Atrial Tachycardia - Thomas Jefferson University
... – Discrete P waves before every QRS, constant PR interval – Rate should vary in response to respirations, vagal stimulation, pain, stress – An isolated sinus tachycardia is a potentially life threatening rhythm until the underlying cause is identified and treated! ...
... – Discrete P waves before every QRS, constant PR interval – Rate should vary in response to respirations, vagal stimulation, pain, stress – An isolated sinus tachycardia is a potentially life threatening rhythm until the underlying cause is identified and treated! ...
Experimental methods for registration of electrical activity of the
... contains a built-in IR filter, which prevents a preparation from heating, and a band-pass filter (560 nm +/- 30 nm), which selects light at excitation maximum of the used dye. The changes in dynamics of transmembrane potential result in amplitude modulation of the emitted light. This is detected by ...
... contains a built-in IR filter, which prevents a preparation from heating, and a band-pass filter (560 nm +/- 30 nm), which selects light at excitation maximum of the used dye. The changes in dynamics of transmembrane potential result in amplitude modulation of the emitted light. This is detected by ...
Non-invasive Vagus Nerve Stimulator (gammaCore®)
... A total of 10 AEs that were related or possibly related to treatment with the nVNS device were noted in 5 subjects ...
... A total of 10 AEs that were related or possibly related to treatment with the nVNS device were noted in 5 subjects ...
Monitoring antipsychotics1
... (<20mg), ziprasidone* usually do not elevate prolactin, but worth measuring if symptoms arise ...
... (<20mg), ziprasidone* usually do not elevate prolactin, but worth measuring if symptoms arise ...
Cardiac Arrhythmias in the Intensive Care Unit
... 250 to 350 bpm. Patients often present with 2:1 AV conduction with a ventricular rate of 150 bpm, although the AV conduction ratio can change abruptly. Acute treatment consists of AV-nodal-blocking drugs for rate control. If the patient becomes clinically unstable, direct current–synchronized (DC-sy ...
... 250 to 350 bpm. Patients often present with 2:1 AV conduction with a ventricular rate of 150 bpm, although the AV conduction ratio can change abruptly. Acute treatment consists of AV-nodal-blocking drugs for rate control. If the patient becomes clinically unstable, direct current–synchronized (DC-sy ...
skeletal muscle
... Action potentials moving through the cardiac muscle produces electrical currents that can be measured on the surface of the body. These currents are measured by electrodes attached to the surface of the body producing an electrocardiogram (ECG). ...
... Action potentials moving through the cardiac muscle produces electrical currents that can be measured on the surface of the body. These currents are measured by electrodes attached to the surface of the body producing an electrocardiogram (ECG). ...
06 Effect of Coughing LQ
... dizziness. You find that his pulse is 35 bpm. You immediately call 911 and are told that it will take 15 minutes for the helicopter to arrive. You know that CPR should not be performed on conscious individuals. Drawing from the knowledge you have gained from this experiment, what might be done to im ...
... dizziness. You find that his pulse is 35 bpm. You immediately call 911 and are told that it will take 15 minutes for the helicopter to arrive. You know that CPR should not be performed on conscious individuals. Drawing from the knowledge you have gained from this experiment, what might be done to im ...
Cardiac Electrophysiology Basics
... EXPERIMENTAL PES IN RODENTS In the animal setting, PES is sometimes performed as survival procedures using sterile surgeries, but increasingly rodent EP models are used in terminal setting. In rodent intracardiac PES set-up, the right atrium (RA) position is used most commonly (2, 3). At this settin ...
... EXPERIMENTAL PES IN RODENTS In the animal setting, PES is sometimes performed as survival procedures using sterile surgeries, but increasingly rodent EP models are used in terminal setting. In rodent intracardiac PES set-up, the right atrium (RA) position is used most commonly (2, 3). At this settin ...
advanced ekg monitoring
... – No trending data (heart rate, AF) – Compliance: Patient must remember to have monitor at all times, patients forget how to use technology due to infrequent use, etc. – Single lead ECG rhythm strip ...
... – No trending data (heart rate, AF) – Compliance: Patient must remember to have monitor at all times, patients forget how to use technology due to infrequent use, etc. – Single lead ECG rhythm strip ...
What`s My Target Heart Rate
... You don't necessarily need to exercise at your target heart rate to lower your risk for heart and blood vessel disease. Even moderate aerobic activity, such as walking, may help improve your health. However, your target heart rate may still be useful to you. It's one reliable way to assess the inten ...
... You don't necessarily need to exercise at your target heart rate to lower your risk for heart and blood vessel disease. Even moderate aerobic activity, such as walking, may help improve your health. However, your target heart rate may still be useful to you. It's one reliable way to assess the inten ...
Ventricular Septal Defect
... the right ventricular wall or on the tricuspid valve. Aortic regurgitation occasionally is associated with a small membranous VSD. The typical pathology of a membranous infracristal defect follows. ...
... the right ventricular wall or on the tricuspid valve. Aortic regurgitation occasionally is associated with a small membranous VSD. The typical pathology of a membranous infracristal defect follows. ...
Cardiac Out Put - FROM 1:45-3
... In the veins, blood can be driven forward only as large veins have one way valve placed at 2 to 4 cm intervals. These valves prevent back flow of blood that tends to occur when a person stands up. ...
... In the veins, blood can be driven forward only as large veins have one way valve placed at 2 to 4 cm intervals. These valves prevent back flow of blood that tends to occur when a person stands up. ...
Extent of the Problem - Miami
... Is victim wearing a transdermal medication patch on his or her chest? Does victim have a pacemaker or implanted defibrillator? ...
