lecture ch1-3 chem161pikul
... • Substances that can t be decomposed into simpler materials by chemical reactions • Substances composed of only one type of atom • Simplest forms of matter that we can work with directly • More complex substances composed of elements ...
... • Substances that can t be decomposed into simpler materials by chemical reactions • Substances composed of only one type of atom • Simplest forms of matter that we can work with directly • More complex substances composed of elements ...
HIGHLIGHTS OF NUCLEOPHILIC SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS
... b) occurs with formation of carbocation intermediates in the rate determining step c) involves one transition state per step. The rate-determining step involves a high polarity transition state d) follows first order (unimolecular) kinetics. That is, rate=k[substrate] In nucleophilic substitutions a ...
... b) occurs with formation of carbocation intermediates in the rate determining step c) involves one transition state per step. The rate-determining step involves a high polarity transition state d) follows first order (unimolecular) kinetics. That is, rate=k[substrate] In nucleophilic substitutions a ...
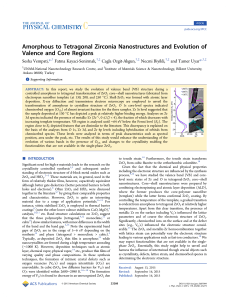
Amorphous to Tetragonal Zirconia
... including the electronic structure are influenced by the synthesis process,9,14 we have studied the valence band (VB) and corelevel ionic states of Zr and O in tetragonal-ZrO2 core−shell nanostructures. Core−shell nanostructures were prepared by combining electrospinning and atomic layer deposition ( ...
... including the electronic structure are influenced by the synthesis process,9,14 we have studied the valence band (VB) and corelevel ionic states of Zr and O in tetragonal-ZrO2 core−shell nanostructures. Core−shell nanostructures were prepared by combining electrospinning and atomic layer deposition ( ...
Answers to NHSCE 2002 Part A Page 1
... The acidity of the hydrides of elements in Group 16 of the Periodic table increases as the group is descended due to the bond energy of the covalent bond (in the undissolved, molecular, form of the acid) becoming weaker as it gets longer. Thus if we compare aqueous solutions of equal concentrations ...
... The acidity of the hydrides of elements in Group 16 of the Periodic table increases as the group is descended due to the bond energy of the covalent bond (in the undissolved, molecular, form of the acid) becoming weaker as it gets longer. Thus if we compare aqueous solutions of equal concentrations ...
Ionic Bonding - KMChemistryMatters
... Drawing Lewis Structures 1. Add the valence electrons. 2. Write symbols for the atoms and show which atoms are connected to which. 3. Complete the octet for the central atom then complete the octets of the other atoms. 4. Place leftover electrons on the central atom. 5. If there are not enough elec ...
... Drawing Lewis Structures 1. Add the valence electrons. 2. Write symbols for the atoms and show which atoms are connected to which. 3. Complete the octet for the central atom then complete the octets of the other atoms. 4. Place leftover electrons on the central atom. 5. If there are not enough elec ...
4/page
... •Be sure to notice that DENSITY is an INTENSIVE PROPERTY of matter. •INTENSIVE — does not depend on quantity of matter. Examples are density and temperature. •Contrast with EXTENSIVE — depends on quantity of matter. Examples are mass and volume. •Subdividing matter does not change intensive properti ...
... •Be sure to notice that DENSITY is an INTENSIVE PROPERTY of matter. •INTENSIVE — does not depend on quantity of matter. Examples are density and temperature. •Contrast with EXTENSIVE — depends on quantity of matter. Examples are mass and volume. •Subdividing matter does not change intensive properti ...
Topic 4
... ( bond formed by) end-on/axial overlap; electrons/electron density between the two (carbon) atoms/OWTTE; (π bond formed by) sideways/parallel overlap; electrons/electron density above and below bond/OWTTE; Marks can be scored from a suitable diagram. ...
... ( bond formed by) end-on/axial overlap; electrons/electron density between the two (carbon) atoms/OWTTE; (π bond formed by) sideways/parallel overlap; electrons/electron density above and below bond/OWTTE; Marks can be scored from a suitable diagram. ...
Answers to examination questions
... Q7 A Hydrogen bonding would only be expected to occur in CH2CH3COOH since it contains hydrogen bonded directly to oxygen. The −OH group is able to engage in hydrogen bonding. In the other two compounds the hydrogen is bonded to carbon. Q8 C Both ethane and neon are non-polar. Hence, the pred ...
... Q7 A Hydrogen bonding would only be expected to occur in CH2CH3COOH since it contains hydrogen bonded directly to oxygen. The −OH group is able to engage in hydrogen bonding. In the other two compounds the hydrogen is bonded to carbon. Q8 C Both ethane and neon are non-polar. Hence, the pred ...
Chapter22_LEC
... • the most abundant elements of the Earth’s crust are O and Si • silicates are covalent atomic solids of Si and O and minor amounts of other elements found in rocks, soils, and clays silicates have variable structures – leading to the variety of properties found in rocks, clays, and soils Tro, Ch ...
... • the most abundant elements of the Earth’s crust are O and Si • silicates are covalent atomic solids of Si and O and minor amounts of other elements found in rocks, soils, and clays silicates have variable structures – leading to the variety of properties found in rocks, clays, and soils Tro, Ch ...
Crown ethers
... Grignard reagents and organolithium compounds are strong nucleophiles capable of opening the ethylene oxide (epoxide) ring. The initial product is a magnesium alkoxide of lithium alkoxide, but after hydrolysis, we obtain a primary alcohol with two carbon atoms than the organometallic reagent. ...
