Test
... smooth. The new substance will burn. The new substance looks like it will tear easily. The new substance looks like it will dissolve in acid easily. 3- Which of their statements would be an inference about a chemical property? a. The new substance forms into thin flat sheets. b. The new substance is ...
... smooth. The new substance will burn. The new substance looks like it will tear easily. The new substance looks like it will dissolve in acid easily. 3- Which of their statements would be an inference about a chemical property? a. The new substance forms into thin flat sheets. b. The new substance is ...
Types of reactions you know:
... on the SI website to the website. The “organic interactive” problems in each chapter are extremely helpful. Even if you don’t use this to study for the final, it is a good quick and easy review after your o-chem-less summer months. --Make notecards! Study them! --You have more than just the old fi ...
... on the SI website to the website. The “organic interactive” problems in each chapter are extremely helpful. Even if you don’t use this to study for the final, it is a good quick and easy review after your o-chem-less summer months. --Make notecards! Study them! --You have more than just the old fi ...
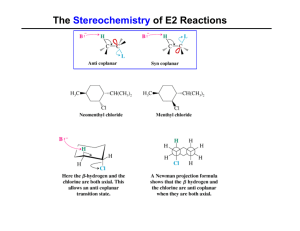
The Stereochemistry of E2 Reactions
... Dehydrohalogenation: Zaitsev’s Rule Hammond-Leffler Postulate: the transition state for a step that is downhill in energy should show a strong resemblance to the reactant of that step. ...
... Dehydrohalogenation: Zaitsev’s Rule Hammond-Leffler Postulate: the transition state for a step that is downhill in energy should show a strong resemblance to the reactant of that step. ...
Organic Chemistry - GZ @ Science Class Online
... Alkenes are unsaturated molecules, that is that not every carbon atom has the maximum amount of atoms bonded to it because it has one or more double bonds. If another atom is added to an alkene the double bond can be broken down to a single bond and the available site can be occupied by another atom ...
... Alkenes are unsaturated molecules, that is that not every carbon atom has the maximum amount of atoms bonded to it because it has one or more double bonds. If another atom is added to an alkene the double bond can be broken down to a single bond and the available site can be occupied by another atom ...
5.7 Quantity Relationships in Chemical Reactions
... • What is the actual percent of the kernels popped? Note that in all the examples of chemical reactions given so far, it is assumed that each reaction works to perfection, and that no product is lost in collecting it, washing it, drying it, transferring it, and weighing it. Under the assumption of p ...
... • What is the actual percent of the kernels popped? Note that in all the examples of chemical reactions given so far, it is assumed that each reaction works to perfection, and that no product is lost in collecting it, washing it, drying it, transferring it, and weighing it. Under the assumption of p ...
OIL GENERATIVE POTENTIAL OF JURASSIC ROCKS
... mature) and reaches maximum (oil window) in the north. The HI values for the Bazhenov Formation totally agree with the level of maturity of OM derived from vitrinite reflectance, showing the lowest values for residual hydrocarbon potential in the north of central part of the territory. Maturity leve ...
... mature) and reaches maximum (oil window) in the north. The HI values for the Bazhenov Formation totally agree with the level of maturity of OM derived from vitrinite reflectance, showing the lowest values for residual hydrocarbon potential in the north of central part of the territory. Maturity leve ...
methods and models
... which is typical for high-spin tetracoordinated complexes of nickel. The calculations on quintet PES have resulted to the structure 26, destabilized relative to planar structure 24 on 5.8 kcal/mol. The spin density distribution in structure 26 shows the localization of two unpaired electrons on meta ...
... which is typical for high-spin tetracoordinated complexes of nickel. The calculations on quintet PES have resulted to the structure 26, destabilized relative to planar structure 24 on 5.8 kcal/mol. The spin density distribution in structure 26 shows the localization of two unpaired electrons on meta ...
10. Factors Affecting the Rate of a Chemical Reaction
... A substance that increases the rate of a reaction (without itself being used up by the reaction) is called a catalyst. Catalysts work by providing an alternate pathway for the reaction: one in which less energy is required in order to have an effective collision. Put another way, a catalyst lowers t ...
... A substance that increases the rate of a reaction (without itself being used up by the reaction) is called a catalyst. Catalysts work by providing an alternate pathway for the reaction: one in which less energy is required in order to have an effective collision. Put another way, a catalyst lowers t ...
Document
... Reactant 1 + Reactant 2 Product 1 + Product 2 (the number of reactants and products will vary) ...
... Reactant 1 + Reactant 2 Product 1 + Product 2 (the number of reactants and products will vary) ...
Ch3pdf.
... 1. write unbalanced equation 2. use coefficients to indicate how many formula units are required to balance equation 3. balance those species that occur in the fewest formulas on each side. 4. reduce coefficients to smallest whole number values 5. when balancing reactions involving organic compounds ...
... 1. write unbalanced equation 2. use coefficients to indicate how many formula units are required to balance equation 3. balance those species that occur in the fewest formulas on each side. 4. reduce coefficients to smallest whole number values 5. when balancing reactions involving organic compounds ...
2004 AP Chemistry Free-Response Questions Form B
... and relevance of the information cited. Explanations should be clear and well organized. Examples and equations may be included in your responses where appropriate. Specific answers are preferable to broad, diffuse responses. Answer BOTH Question 5 below AND Question 6 printed on page 11. Both of th ...