... Is victim wearing a transdermal medication patch on his or her chest? Does victim have a pacemaker or implanted defibrillator? ...
Pre-Course Study Session I Notes
... Overload Principle – a principle of human performance that states that beneficial adaptations occur in response to demands applied to the body at levels beyond a certain threshold (overload), but within the limits of tolerance and safety. Maxiload - The maximum load method positively influences spee ...
... Overload Principle – a principle of human performance that states that beneficial adaptations occur in response to demands applied to the body at levels beyond a certain threshold (overload), but within the limits of tolerance and safety. Maxiload - The maximum load method positively influences spee ...
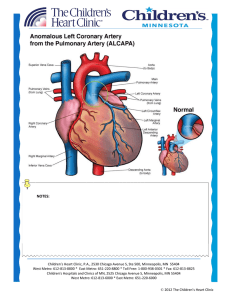
notes - Children`s Heart Clinic
... Mitral regurgitation may occur in the setting of left myocardial infarction. In this case, a regurgitant systolic murmur may be present, heard best at the heart apex. Diagnostics: EKG: Deep & wide Q waves, inverted T waves and ST segment changes. Coronary angiography: Gold standard for diagnos ...
... Mitral regurgitation may occur in the setting of left myocardial infarction. In this case, a regurgitant systolic murmur may be present, heard best at the heart apex. Diagnostics: EKG: Deep & wide Q waves, inverted T waves and ST segment changes. Coronary angiography: Gold standard for diagnos ...
ST-elevation acute myocardial infarction due to
... (Table 1) were normal with the exception of an elevated Creactive protein level. The patient was started on dual antiplatelet therapy with aspirin 81 mg daily and prasugrel 10 mg daily. In addition, a high-intensity statin, oral beta-blocker, and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor were also ini ...
... (Table 1) were normal with the exception of an elevated Creactive protein level. The patient was started on dual antiplatelet therapy with aspirin 81 mg daily and prasugrel 10 mg daily. In addition, a high-intensity statin, oral beta-blocker, and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor were also ini ...
Subcutaneous ICD
... added any time after initial S-ICD implant with femoral access, instead of adding a transvenous system. Give even more people access to the S-ICD by offering a combined S-ICD plus Leadless pacemaker system. ...
... added any time after initial S-ICD implant with femoral access, instead of adding a transvenous system. Give even more people access to the S-ICD by offering a combined S-ICD plus Leadless pacemaker system. ...
Redalyc.Transapical Closure of Left Ventricular to Right Atrial Shunt
... define the puncture site and with 3D TEE for guidance during the procedure. Right femoral vein puncture to access the Gerbode defect was also performed, forming a loop with the transapical access. A pigtail catheter was advanced through the left femoral artery into the LV for contrast injections. An ...
... define the puncture site and with 3D TEE for guidance during the procedure. Right femoral vein puncture to access the Gerbode defect was also performed, forming a loop with the transapical access. A pigtail catheter was advanced through the left femoral artery into the LV for contrast injections. An ...
Cardiac Arrhythmias: What to Treat, When and How
... cause (e.g. therapy of pulmonary edema to reduce hypoxiarelated arrhythmias). In the case of systemic disease-related arrhythmias, it is especially important to treat the disease, not necessarily the arrhythmia (e.g. hyperkalemia-related bradyarrhythmias require fluid therapy and sodium bicarbonate ...
... cause (e.g. therapy of pulmonary edema to reduce hypoxiarelated arrhythmias). In the case of systemic disease-related arrhythmias, it is especially important to treat the disease, not necessarily the arrhythmia (e.g. hyperkalemia-related bradyarrhythmias require fluid therapy and sodium bicarbonate ...
The Cardiovascular System CHAPTER 8
... • ________ ventricle - long and narrow, thick-walled, makes up the apex of heart • ________ ventricle - broader surface area, thinner walls • The borders of the ventricles contain interventricular sulci, which are grooves of fat and blood vessels that are part of ____________ circulation of heart. ...
... • ________ ventricle - long and narrow, thick-walled, makes up the apex of heart • ________ ventricle - broader surface area, thinner walls • The borders of the ventricles contain interventricular sulci, which are grooves of fat and blood vessels that are part of ____________ circulation of heart. ...
Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG*) is the process of recording the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time using electrodes placed on a patient's body. These electrodes detect the tiny electrical changes on the skin that arise from the heart muscle depolarizing during each heartbeat.In a conventional 12 lead ECG, ten electrodes are placed on the patient's limbs and on the surface of the chest. The overall magnitude of the heart's electrical potential is then measured from twelve different angles (""leads"") and is recorded over a period of time (usually 10 seconds). In this way, the overall magnitude and direction of the heart's electrical depolarization is captured at each moment throughout the cardiac cycle. The graph of voltage versus time produced by this noninvasive medical procedure is referred to as an electrocardiogram (abbreviated ECG or EKG).During each heartbeat, a healthy heart will have an orderly progression of depolarization that starts with pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial node, spreads out through the atrium, passes through the atrioventricular node down into the bundle of His and into the Purkinje fibers spreading down and to the left throughout the ventricles. This orderly pattern of depolarization gives rise to the characteristic ECG tracing. To the trained clinician, an ECG conveys a large amount of information about the structure of the heart and the function of its electrical conduction system. Among other things, an ECG can be used to measure the rate and rhythm of heartbeats, the size and position of the heart chambers, the presence of any damage to the heart's muscle cells or conduction system, the effects of cardiac drugs, and the function of implanted pacemakers.