... Grignard reagents and organolithium compounds are strong nucleophiles capable of opening the ethylene oxide (epoxide) ring. The initial product is a magnesium alkoxide of lithium alkoxide, but after hydrolysis, we obtain a primary alcohol with two carbon atoms than the organometallic reagent. ...
reaction rate - davis.k12.ut.us
... • Some substances react more readily than others. (Alkali metals, halogens) • The phase of the reactants matters. Some substances react faster in aqueous solutions than if combined as solids. ...
... • Some substances react more readily than others. (Alkali metals, halogens) • The phase of the reactants matters. Some substances react faster in aqueous solutions than if combined as solids. ...
Document
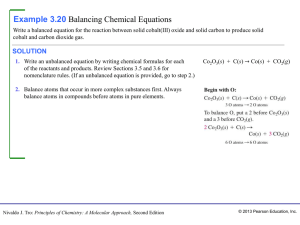
... SORT The problem gives the mass of carbon dioxide and asks you to find the mass of glucose that can be produced. ...
... SORT The problem gives the mass of carbon dioxide and asks you to find the mass of glucose that can be produced. ...
Atoms and Molecules
... equally by the two atoms, then this is a polar covalent bond. • The bonds between oxygen and hydrogen in water are polar covalent because oxygen has a much higher electronegativity than does hydrogen. • Compounds with a polar covalent bond have regions that have a partial negative charge near the st ...
... equally by the two atoms, then this is a polar covalent bond. • The bonds between oxygen and hydrogen in water are polar covalent because oxygen has a much higher electronegativity than does hydrogen. • Compounds with a polar covalent bond have regions that have a partial negative charge near the st ...
Organic Chemistry
... • bitumen is used for making roads Describe an homologous series of compounds as: • having the same functional group with similar properties and the same general formula Understand that alkanes: • are saturated hydrocarbons which are generally unreactive but will burn • can be burnt in excess air to ...
... • bitumen is used for making roads Describe an homologous series of compounds as: • having the same functional group with similar properties and the same general formula Understand that alkanes: • are saturated hydrocarbons which are generally unreactive but will burn • can be burnt in excess air to ...
Ch.1-Matter and Change
... A chemical property relates to a substance’s ability to undergo changes that transform it into different substances. reactivity toxicity heat of combustion A change in which one or more substances are converted into different substances is called a chemical change or chemical reaction. ...
... A chemical property relates to a substance’s ability to undergo changes that transform it into different substances. reactivity toxicity heat of combustion A change in which one or more substances are converted into different substances is called a chemical change or chemical reaction. ...
rate - Killeen ISD
... Collision frequency increases due to particles moving faster The also collide harder Increases the chance for collision ...
... Collision frequency increases due to particles moving faster The also collide harder Increases the chance for collision ...
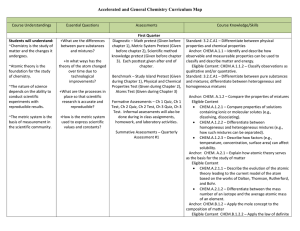
Chemistry Curriculum Map - Belle Vernon Area School District
... substances can result in physical and/or chemical changes. Standard: 3.2.C.A4 – Interpret and apply the Laws of Conservation of Mass, Constant Composition (Definite Proportions), and Multiple Proportions. Anchor: CHEM.B.1.2 – Apply the mole concept to the composition of matter Eligible Content CHEM. ...
... substances can result in physical and/or chemical changes. Standard: 3.2.C.A4 – Interpret and apply the Laws of Conservation of Mass, Constant Composition (Definite Proportions), and Multiple Proportions. Anchor: CHEM.B.1.2 – Apply the mole concept to the composition of matter Eligible Content CHEM. ...
In Situ Soft X‑ray Absorption Spectroscopy Applied to Solid
... reflection IR (ATR-IR)10−14 have been frequently used. In this target, since liquid substrate is usually diluted by solvent and other reactants, the observation of minor liquid component in the reaction system is highly required. However, these methods have different drawback for the detection of mino ...
... reflection IR (ATR-IR)10−14 have been frequently used. In this target, since liquid substrate is usually diluted by solvent and other reactants, the observation of minor liquid component in the reaction system is highly required. However, these methods have different drawback for the detection of mino ...
Chemistry in Action: Question paper - A
... (b) The students deduced that the heat change was due only to the formation of intermolecular forces between ethyl ethanoate molecules and trichloromethane molecules. Ignoring all experimental errors, give one reason why the students may have made an incorrect deduction. ...
... (b) The students deduced that the heat change was due only to the formation of intermolecular forces between ethyl ethanoate molecules and trichloromethane molecules. Ignoring all experimental errors, give one reason why the students may have made an incorrect deduction. ...
Bonding and Nomenclature
... of the dipole within a molecule (Polarity) The greater the difference in electronegativity between atoms, the greater the polarity/dipole moment. The higher the dipole moment, the stronger the intermolecular forces. The stronger the IMF’s the higher the melting and boiling point. ...
... of the dipole within a molecule (Polarity) The greater the difference in electronegativity between atoms, the greater the polarity/dipole moment. The higher the dipole moment, the stronger the intermolecular forces. The stronger the IMF’s the higher the melting and boiling point. ...
Future perspectives in catalysis - NRSC
... catalysts within reach. Scientists have found a common molecular basis for the chemical processes for which catalysis is used. These research fields have now been unified to form a general scientific framework. That means heterogeneous, homogeneous and bio-catalysis can now be studied within a singl ...
... catalysts within reach. Scientists have found a common molecular basis for the chemical processes for which catalysis is used. These research fields have now been unified to form a general scientific framework. That means heterogeneous, homogeneous and bio-catalysis can now be studied within a singl ...