Section 1: The Land
... that make up the Philippines together have a coastline that measures 22,554 miles (36,289 km). The two large islands of Luzon and Mindanao account for about 66 percent of the country’s land area. ...
... that make up the Philippines together have a coastline that measures 22,554 miles (36,289 km). The two large islands of Luzon and Mindanao account for about 66 percent of the country’s land area. ...
Tropical Climate Regions (cont.)
... that make up the Philippines together have a coastline that measures 22,554 miles (36,289 km). The two large islands of Luzon and Mindanao account for about 66 percent of the country’s land area. ...
... that make up the Philippines together have a coastline that measures 22,554 miles (36,289 km). The two large islands of Luzon and Mindanao account for about 66 percent of the country’s land area. ...
Document
... - The Indus River valley was the cradle of ancient India, one of the world’s earliest civilizations. - The Brahmaputra River flows east through the Himalaya and then west into India and Bangladesh, where it meets the Ganges River. - The two rivers form a delta before emptying into the Bay of Ben ...
... - The Indus River valley was the cradle of ancient India, one of the world’s earliest civilizations. - The Brahmaputra River flows east through the Himalaya and then west into India and Bangladesh, where it meets the Ganges River. - The two rivers form a delta before emptying into the Bay of Ben ...
South Asia - Vanlue Local School
... Kush. The most famous of these is the Khyber Pass between Afghanistan and Pakistan. For centuries, trading caravans and conquering armies marched through the Khyber Pass and on to India. Scientists believe that South Asia’s northern mountain ranges were formed by tectonic plate movements. About 60 m ...
... Kush. The most famous of these is the Khyber Pass between Afghanistan and Pakistan. For centuries, trading caravans and conquering armies marched through the Khyber Pass and on to India. Scientists believe that South Asia’s northern mountain ranges were formed by tectonic plate movements. About 60 m ...
CHAPTER II SOUTHEAST ASIA ECONOMIC SECURITY
... and Tourism believes that the Straits will serve 114,000 ships annually by the year 2020. (International Hydrographic Organization, 2013) In terms of responsibility, user nations come second to the littoral states, consisting of foreign countries that depend highly on sea-based imports and exports. ...
... and Tourism believes that the Straits will serve 114,000 ships annually by the year 2020. (International Hydrographic Organization, 2013) In terms of responsibility, user nations come second to the littoral states, consisting of foreign countries that depend highly on sea-based imports and exports. ...
Asia is the largest of the 7 continents. Most
... What is the climate like in the different regions in Asia? The southern sections of Asia are warm to cold, while far north eastern areas such as Siberia are very cold. The highest temperature recorded in Asia was 54.0 °C (129.2 °F) at Tirat Zvi, Israel on June 21, 1942. North Asia This part of Asia ...
... What is the climate like in the different regions in Asia? The southern sections of Asia are warm to cold, while far north eastern areas such as Siberia are very cold. The highest temperature recorded in Asia was 54.0 °C (129.2 °F) at Tirat Zvi, Israel on June 21, 1942. North Asia This part of Asia ...
Southeast Asia - Judson Independent School District
... What countries that are not part of Southeast Asia are also affected by the Ring of Fire around the Pacific Ocean? Answer: Countries not in Southeast Asia that are also affected by the Ring of Fire include the west coast of the United States, Japan, Chile, New Zealand and ...
... What countries that are not part of Southeast Asia are also affected by the Ring of Fire around the Pacific Ocean? Answer: Countries not in Southeast Asia that are also affected by the Ring of Fire include the west coast of the United States, Japan, Chile, New Zealand and ...
Std. 6, History, Civics and Geography, Maharashtra
... Towards east: The mountains of ‘Eastern Ghats’. v. To the west of Sahyadris, is the coastal region of Konkan and Malabar. vi. Deccan plateau has fertile land due to which many post-Harappan agrarian cultures flourished in this region. vii. Many kingdoms and smaller empires flourished in the Deccan P ...
