File
... • They are white crystalline solids that readily dissolve in water. • Solubility is due to their OH groups which readily form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. • All monosaccharides are sweet tasting to varying degrees. • The most common and biologically important simple sugar is glucose. ...
... • They are white crystalline solids that readily dissolve in water. • Solubility is due to their OH groups which readily form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. • All monosaccharides are sweet tasting to varying degrees. • The most common and biologically important simple sugar is glucose. ...
Get cached
... The I R spectra of Cr°(CN—R) and Ni°(CN—R) could provide further criteria to test the validity of the V B and M O models. Since both complexes are highly symmetric (octahedral and tetrahedral configurations) they should exhibit only one N C stretching frequency unless back donation lowers the symmet ...
... The I R spectra of Cr°(CN—R) and Ni°(CN—R) could provide further criteria to test the validity of the V B and M O models. Since both complexes are highly symmetric (octahedral and tetrahedral configurations) they should exhibit only one N C stretching frequency unless back donation lowers the symmet ...
TOPIC 2. ORGANIC COMPOUNDS (Chapter 2)
... Problem: Using the concepts from topic 1…. - What is the geometry around the nitrogen of an amine - What is the hybridization of the nitrogen of an amine - What is the hybridization of the orbital containing the lone pairs of electrons on the nitrogen atom of amines? ...
... Problem: Using the concepts from topic 1…. - What is the geometry around the nitrogen of an amine - What is the hybridization of the nitrogen of an amine - What is the hybridization of the orbital containing the lone pairs of electrons on the nitrogen atom of amines? ...
From (2)
... Why is it important to investigate the rates of this reaction for metallurgical engineering? Disposal problems of radioactive wastes generated from treatment of uranium and thorium ores. Traces of uranium and thorium in other ores. Example: the slag resulted from the production of ferro-noibium is r ...
... Why is it important to investigate the rates of this reaction for metallurgical engineering? Disposal problems of radioactive wastes generated from treatment of uranium and thorium ores. Traces of uranium and thorium in other ores. Example: the slag resulted from the production of ferro-noibium is r ...
C - mvhs-fuhsd.org
... 63. Which of the following best represents the products of the net ionic equation for the reaction that occurs when solid barium phosphate and solid magnesium sulfide are added to water? A. Mg2+ + PO43- + BaS B. Mg3(PO4)2 + Ba2+ + S2C. Mg3(PO4)2 + BaS D. Mg2+ + PO43- + Ba2+ + S2E. BaMg + SPO4 64. W ...
... 63. Which of the following best represents the products of the net ionic equation for the reaction that occurs when solid barium phosphate and solid magnesium sulfide are added to water? A. Mg2+ + PO43- + BaS B. Mg3(PO4)2 + Ba2+ + S2C. Mg3(PO4)2 + BaS D. Mg2+ + PO43- + Ba2+ + S2E. BaMg + SPO4 64. W ...
Chapter 18 Electrochemistry
... Standard Reduction Potentials Standard reduction potential (E0) is the voltage associated with a reduction reaction at an electrode when all solutes are 1 M and all gases are at 1 atm. ...
... Standard Reduction Potentials Standard reduction potential (E0) is the voltage associated with a reduction reaction at an electrode when all solutes are 1 M and all gases are at 1 atm. ...
A Lesson on the Science and Art of Perfumery
... To understand just how these notes behave and why a certain perfume smells the way it does, we turn to some very simple chemistry. Evaporation is the process by which molecules in the liquid phase become gaseous. This phenomenon can be controlled by the attractive forces between the molecules in the ...
... To understand just how these notes behave and why a certain perfume smells the way it does, we turn to some very simple chemistry. Evaporation is the process by which molecules in the liquid phase become gaseous. This phenomenon can be controlled by the attractive forces between the molecules in the ...
Hebden V.2 – Oxidation Numbers
... the alkali metals are usually +1 the alkali earth metals are usually +2 the halogens are usually –1 (Cl, Br, I, F) Polyatomic ions have an overall charge that will be shown like OHNeutral molecules do not have a charge shown – it is zero – H4P2O7 has a charge of 0 7. All atoms have charge of 0 8. Hy ...
... the alkali metals are usually +1 the alkali earth metals are usually +2 the halogens are usually –1 (Cl, Br, I, F) Polyatomic ions have an overall charge that will be shown like OHNeutral molecules do not have a charge shown – it is zero – H4P2O7 has a charge of 0 7. All atoms have charge of 0 8. Hy ...
Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Catalysis
... stones, can be mainly ascribed to its strong acidic nature and, if concentrated, strong dehydrating and oxidizing property. Sulfuric acid at a high concentration can cause very serious damage upon contact, as it not only causes chemical burns via hydrolysis, but also secondary thermal burns via dehy ...
... stones, can be mainly ascribed to its strong acidic nature and, if concentrated, strong dehydrating and oxidizing property. Sulfuric acid at a high concentration can cause very serious damage upon contact, as it not only causes chemical burns via hydrolysis, but also secondary thermal burns via dehy ...
Fundamental Knowledge for Analysis of Chemical Reactor
... A chemical species is composed of atoms The chemical identity of a chemical species: kind, number,structure and configuration example: water, methane and ethylene Identity response for the chemical and physical properties: nicotine fits Difference between structure and configuration example: graphit ...
... A chemical species is composed of atoms The chemical identity of a chemical species: kind, number,structure and configuration example: water, methane and ethylene Identity response for the chemical and physical properties: nicotine fits Difference between structure and configuration example: graphit ...
Organic Chemistry
... The aldehyde, ethanal, is formed and immediately distils off, thereby preventing further oxidation to ethanoic acid, because the boiling point of ethanal (23 °C) is much lower than that of either the original alcohol ethanol (78 °C) or of ethanoic acid (118 °C). Both the alcohol and the acid have hi ...
... The aldehyde, ethanal, is formed and immediately distils off, thereby preventing further oxidation to ethanoic acid, because the boiling point of ethanal (23 °C) is much lower than that of either the original alcohol ethanol (78 °C) or of ethanoic acid (118 °C). Both the alcohol and the acid have hi ...
Nucleophilic
... Nucleophilicity usually increases going down a column of the periodic chart. Thus, sulfur nucleophiles are more reactive than oxygen nucleophiles. Halides: I– > Br– > Cl– > F–. Negatively charged nucleophiles are usually more reactive than ...
... Nucleophilicity usually increases going down a column of the periodic chart. Thus, sulfur nucleophiles are more reactive than oxygen nucleophiles. Halides: I– > Br– > Cl– > F–. Negatively charged nucleophiles are usually more reactive than ...
Klein, 2e
... • In SN1, proton transfer steps often occur after the substitution process. Examine the following example • The leaving group is good, but what about the nucleophile? • Draw a complete mechanism. Each step is an equilibrium. Which side will the equilibrium favor? • If the nucleophile were used as th ...
... • In SN1, proton transfer steps often occur after the substitution process. Examine the following example • The leaving group is good, but what about the nucleophile? • Draw a complete mechanism. Each step is an equilibrium. Which side will the equilibrium favor? • If the nucleophile were used as th ...
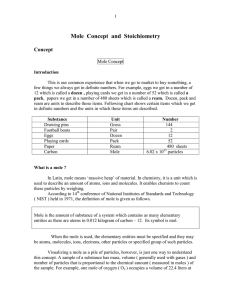
Stoichiometry
... empty. The chemist see the glass completely full, half in the liquid state and half in the vapor state. ...
... empty. The chemist see the glass completely full, half in the liquid state and half in the vapor state. ...
Multiple Choice Practice. A) P B) S C) Cl D) Li E) 1 F 1. Has the
... A) The vapor pressure of the solid phase equals the vapor pressure of the liquid phase B) The temperature is 0.01K lower than the normal melting point C) The liquid and gas phases have the same density and are therefore indistinguishable D) The solid phase melts if the pressure increases at constan ...
... A) The vapor pressure of the solid phase equals the vapor pressure of the liquid phase B) The temperature is 0.01K lower than the normal melting point C) The liquid and gas phases have the same density and are therefore indistinguishable D) The solid phase melts if the pressure increases at constan ...
Chapter 10 Chemical Reactions
... Oxidation = charge goes up, electrons are lost (ox = up) Reduction = charge goes down, electrons are gained (reduced = down) Oxidizing agent = the chemical than is reduced because it helped another chemical get oxidized, thus it was the agent for oxidation for another chemical Reducing agent ...
... Oxidation = charge goes up, electrons are lost (ox = up) Reduction = charge goes down, electrons are gained (reduced = down) Oxidizing agent = the chemical than is reduced because it helped another chemical get oxidized, thus it was the agent for oxidation for another chemical Reducing agent ...
ert207 analytical chemistry
... What is Analytical Chemistry? • Concerned with the chemical characterization of matter and the answer of : 1) What is it (Qualitative) –identification of elements, ions or compound 2) How much is it (Quantitative) ...
... What is Analytical Chemistry? • Concerned with the chemical characterization of matter and the answer of : 1) What is it (Qualitative) –identification of elements, ions or compound 2) How much is it (Quantitative) ...