Chapter 10 Chemical Calculations and Chemical Equations
... chemists would prefer that the substance in excess be a substance that is easy to separate from the primary product. 13. The tip-off for limiting reactant problems is that you are given two or more amounts of reactants in a chemical reaction, and you are asked to calculate the maximum amount of prod ...
... chemists would prefer that the substance in excess be a substance that is easy to separate from the primary product. 13. The tip-off for limiting reactant problems is that you are given two or more amounts of reactants in a chemical reaction, and you are asked to calculate the maximum amount of prod ...
Topic 1 Quantitative Chemistry Answers - slider-dpchemistry-11
... A substance that cannot be divided into simpler, smaller substances. In an element, all the atoms have the same number of protons or electrons, but the number of neutrons may vary (more about this Topic 2) b) atom The smallest part of an element that can exist. An atom consists of an extremely tiny ...
... A substance that cannot be divided into simpler, smaller substances. In an element, all the atoms have the same number of protons or electrons, but the number of neutrons may vary (more about this Topic 2) b) atom The smallest part of an element that can exist. An atom consists of an extremely tiny ...
Stoichiometry
... – Atoms are neither created nor destroyed (they only change bonding partners) – Same atoms are present in the reactants as in the products ...
... – Atoms are neither created nor destroyed (they only change bonding partners) – Same atoms are present in the reactants as in the products ...
Ozone decomposition
... above 105 °C. The gaseous ozone is characterized by different times of half-life, depending on the temperature (Table 1). The ozone structure is resonance stabilized, which is one of the reasons for its resistance against decomposition at low temperatures (Figure 2). In most reactions with inorganic ...
... above 105 °C. The gaseous ozone is characterized by different times of half-life, depending on the temperature (Table 1). The ozone structure is resonance stabilized, which is one of the reasons for its resistance against decomposition at low temperatures (Figure 2). In most reactions with inorganic ...
SUPPORTED LIGANDS FOR METAL CATALYZED REACTIONS Rocío Marcos Escartín ISBN:
... Homogeneous metal catalysts are composed by a metal complex modified with organic ligands. Although the first non enzymatic asymmetric catalysts known were simple organic molecules,[1] the research regarding catalysis reached full development with metal-based systems, which have been predominant for ...
... Homogeneous metal catalysts are composed by a metal complex modified with organic ligands. Although the first non enzymatic asymmetric catalysts known were simple organic molecules,[1] the research regarding catalysis reached full development with metal-based systems, which have been predominant for ...
Modern Analytical Chemistry
... An additional problem is encountered when the isolated solid is nonstoichiometric. For example, precipitating Mn2+ as Mn(OH)2, followed by heating to produce the oxide, frequently produces a solid with a stoichiometry of MnOx , where x varies between 1 and 2. In this case the nonstoichiometric produ ...
... An additional problem is encountered when the isolated solid is nonstoichiometric. For example, precipitating Mn2+ as Mn(OH)2, followed by heating to produce the oxide, frequently produces a solid with a stoichiometry of MnOx , where x varies between 1 and 2. In this case the nonstoichiometric produ ...
Soot Formation Modeling during Hydrocarbon
... their mixtures behind shock wave, for a wide range of reaction conditions (temperature, pressure and mixture composition). The calculation results were compared with the usually measured characteristics of soot formation, e. g., induction delay time, observable rate of soot particle growth, soot par ...
... their mixtures behind shock wave, for a wide range of reaction conditions (temperature, pressure and mixture composition). The calculation results were compared with the usually measured characteristics of soot formation, e. g., induction delay time, observable rate of soot particle growth, soot par ...
Chiral Enolate Equivalents
... halides, as well as aryl or vinyl halides, imines, unactivated alkenes or alkynes, and many other less reactive functional groups are not able to react directly with enolates. In addition, reactions of enolates seldom tolerate more than one substituent on the nucleophilic carbon of the enolate, cycl ...