... and relevance of the information cited. Explanations should be clear and well organized. Examples and equations may be included in your responses where appropriate. Specific answers are preferable to broad, diffuse responses. Answer BOTH Question 5 below AND Question 6 printed on page 11. Both of th ...
01.CN_Other pages/p1-9
... • Recognize that rocks are the source of minerals. • Learn the method of isolating useful materials from minerals, for example, the extraction of metals from their ores. • Recognize that limestone, chalk and marble are different forms of calcium carbonate. • Study the weathering and erosion of rocks ...
... • Recognize that rocks are the source of minerals. • Learn the method of isolating useful materials from minerals, for example, the extraction of metals from their ores. • Recognize that limestone, chalk and marble are different forms of calcium carbonate. • Study the weathering and erosion of rocks ...
Midterm 2 Review slides from November 15
... Bonding strengthens as electrons are added to bonding orbitals strength of bonding in the transition metals increases until the band structure is roughly half-full roughly 6-7 electrons strength decreases with more than 67 valence electrons because some electrons are in antibonding orbitals valence ...
... Bonding strengthens as electrons are added to bonding orbitals strength of bonding in the transition metals increases until the band structure is roughly half-full roughly 6-7 electrons strength decreases with more than 67 valence electrons because some electrons are in antibonding orbitals valence ...
IE EA
... bond dissociation energies of the N-H and P-H bonds and the electron affinities of NH2 and PH2 are needed. However, if one assumes that the differences in these quantities are about the same as the differences in the average bond dissociation energies (386 kJ mol-1 for NH3 and 322 kJ mol-1 for PH3) ...
... bond dissociation energies of the N-H and P-H bonds and the electron affinities of NH2 and PH2 are needed. However, if one assumes that the differences in these quantities are about the same as the differences in the average bond dissociation energies (386 kJ mol-1 for NH3 and 322 kJ mol-1 for PH3) ...
Grant MacEwan College - Faculty Web Pages
... Description: This is the second course in organic chemistry. The topics covered include structural and chemical properties of alkenes, alkynes, alcohols, phenols, ethers, aromatic compounds. Aldehyde, ketones, amines, carboxylic acids, and carboxylic acid derivatives. Illustration of these functiona ...
... Description: This is the second course in organic chemistry. The topics covered include structural and chemical properties of alkenes, alkynes, alcohols, phenols, ethers, aromatic compounds. Aldehyde, ketones, amines, carboxylic acids, and carboxylic acid derivatives. Illustration of these functiona ...
Enzymes
... D. Standard free energy change, ΔGº - ΔGº is called standard free energy change because it is equal to free energy change, ΔG, under standard conditions i.e., when reactants & products are kept at 1 mol/L. under these conditions ln [B]/[A] = 0, and ΔG = ΔGº + 0 1. ΔGº is predictive only under stand ...
... D. Standard free energy change, ΔGº - ΔGº is called standard free energy change because it is equal to free energy change, ΔG, under standard conditions i.e., when reactants & products are kept at 1 mol/L. under these conditions ln [B]/[A] = 0, and ΔG = ΔGº + 0 1. ΔGº is predictive only under stand ...
Chapter 8 - Chemical Equations
... Step 2 – You will compare the type of element by itself to the similar type of element in the compound. In this case, aluminum is a metal, so I will compare it with the metal in the compound (which is Pb). Step 3 – RULE: The element that is by itself must be HIGHER on (closer to the top of) the Acti ...
... Step 2 – You will compare the type of element by itself to the similar type of element in the compound. In this case, aluminum is a metal, so I will compare it with the metal in the compound (which is Pb). Step 3 – RULE: The element that is by itself must be HIGHER on (closer to the top of) the Acti ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034 PART-A
... 21. Explain the stability of various conformers of disubstituted cyclohexanes with energy. 22. State and explain Octant rule. Draw the octants and predict the sign of Cotton effect to the following compounds. a) (+)-3-methylcyclohexanone ...
... 21. Explain the stability of various conformers of disubstituted cyclohexanes with energy. 22. State and explain Octant rule. Draw the octants and predict the sign of Cotton effect to the following compounds. a) (+)-3-methylcyclohexanone ...
Chapters 19 & 20
... binary compounds (except NH3) containing N decompose exothermically to the elements In the preparation of NH3 from N2 and H2, too much energy is needed to disrupt the N≡N bond. Thus, though K (106) is high the reaction is very slow ...
... binary compounds (except NH3) containing N decompose exothermically to the elements In the preparation of NH3 from N2 and H2, too much energy is needed to disrupt the N≡N bond. Thus, though K (106) is high the reaction is very slow ...
Student 2 response
... (iii) Identify the glassware that must be rinsed with distilled water only, and state the reason why this glassware must not be rinsed with the original solution of KHP. Volumetric flask. This is because it would affect the concentration and so it would affect the results. (2 marks) ...
... (iii) Identify the glassware that must be rinsed with distilled water only, and state the reason why this glassware must not be rinsed with the original solution of KHP. Volumetric flask. This is because it would affect the concentration and so it would affect the results. (2 marks) ...
Organic Chemistry - Snow College | It's SNOWing
... • Cyclic compounds with ether linkages • Bind cations as “host” and “guest” ...
... • Cyclic compounds with ether linkages • Bind cations as “host” and “guest” ...