(a) From , 2013 General Chemistry I
... U is a state function: a property that depends only on the current state of the system and is independent of how that state was prepared. ...
... U is a state function: a property that depends only on the current state of the system and is independent of how that state was prepared. ...
Two electrons in a cylindrical quantum dot under constant magnetic
... numbers (M,s), which form separate infinite-dimensional subspaces within the Hilbert space of the problem. The accuracy of results obtained through linear variational analysis for each such case, depends on how well the basis set span over the subspace of interest. Though the lower energy states are ...
... numbers (M,s), which form separate infinite-dimensional subspaces within the Hilbert space of the problem. The accuracy of results obtained through linear variational analysis for each such case, depends on how well the basis set span over the subspace of interest. Though the lower energy states are ...
Subject Area Assessment Guides
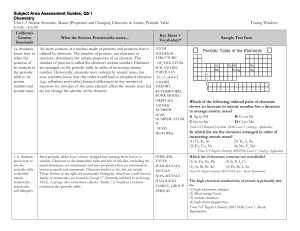
... element from Group 2 will most often combine with two atoms of an element from Group 17 (e.g., MgCl2) because Group 2 elements have two electrons available for bonding, and Group 17 elements have only one electron position open in the outermost energy level. (Note that some periodic tables indicate ...
... element from Group 2 will most often combine with two atoms of an element from Group 17 (e.g., MgCl2) because Group 2 elements have two electrons available for bonding, and Group 17 elements have only one electron position open in the outermost energy level. (Note that some periodic tables indicate ...
Chemistry I Exams and Answer Keys 2015 Season
... As we proceed from left to right in period 3 of the Periodic Table of the elements, we note a decrease in the atomic radius. Which statement correctly explains this phenomenon? A. The number of valence electrons increases, causing an increased attraction between the nucleus and valence electrons. B. ...
... As we proceed from left to right in period 3 of the Periodic Table of the elements, we note a decrease in the atomic radius. Which statement correctly explains this phenomenon? A. The number of valence electrons increases, causing an increased attraction between the nucleus and valence electrons. B. ...
2002 Final Exam for Practice - Department of Chemistry | Oregon
... 3. Consider the following operation (23.500 cm)(1.1 cm) = ? Which answer below contains the correct number of significant figures? a. 30 cm2 b. 26 cm2 c. 25.9 cm2 d. 25.85 cm2 e. 25.850 cm2 4. Which of the following chemical formulas is correct? a. NaO2 b. AlO2 c. CaO2 d. AlS e. CaO 5. Determine the ...
... 3. Consider the following operation (23.500 cm)(1.1 cm) = ? Which answer below contains the correct number of significant figures? a. 30 cm2 b. 26 cm2 c. 25.9 cm2 d. 25.85 cm2 e. 25.850 cm2 4. Which of the following chemical formulas is correct? a. NaO2 b. AlO2 c. CaO2 d. AlS e. CaO 5. Determine the ...
Syllabus
... What is Chemistry ? Chemistry is the study of how matter and energy behave. It is also a scientific method for observing the world and all of life. Knowledge of chemistry is used to make new discoveries about the world (research) and to change some aspects of the world by the invention of new materi ...
... What is Chemistry ? Chemistry is the study of how matter and energy behave. It is also a scientific method for observing the world and all of life. Knowledge of chemistry is used to make new discoveries about the world (research) and to change some aspects of the world by the invention of new materi ...
Computational Study of protonation of ozone
... by recycling. When this was done the technical and economic assessment of energy costs on the disposal. Was shown the economic feasibility of the use of technological methods of separation of aromatic hydrocarbons contained in the effluent from the subsequent use of ozonation technology for final cl ...
... by recycling. When this was done the technical and economic assessment of energy costs on the disposal. Was shown the economic feasibility of the use of technological methods of separation of aromatic hydrocarbons contained in the effluent from the subsequent use of ozonation technology for final cl ...
Problem 1: “A brief history” of life in the universe
... chemical reactions involving atoms and molecules. It is only natural then to ask where atoms came from. According to a widely accepted model, the universe began about 15 billion years ago in a big bang and has been expanding ever since. The history of the universe as a whole can be viewed in terms o ...
... chemical reactions involving atoms and molecules. It is only natural then to ask where atoms came from. According to a widely accepted model, the universe began about 15 billion years ago in a big bang and has been expanding ever since. The history of the universe as a whole can be viewed in terms o ...
Review # 3
... A gas at STP which contains 6.02 x 1023 atoms and forms diatomic molecules will occupy a. 11.2 L b. 22.4 L c. 33.6 L d. 67.2 L ...
... A gas at STP which contains 6.02 x 1023 atoms and forms diatomic molecules will occupy a. 11.2 L b. 22.4 L c. 33.6 L d. 67.2 L ...
My English expressions for technical paper writing 1 ~be based on
... As a solution to this issue and following work by (Pratt et al., 2004), we created another control paradigm at the single-joint level that we dubbed \impedance control mode", which allowed the position and velocity feedback to occur locally on the single-joint ...
