the reactants is equal to the total mass of the products. Atoms are not created nor destroyed. ...
... total mass of the reactants is equal to the total mass of the products. Atoms are not created nor destroyed. ...
Chapter 6 Chemical Bonding
... the sharing of one pair of electrons between two atoms Ex: Calcium Oxide A triple covalent bond is a covalent bond produced by the sharing of three pairs of electrons between two atoms Ex: Ethyne C2H2 Resonance refers to bonding in molecules or ions that cannot be correctly represented by a single s ...
... the sharing of one pair of electrons between two atoms Ex: Calcium Oxide A triple covalent bond is a covalent bond produced by the sharing of three pairs of electrons between two atoms Ex: Ethyne C2H2 Resonance refers to bonding in molecules or ions that cannot be correctly represented by a single s ...
Review of Moles and Stoichiometry
... decomposed into its elements, what mass of each element will be recovered? ...
... decomposed into its elements, what mass of each element will be recovered? ...
Bonds - MCAT Cooperative
... In the reaction above, if the reagents in the first step were replaced with LiAlH4, what product would result? ...
... In the reaction above, if the reagents in the first step were replaced with LiAlH4, what product would result? ...
Document
... – No chemical bonding between components – Can be separated by physical means, such as straining or filtering – Heterogeneous or homogeneous ...
... – No chemical bonding between components – Can be separated by physical means, such as straining or filtering – Heterogeneous or homogeneous ...
Chapter 1 Glossary The Nature of Chemistry
... The intermolecular attraction between the partial negative end of one polar molecule and the partial positive end of another polar molecule. Hydrogen bond The intermolecular attraction between a nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine atom of one molecule and a hydrogen atom bonded to a nitrogen, oxygen, or f ...
... The intermolecular attraction between the partial negative end of one polar molecule and the partial positive end of another polar molecule. Hydrogen bond The intermolecular attraction between a nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine atom of one molecule and a hydrogen atom bonded to a nitrogen, oxygen, or f ...
The separation, purification and identification of the components of a
... 5. When extracting an aqueous solution with an organic solvent, if you are unsure as to which layer in the separatory funnel is aqueous, how could you settle the issue with a simple test without looking up their density ? ...
... 5. When extracting an aqueous solution with an organic solvent, if you are unsure as to which layer in the separatory funnel is aqueous, how could you settle the issue with a simple test without looking up their density ? ...
Nothing Lost, Nothing Gained
... There are all sorts of equations, some for math, some for life. Now you know a little about the ones that show chemical changes. It's easy if you think about it. You have some things that come together and make something new. While the atoms may change, they never go away and no new ones are ever ma ...
... There are all sorts of equations, some for math, some for life. Now you know a little about the ones that show chemical changes. It's easy if you think about it. You have some things that come together and make something new. While the atoms may change, they never go away and no new ones are ever ma ...
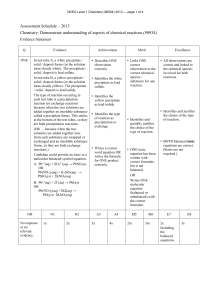
82KB - NZQA
... A: Pb2+(aq) + SO42–(aq) → PbSO4(s) OR Pb(NO3)2(aq) + K2SO4(aq) → PbSO4(s) + 2KNO3(aq) ...
... A: Pb2+(aq) + SO42–(aq) → PbSO4(s) OR Pb(NO3)2(aq) + K2SO4(aq) → PbSO4(s) + 2KNO3(aq) ...
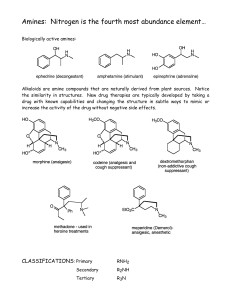
Amines: Nitrogen is the fourth most abundance element…
... benzoic acid. What would you add to get the pyridine back, uncharged? Base. What would you add to get the benzoic acid back, uncharged? Acid. By utilizing acid-base characteristics, you can separate organic compounds during the extraction process. ...
... benzoic acid. What would you add to get the pyridine back, uncharged? Base. What would you add to get the benzoic acid back, uncharged? Acid. By utilizing acid-base characteristics, you can separate organic compounds during the extraction process. ...
CHEMISTRY 112 LECTURE
... of each substituent group on the chain is then denoted by the corresponding number. 3. The position of each branching alkyl group is specified by the number of the carbon atom to which it is attached in the basic chain. 4. The number designating the position of each of the various substituent groups ...
... of each substituent group on the chain is then denoted by the corresponding number. 3. The position of each branching alkyl group is specified by the number of the carbon atom to which it is attached in the basic chain. 4. The number designating the position of each of the various substituent groups ...