Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes
... The Diels-Alder Cycloaddition Reaction • A few biological Diels-Alder reactions are known • Biosynthesis of lovastatin involves an intramolecular Diels- ...
... The Diels-Alder Cycloaddition Reaction • A few biological Diels-Alder reactions are known • Biosynthesis of lovastatin involves an intramolecular Diels- ...
The Reaction Rates of O2 with Closed-Shell and Open
... of the last four species eliminates hindrances caused by the violation of the spin conservation rule and allows one to compare these rate coefficients with those of the spin-allowed Cl2 reactions. In order to show the importance of this rule, O2 reactions with Al13H− (open shell) and Al14H− (closed sh ...
... of the last four species eliminates hindrances caused by the violation of the spin conservation rule and allows one to compare these rate coefficients with those of the spin-allowed Cl2 reactions. In order to show the importance of this rule, O2 reactions with Al13H− (open shell) and Al14H− (closed sh ...
or H - No Brain Too Small
... C=C double bond in alkanes is fixed and cannot be rotated (“is no free rotation about the C=C double bond”). This allows for different arrangements of the atoms/groups of atoms in space. o groups on same side, ciso groups on opposite sides, trans ...
... C=C double bond in alkanes is fixed and cannot be rotated (“is no free rotation about the C=C double bond”). This allows for different arrangements of the atoms/groups of atoms in space. o groups on same side, ciso groups on opposite sides, trans ...
to view
... It decreases with increase in temperature It does not change with change in (as V α T) temperature Since molality does not change with a change in temperature therefore it is a better method to express the concentration of a solution. Q4. What is meant by colligative property. List any four factors ...
... It decreases with increase in temperature It does not change with change in (as V α T) temperature Since molality does not change with a change in temperature therefore it is a better method to express the concentration of a solution. Q4. What is meant by colligative property. List any four factors ...
Chem341_outcomes
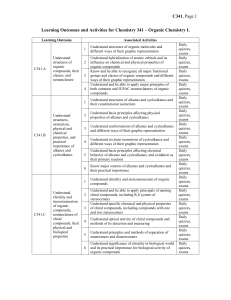
... Understand structure and nomenclature of alcohols and thiols, including primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols, diols, and poliols Understand the presence of hydroxyl as a major factor determining specific physical and chemical properties of alcohols, including their high boiling points, their ac ...
... Understand structure and nomenclature of alcohols and thiols, including primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols, diols, and poliols Understand the presence of hydroxyl as a major factor determining specific physical and chemical properties of alcohols, including their high boiling points, their ac ...
Міністерство охорони здоров`я України
... molecules are oriented around salt as follows: negative poles of water dipoles turn towards the positive center of NaCl molecule, and positive poles — to the side of negative center of the molecule and attract them to itself. Due to this process, chemical bonds between the ions in the molecule weake ...
... molecules are oriented around salt as follows: negative poles of water dipoles turn towards the positive center of NaCl molecule, and positive poles — to the side of negative center of the molecule and attract them to itself. Due to this process, chemical bonds between the ions in the molecule weake ...
MECH 558 Combustion Class Notes
... Before learning how hydrocarbons react with oxygen in flames, we must first go over some nomenclature for the different classes of hydrocarbons. 2.1. Alkanes (paraffins): These molecules consist of carbon atoms which are all connected by single bonds and are saturated with hydrogen atoms (i.e. no mo ...
... Before learning how hydrocarbons react with oxygen in flames, we must first go over some nomenclature for the different classes of hydrocarbons. 2.1. Alkanes (paraffins): These molecules consist of carbon atoms which are all connected by single bonds and are saturated with hydrogen atoms (i.e. no mo ...
Philicities, Fugalities, and Equilibrium Constants
... Benzhydrylium ions (diarylcarbenium ions) with para- and meta-substituents are used as reference compounds for these investigations, because their Lewis acidities and electrophilicities can be varied by many orders of magnitude, while the steric surroundings of the reaction centers are kept constant ...
... Benzhydrylium ions (diarylcarbenium ions) with para- and meta-substituents are used as reference compounds for these investigations, because their Lewis acidities and electrophilicities can be varied by many orders of magnitude, while the steric surroundings of the reaction centers are kept constant ...
Organic Chemistry
... Organic chemistry looks at “oxidation” differently than we discussed in redox reactions where “oxidation” was all about losing electrons. In Organic Chemistry, “oxidation” is all about gaining OXYGEN! The more oxygen attached to the carbon, the more “oxidized” the carbon is considered. ...