... As a solution to this issue and following work by (Pratt et al., 2004), we created another control paradigm at the single-joint level that we dubbed \impedance control mode", which allowed the position and velocity feedback to occur locally on the single-joint ...
Problem 1: “A brief history” of life in the universe
... The chemical composition of the atmosphere of a planet depends on the temperature of the planet’s atmosphere (which in turn depends on the distance from the sun, internal temperature, etc.), tectonic activity, and the existence of life. As the sun generated heat, light, and solar wind through nuclea ...
... The chemical composition of the atmosphere of a planet depends on the temperature of the planet’s atmosphere (which in turn depends on the distance from the sun, internal temperature, etc.), tectonic activity, and the existence of life. As the sun generated heat, light, and solar wind through nuclea ...
Problem 1: A brief history of life in the universe
... The chemical composition of the atmosphere of a planet depends on the temperature of the planet’s atmosphere (which in turn depends on the distance from the sun, internal temperature, etc.), tectonic activity, and the existence of life. As the sun generated heat, light, and solar wind through nuclea ...
... The chemical composition of the atmosphere of a planet depends on the temperature of the planet’s atmosphere (which in turn depends on the distance from the sun, internal temperature, etc.), tectonic activity, and the existence of life. As the sun generated heat, light, and solar wind through nuclea ...
Marsden, Jerrold E. (1-CA)
... 15. E. Marsden and T. J. R. Hughes [1983], Mathematical foundations of elasticity, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, N.J. 16. E. Marsden and A. Weinstein [1974], Reduction of symplectic manifolds with symmetry, Rep. Math. Phys. 5, 121-130. MR0402819 (53 #6633) 17. E. Marsden and A. Weinstein [1974] [ ...
... 15. E. Marsden and T. J. R. Hughes [1983], Mathematical foundations of elasticity, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, N.J. 16. E. Marsden and A. Weinstein [1974], Reduction of symplectic manifolds with symmetry, Rep. Math. Phys. 5, 121-130. MR0402819 (53 #6633) 17. E. Marsden and A. Weinstein [1974] [ ...
physical setting chemistry
... Record the number of your choice for each Part A and Part B–1 multiple-choice question on your separate answer sheet. Write your answers to the Part B–2 and Part C questions in your answer booklet. All work should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, which should be done in pencil. You ...
... Record the number of your choice for each Part A and Part B–1 multiple-choice question on your separate answer sheet. Write your answers to the Part B–2 and Part C questions in your answer booklet. All work should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, which should be done in pencil. You ...
hit and lead generation: beyond high-throughput screening
... prioritization of series with the best development potential. In this regard, it is important that at least two lead series of significantly different pharmacological and/or structural profile are advanced as reserve, or ‘back-up’, lead series. This insures against unexpected failures due to unpredi ...
... prioritization of series with the best development potential. In this regard, it is important that at least two lead series of significantly different pharmacological and/or structural profile are advanced as reserve, or ‘back-up’, lead series. This insures against unexpected failures due to unpredi ...
Computational Aspects of Incrementally Objective Algorithms for
... Each of the three strategies has certain advantages and disadvantages. The first strategy advocating “consistent linearization at any cost” has the advantage of maintaining quadratic asymptotic rate of convergence while advancing solution in large increments. On the negative side, the cost of stress ...
... Each of the three strategies has certain advantages and disadvantages. The first strategy advocating “consistent linearization at any cost” has the advantage of maintaining quadratic asymptotic rate of convergence while advancing solution in large increments. On the negative side, the cost of stress ...
Chapter 8 - profpaz.com
... Consequently, unless there are more ingredients, only 15 pancakes can be made from the combination of the above ingredients. This is due to the flour being completely used up after making 15 pancakes. ...
... Consequently, unless there are more ingredients, only 15 pancakes can be made from the combination of the above ingredients. This is due to the flour being completely used up after making 15 pancakes. ...
9/10/10 1 Chemistry 121: Atomic and Molecular Chemistry
... • ie., analyze samples of carbon dioxide gas different sources, find the same ratio by mass of carbon to oxygen. The law of multiple proportions: Two (or more) elements can combine to form more than one compound. Different compounds made up of the same elements differ in the number of atoms of each ...
... • ie., analyze samples of carbon dioxide gas different sources, find the same ratio by mass of carbon to oxygen. The law of multiple proportions: Two (or more) elements can combine to form more than one compound. Different compounds made up of the same elements differ in the number of atoms of each ...
Hydrogen Bonding
... the Earth, ability to dissolve many other substances, serves as a medium in which a great variety of chemical changes occur Hydrogen Bonding – Caused by the polar nature of covalent H—O bonds that hold together water molecules Hydrogen atoms of water molecules are attracted to the unshared electro ...
... the Earth, ability to dissolve many other substances, serves as a medium in which a great variety of chemical changes occur Hydrogen Bonding – Caused by the polar nature of covalent H—O bonds that hold together water molecules Hydrogen atoms of water molecules are attracted to the unshared electro ...