Q1. Particles A and B are electrically neutral and are separated by
... They are extended away from a negative point charge. They are the path followed by a unit positive charge. Two electric field lines never cross each other. They are imaginary lines used to visualize the patterns in the electric field. The direction of the electric field at a point in the field line ...
... They are extended away from a negative point charge. They are the path followed by a unit positive charge. Two electric field lines never cross each other. They are imaginary lines used to visualize the patterns in the electric field. The direction of the electric field at a point in the field line ...
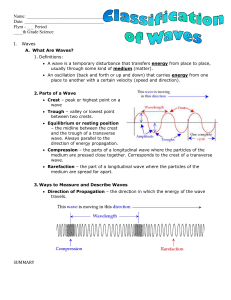
Waves What Are Waves? Definitions: A wave is a temporary
... gives rise to the electric force, which causes static electricity and drives the flow of electric current in electrical conductors. The magnetic field can be produced by the motion of electric charges, such as an electric current flowing along a wire, and gives rise to the magnetic force one assoc ...
... gives rise to the electric force, which causes static electricity and drives the flow of electric current in electrical conductors. The magnetic field can be produced by the motion of electric charges, such as an electric current flowing along a wire, and gives rise to the magnetic force one assoc ...
L05_Capacitance
... Mica: Similar to metal film. Often high voltage. Suitable for high frequencies. Paper: Used for high voltages. Glass: Used for high voltages. Stable temperature coefficient in a wide range of temperatures. Ceramic: Chips of altering layers of metal and ceramic. Very common, they find use in low-prec ...
... Mica: Similar to metal film. Often high voltage. Suitable for high frequencies. Paper: Used for high voltages. Glass: Used for high voltages. Stable temperature coefficient in a wide range of temperatures. Ceramic: Chips of altering layers of metal and ceramic. Very common, they find use in low-prec ...
Summary: Applications of Gauss` Law Suggested Reading:
... where “A” is the area of the top surface of the pillbox. The electric field above the plane then is just ~ = E0 ẑ = σ ẑ E ...
... where “A” is the area of the top surface of the pillbox. The electric field above the plane then is just ~ = E0 ẑ = σ ẑ E ...
Chapter 24
... We start with the simplest form – two parallel conducting plates separated by vacuum Let the conducting plates have area A and be separated by a distance d The magnitude of the electric field between the two plates is given by We treat the field as being uniform allowing us to write ...
... We start with the simplest form – two parallel conducting plates separated by vacuum Let the conducting plates have area A and be separated by a distance d The magnitude of the electric field between the two plates is given by We treat the field as being uniform allowing us to write ...
1 Determining the Charge of an Electron: The Millikan Oil Drop
... divisions, you will be able to determine its actual speed in meters per second. 7) Pump the atomizer bulb 2 times to inject a cloud of particles into the electrode chamber. Allow the faster moving particles to clear, and then pick a particle that is slowly moving upward. Wait for it to cross a scale ...
... divisions, you will be able to determine its actual speed in meters per second. 7) Pump the atomizer bulb 2 times to inject a cloud of particles into the electrode chamber. Allow the faster moving particles to clear, and then pick a particle that is slowly moving upward. Wait for it to cross a scale ...
English Medium
... 3. Write the effect of pressure, on melting of ice? A. With increase in pressure the melting point of ice reduces. 4. Equal amounts of water kept in a cup and in a dish. Which will evaporate faster? Why? A. The surface area of water in dish is more than the surface area of water in cup. Evaporation ...
... 3. Write the effect of pressure, on melting of ice? A. With increase in pressure the melting point of ice reduces. 4. Equal amounts of water kept in a cup and in a dish. Which will evaporate faster? Why? A. The surface area of water in dish is more than the surface area of water in cup. Evaporation ...
Mathematics is the language of physics
... speed and time are taken as fundamental quantities, length will become a derived quantity because then length will be expressed as Speed Time. and if force and acceleration are taken as fundamental quantities, then mass will be defined as Force / acceleration and will be termed as a derived quanti ...
... speed and time are taken as fundamental quantities, length will become a derived quantity because then length will be expressed as Speed Time. and if force and acceleration are taken as fundamental quantities, then mass will be defined as Force / acceleration and will be termed as a derived quanti ...
Three-dimensional electromagnetic breathers in carbon
... the overlap integral, and dx ¼ 3b=2.2,3 For definiteness, we consider the propagation of a laser beam in an array of CNTs in the direction perpendicular to the their axes, namely along the Oz-axis with our choice of spatial coordinates. Further, we assume that the electric field of the laser beam, E ...