... Organic chemistry looks at “oxidation” differently than we discussed in redox reactions where “oxidation” was all about losing electrons. In Organic Chemistry, “oxidation” is all about gaining OXYGEN! The more oxygen attached to the carbon, the more “oxidized” the carbon is considered. ...
exercise on Chapter 13 - Louisiana Tech University
... Reactant - a substance that is consumed by a chemical reaction Product - a substance that is produced by a chemical reaction. New Concepts Irreversible or complete reactions: Chemical reactions can be considered to have forward and backward reactions. In most chemical reactions, the rate of backward ...
... Reactant - a substance that is consumed by a chemical reaction Product - a substance that is produced by a chemical reaction. New Concepts Irreversible or complete reactions: Chemical reactions can be considered to have forward and backward reactions. In most chemical reactions, the rate of backward ...
AH 2015 incl MG
... standard enthalpy of formation, ∆H f , in kJ mol−1, for Cu2+(Cl−)2(s). Using selected information from the thermochemical cycle above and the equation below calculate the standard enthalpy of formation, ∆H of , in kJ mol−1, of Cu+Cl−(s). Cu+(g) + Cl−(g) ...
... standard enthalpy of formation, ∆H f , in kJ mol−1, for Cu2+(Cl−)2(s). Using selected information from the thermochemical cycle above and the equation below calculate the standard enthalpy of formation, ∆H of , in kJ mol−1, of Cu+Cl−(s). Cu+(g) + Cl−(g) ...
Option A Materials - Cambridge Resources for the IB Diploma
... point, permeability (to liquids and gases), elasticity, brittleness etc. We can generally explain properties in terms of the structure and bonding – properties such as melting point, malleability/ductility and brittleness were discussed in Topic 4. Most materials behave elastically under certain con ...
... point, permeability (to liquids and gases), elasticity, brittleness etc. We can generally explain properties in terms of the structure and bonding – properties such as melting point, malleability/ductility and brittleness were discussed in Topic 4. Most materials behave elastically under certain con ...
29th INTERNATIONAL CHEMISTRY OLYMPIAD PREPARATORY
... of the topics were felt to greatly exceed the knowledge base which a high school student, albeit even some of the best high school students in the world, could be reasonably expected to have without being exposed to rigorous and extensive additional study. It was strongly felt by some delegates that ...
... of the topics were felt to greatly exceed the knowledge base which a high school student, albeit even some of the best high school students in the world, could be reasonably expected to have without being exposed to rigorous and extensive additional study. It was strongly felt by some delegates that ...
IChO_Comp_Prob_Answ 1997
... of the topics were felt to greatly exceed the knowledge base which a high school student, albeit even some of the best high school students in the world, could be reasonably expected to have without being exposed to rigorous and extensive additional study. It was strongly felt by some delegates that ...
... of the topics were felt to greatly exceed the knowledge base which a high school student, albeit even some of the best high school students in the world, could be reasonably expected to have without being exposed to rigorous and extensive additional study. It was strongly felt by some delegates that ...
Stability and Kinetics of the Acid
... cryptand, reacts with NH3, KSCN and NaN3 to form the binuclear tertiary complexes Cu2L(NH3)24+, Cu2L(SCN)3+ and Cu2L(N3)3+. The equilibrium constants show a special stabilisation of the complexes with ligands able to bridge the CuII centres, with a maximum stabilisation for azide. Upon addition of a ...
... cryptand, reacts with NH3, KSCN and NaN3 to form the binuclear tertiary complexes Cu2L(NH3)24+, Cu2L(SCN)3+ and Cu2L(N3)3+. The equilibrium constants show a special stabilisation of the complexes with ligands able to bridge the CuII centres, with a maximum stabilisation for azide. Upon addition of a ...
chemical kinetics - Berkeley City College
... The graphical method to determine a first-order and second-order reaction. The meaning and calculation half-life of a first order reaction; Determination of the activation energy, Ea, either graphically or from rate constants at different temperatures. Derive rate law from reaction mechanism. The ro ...
... The graphical method to determine a first-order and second-order reaction. The meaning and calculation half-life of a first order reaction; Determination of the activation energy, Ea, either graphically or from rate constants at different temperatures. Derive rate law from reaction mechanism. The ro ...