... halides, as well as aryl or vinyl halides, imines, unactivated alkenes or alkynes, and many other less reactive functional groups are not able to react directly with enolates. In addition, reactions of enolates seldom tolerate more than one substituent on the nucleophilic carbon of the enolate, cycl ...
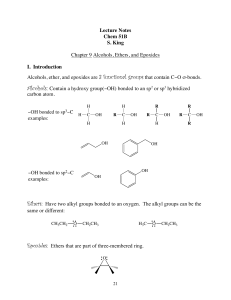
Alcohols, Ethers, and Epoxides
... The bond angle around the O atom in an alcohol or ether is similar to the tetrahedral bond angle of 109.5°. In contrast, the C – O – C bond angle of an epoxide must be 60°, a considerable deviation from the tetrahedral bond angle. For this reason, epoxides have angle strain, making them much more re ...
... The bond angle around the O atom in an alcohol or ether is similar to the tetrahedral bond angle of 109.5°. In contrast, the C – O – C bond angle of an epoxide must be 60°, a considerable deviation from the tetrahedral bond angle. For this reason, epoxides have angle strain, making them much more re ...
Metal cluster aggregates of the composition Nbn +
... Molecules containing transition metal atoms have often proven valuable in the catalytic synthesis of numerous compounds [1-5]. Hydrocarbon adsorption and subsequent C-H bond activation are amongst the most important steps in many catalyzed reactions [6-11]. Their exact mechanism is often not underst ...
... Molecules containing transition metal atoms have often proven valuable in the catalytic synthesis of numerous compounds [1-5]. Hydrocarbon adsorption and subsequent C-H bond activation are amongst the most important steps in many catalyzed reactions [6-11]. Their exact mechanism is often not underst ...
Study Guide Chapter 10: An Introduction to Chemistry
... chemists would prefer that the substance in excess be a substance that is easy to separate from the primary product. 13. The tip-off for limiting reactant problems is that you are given two or more amounts of reactants in a chemical reaction, and you are asked to calculate the maximum amount of prod ...
... chemists would prefer that the substance in excess be a substance that is easy to separate from the primary product. 13. The tip-off for limiting reactant problems is that you are given two or more amounts of reactants in a chemical reaction, and you are asked to calculate the maximum amount of prod ...
Derivatization - Sigma
... reagents that can modify the behavior of complex compounds and allow their detection in chromatographic analysis. Since the release of the last Derivatization guide in 2009, several innovative derivatization reagents have been introduced for various detection methods, and many other products and pac ...
... reagents that can modify the behavior of complex compounds and allow their detection in chromatographic analysis. Since the release of the last Derivatization guide in 2009, several innovative derivatization reagents have been introduced for various detection methods, and many other products and pac ...
SCH3U: Final Exam Review
... b. neon c. hydrogen d. cesium e. fluorine f. iodine g. helium h. lithium ...
... b. neon c. hydrogen d. cesium e. fluorine f. iodine g. helium h. lithium ...
Maps of Odorant Molecular Features in the Mammalian Olfactory Bulb
... ual odorants are represented in the space of entire glomerular sheet of the OB. For many different odorants, these studies revealed the odorant-specific spatial pattern of glomerular activities in the OB. These studies showed also that the odorant-induced activity maps are arranged in a symmetric fa ...
... ual odorants are represented in the space of entire glomerular sheet of the OB. For many different odorants, these studies revealed the odorant-specific spatial pattern of glomerular activities in the OB. These studies showed also that the odorant-induced activity maps are arranged in a symmetric fa ...
aa-2005-38-71-negishi - University of Windsor
... The palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling of an organometal (R1M) with an organic electrophile (R2X) has emerged over the past thirty years as one of the most general and selective methods for carbon–carbon-bond formation (eq 1). Currently, it appears to be generally superior to related methods involvi ...
... The palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling of an organometal (R1M) with an organic electrophile (R2X) has emerged over the past thirty years as one of the most general and selective methods for carbon–carbon-bond formation (eq 1). Currently, it appears to be generally superior to related methods involvi ...