... the overlap integral, and dx ¼ 3b=2.2,3 For definiteness, we consider the propagation of a laser beam in an array of CNTs in the direction perpendicular to the their axes, namely along the Oz-axis with our choice of spatial coordinates. Further, we assume that the electric field of the laser beam, E ...
Quantum Confinement in Nanometric Structures
... Abstract: This paper discusses the quantum confinement effects in nanometric structures that form low dimensional systems. In such systems, each surface/interface acts like a potential barrier, i.e. the wall of a quantum well, generating new energy levels. These levels are computed in a model that u ...
... Abstract: This paper discusses the quantum confinement effects in nanometric structures that form low dimensional systems. In such systems, each surface/interface acts like a potential barrier, i.e. the wall of a quantum well, generating new energy levels. These levels are computed in a model that u ...
Summary of Class 4 8.02 Tuesday 2/8/05 / Wednesday 2/9/05 Topics
... feels due to the field it is sitting in. For example, if a gravitational field g is pushing down on a mass m and you want to lift it, you must apply a force mg upwards, equal and opposite the gravitational force. Why equal? If you don’t push enough then gravity will win and push it down and if you p ...
... feels due to the field it is sitting in. For example, if a gravitational field g is pushing down on a mass m and you want to lift it, you must apply a force mg upwards, equal and opposite the gravitational force. Why equal? If you don’t push enough then gravity will win and push it down and if you p ...
Giessler/Crookes Tube and Cathode Ray
... Through a series of experiments, we have determined that Cathode Rays are composed of particles, not waves. The next step is to figure out whether the particles are molecules, atoms, or subatomic particles. To help, let’s figure out a way to measure the ratio of the particle’s mass to its charge. Ob ...
... Through a series of experiments, we have determined that Cathode Rays are composed of particles, not waves. The next step is to figure out whether the particles are molecules, atoms, or subatomic particles. To help, let’s figure out a way to measure the ratio of the particle’s mass to its charge. Ob ...
Patent-description-adapted
... which themselves lead to further processes of fusion, fission and fusion/fission (called semifusion). Our materials don’t need to be “injected― like in Campbell’s patent but can enter the reactor embodiment by non-pressurized ports. Campbell claims in claim 1 and 12 to use “gas molecules†...
... which themselves lead to further processes of fusion, fission and fusion/fission (called semifusion). Our materials don’t need to be “injected― like in Campbell’s patent but can enter the reactor embodiment by non-pressurized ports. Campbell claims in claim 1 and 12 to use “gas molecules†...
Measurements - Singapore A Level Notes
... During the braking phase, the brake exerts a retarding force on the car hence there is deceleration. The speed decreases non-linearly with distance hence braking distance cannot be proportional to speed. Using the equation v²=u²-2as s=u²/2a. The braking distance is thus proportional to the square ...
... During the braking phase, the brake exerts a retarding force on the car hence there is deceleration. The speed decreases non-linearly with distance hence braking distance cannot be proportional to speed. Using the equation v²=u²-2as s=u²/2a. The braking distance is thus proportional to the square ...
Advancing Physics A2
... You must understand what is meant by ‘half-life’ from work covered at GCSE. It is important to appreciate that radioactive substances do not last forever and that some decay very quickly whereas others seem to have an infinite life. Notes: ...
... You must understand what is meant by ‘half-life’ from work covered at GCSE. It is important to appreciate that radioactive substances do not last forever and that some decay very quickly whereas others seem to have an infinite life. Notes: ...
Dynamic Line Integral Convolution: A Guide to the Java Software
... lines in space, where the direction of the straight line is determined by the local direction of the field at (for example) pixel 1, we would get a visual representation of the field but it would be inaccurate, because we would be assuming that the local streamline can be reasonably approximated by ...
... lines in space, where the direction of the straight line is determined by the local direction of the field at (for example) pixel 1, we would get a visual representation of the field but it would be inaccurate, because we would be assuming that the local streamline can be reasonably approximated by ...
Time in physics

Time in physics is defined by its measurement: time is what a clock reads. In classical, non-relativistic physics it is a scalar quantity and, like length, mass, and charge, is usually described as a fundamental quantity. Time can be combined mathematically with other physical quantities to derive other concepts such as motion, kinetic energy and time-dependent fields. Timekeeping is a complex of technological and scientific issues, and part of the foundation of recordkeeping.