... Towards east: The mountains of ‘Eastern Ghats’. v. To the west of Sahyadris, is the coastal region of Konkan and Malabar. vi. Deccan plateau has fertile land due to which many post-Harappan agrarian cultures flourished in this region. vii. Many kingdoms and smaller empires flourished in the Deccan P ...
Chapter 31 - Air Academy High School
... interdependent through trade. Rich in natural resources, Southeast Asia is a vital crossroads of trade. As the region becomes more urbanized and uses its natural resources to industrialize, it faces a variety of environmental problems. ...
... interdependent through trade. Rich in natural resources, Southeast Asia is a vital crossroads of trade. As the region becomes more urbanized and uses its natural resources to industrialize, it faces a variety of environmental problems. ...
Chapter 23 Section 1 Novelist Paul Theroux described the varied
... southern lands include eroded mountains and flat plateaus. The Himalaya According to the theory of continental drift, about 60 million years ago the Indian subcontinent was part of the same large landmass as Africa. After the subcontinent broke away, it collided with the southern edge of Asia. The f ...
... southern lands include eroded mountains and flat plateaus. The Himalaya According to the theory of continental drift, about 60 million years ago the Indian subcontinent was part of the same large landmass as Africa. After the subcontinent broke away, it collided with the southern edge of Asia. The f ...
Human Geography of Southeast Asia
... several urban centers that have high population densities. • Indonesia is the fourth most populous country in the world. ...
... several urban centers that have high population densities. • Indonesia is the fourth most populous country in the world. ...
india – size and location
... The Indian landmass has a central location between the East and the West Asia. India is a southward extension of the Asian Continent. The trans Indian Ocean routes which connect the countries of Europe in the West and the countries of East Asia provide a strategic central location to India. Note tha ...
... The Indian landmass has a central location between the East and the West Asia. India is a southward extension of the Asian Continent. The trans Indian Ocean routes which connect the countries of Europe in the West and the countries of East Asia provide a strategic central location to India. Note tha ...
Teacher: Christine Thompson Subject: AP U.S. History/Pre
... TEKS: WG.1A, 4B, 6A, 6B, 9A, 13A O: Review and peer teach questions about the history, economy, society, politics, and physical geography of India and the Indian Perimeter countries. P: Work with peers to complete corrections for Unit 14 Exam. ...
... TEKS: WG.1A, 4B, 6A, 6B, 9A, 13A O: Review and peer teach questions about the history, economy, society, politics, and physical geography of India and the Indian Perimeter countries. P: Work with peers to complete corrections for Unit 14 Exam. ...
Regional Comparisons of South Asia, East Asia, and Southeast Asia
... All of Southeast Asia falls within the warm, humid tropics, and its climate generally can be characterized as monsoonal (i.e., marked by wet and dry periods). Changing seasons are more associated with rainfall than with temperature variations. There is, however, a high degree of climatic complexity ...
... All of Southeast Asia falls within the warm, humid tropics, and its climate generally can be characterized as monsoonal (i.e., marked by wet and dry periods). Changing seasons are more associated with rainfall than with temperature variations. There is, however, a high degree of climatic complexity ...
File
... Sea, serves as an important waterway and water source. The Indus River valley was the cradle of ancient India, one of the world’s earliest civilizations. The Brahmaputra River flows east through the Himalaya and then west into India and Bangladesh, where it meets the Ganges River. The two rive ...
... Sea, serves as an important waterway and water source. The Indus River valley was the cradle of ancient India, one of the world’s earliest civilizations. The Brahmaputra River flows east through the Himalaya and then west into India and Bangladesh, where it meets the Ganges River. The two rive ...
Southeast Asia - DePaul GIS Collaboratory
... Population is concentrated in deltas or volcanic islands due to its fertile soil ...
... Population is concentrated in deltas or volcanic islands due to its fertile soil ...
here - Carolina Asia Center
... Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations maintains a Statistical Database called FAOSTAT. The interactive database is a research tool that provides data on agricultural production (crops, yields, inputs, land area, labor, etc.), fisheries, and forestry--all according to time. FAOSTAT ...
... Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations maintains a Statistical Database called FAOSTAT. The interactive database is a research tool that provides data on agricultural production (crops, yields, inputs, land area, labor, etc.), fisheries, and forestry--all according to time. FAOSTAT ...
70- Landforms and Resources of South Asia
... subcontinent, a large landmass that is smaller than a continent. In fact, it is often referred to as the Indian subcontinent because India dominates the region. Although South Asia is about half the size of the continental United States, it has more than one billion inhabitants—one-fifth of the worl ...
... subcontinent, a large landmass that is smaller than a continent. In fact, it is often referred to as the Indian subcontinent because India dominates the region. Although South Asia is about half the size of the continental United States, it has more than one billion inhabitants—one-fifth of the worl ...
Geography of South Asia PowerPoint
... The Indian Subcontinent • A part of Gondwanaland broke off and collided with Eurasia. • The Himalayas and Hindu Kush were formed. ...
... The Indian Subcontinent • A part of Gondwanaland broke off and collided with Eurasia. • The Himalayas and Hindu Kush were formed. ...
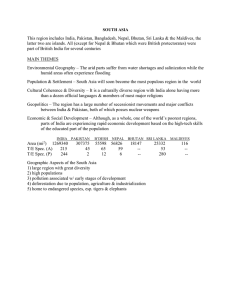
SOUTH ASIA This region includes India, Pakistan, Bangladesh
... CULTURAL COHERENCE & DIVERSITY Religion Hinduism emerged from the foothills of the Himalayas over 5,000 years ago. It’s real name is Sanatana Dharma (Eternal Order), Hindu is a British term derived from the Indus River; world’s 3rd largest & oldest religion; it is not just a religion but an intricat ...
... CULTURAL COHERENCE & DIVERSITY Religion Hinduism emerged from the foothills of the Himalayas over 5,000 years ago. It’s real name is Sanatana Dharma (Eternal Order), Hindu is a British term derived from the Indus River; world’s 3rd largest & oldest religion; it is not just a religion but an intricat ...
India - Ziyonet.uz
... world's major religions—Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism—originated here, whereas Zoroastrianism, Christianity, and Islam arrived in the 1st millennium CE and also helped shape the region's diverse culture. Gradually annexed by and brought under the administration of the British East India C ...
... world's major religions—Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism—originated here, whereas Zoroastrianism, Christianity, and Islam arrived in the 1st millennium CE and also helped shape the region's diverse culture. Gradually annexed by and brought under the administration of the British East India C ...
Ancient India: Geography
... The rich plains these two rivers create made ancient India a good area for agriculture. They also supplied water for people, plants, and animals. This made the Indian subcontinent an ideal location for civilizations to develop. The Indus and the Ganges also presented challenges to early settlers. Th ...
... The rich plains these two rivers create made ancient India a good area for agriculture. They also supplied water for people, plants, and animals. This made the Indian subcontinent an ideal location for civilizations to develop. The Indus and the Ganges also presented challenges to early settlers. Th ...
Harappan Culture
... • In India, mountains and seasonal winds shaped the climate and affect agriculture. • The earliest Indian civilization built well-organized cities near the Indus River. • Harappan civilization produced writing, a prosperous way of life, and a widely shared culture. ...
... • In India, mountains and seasonal winds shaped the climate and affect agriculture. • The earliest Indian civilization built well-organized cities near the Indus River. • Harappan civilization produced writing, a prosperous way of life, and a widely shared culture. ...
Greater India
Greater India was the historical extent of the culture of India beyond the Indian subcontinent. This particularly concerns the spread of Hinduism and Buddhism from India to Southeast Asia, Central Asia and China by the Silk Road during the early centuries of the Common Era, and the spread of the Indian writing systems like the Pallava script of the south Indian Pallava dynasty to Southeast Asia by the travellers and maritime traders of the 5th to 15th centuries. It also describes the establishment of Indianized Kingdoms in Southeast Asia and the spread of the Indian script, architecture and administration. To the west, Greater India overlaps with Greater Persia in the Hindu Kush and Pamir Mountains. The term is tied to the geographic uncertainties surrounding the ""Indies"" during the Age of Exploration.