Sources of microorganisms in food.
... • Many ingredients can be a source of both spoilage and pathogenic microorganisms • various spices can possess very high populations of mold and bacterial spores. ...
... • Many ingredients can be a source of both spoilage and pathogenic microorganisms • various spices can possess very high populations of mold and bacterial spores. ...
Objective: You will be able to identify all of the glands of the
... • Read all of p. 591 • How are the functions of LH and FSH different in males and females? ...
... • Read all of p. 591 • How are the functions of LH and FSH different in males and females? ...
Phosphorus cycle
... erode, small amounts of phosphorus dissolve as phosphate in soil and water -plants absorb phosphates in the soil through ...
... erode, small amounts of phosphorus dissolve as phosphate in soil and water -plants absorb phosphates in the soil through ...
Spore Forming and Non-Spore Forming Gram
... Classification Definition = a resting cell, highly resistant to dessication, heat, and chemical agents; when returned to favourable conditions bacteria re-activated, the spores germinate to produce single vegetative cells. ...
... Classification Definition = a resting cell, highly resistant to dessication, heat, and chemical agents; when returned to favourable conditions bacteria re-activated, the spores germinate to produce single vegetative cells. ...
65KB - NZQA
... Micro-organisms need water to reproduce, milk contains water and needs to be stored in the fridge / at a low temperature to limit bacterial reproduction. Powder does not need to be stored in the fridge/at a low temperature as bacterial growth is already limited by a lack of water. OR Milk powder ...
... Micro-organisms need water to reproduce, milk contains water and needs to be stored in the fridge / at a low temperature to limit bacterial reproduction. Powder does not need to be stored in the fridge/at a low temperature as bacterial growth is already limited by a lack of water. OR Milk powder ...
OBJECTIVE: -
... place. There are many reasons responsible for bare area formation like landslides, soil erosion, flooding, long and continuous drought, volcanic eruption, deposition, fire and diseases. During invasion, plants and animals from surrounding areas reach the bare area, establish there and aggregate by t ...
... place. There are many reasons responsible for bare area formation like landslides, soil erosion, flooding, long and continuous drought, volcanic eruption, deposition, fire and diseases. During invasion, plants and animals from surrounding areas reach the bare area, establish there and aggregate by t ...
Why is ecology important?
... (1) the circumstances or conditions that surround an organism or group of organisms, or (2) the complex of social or cultural conditions that affect an individual or community ...
... (1) the circumstances or conditions that surround an organism or group of organisms, or (2) the complex of social or cultural conditions that affect an individual or community ...
A1981LC33200001
... The RGCA medium contained .2 percent each of glucose and cellobiose which resulted in very large colony formation and spreading such that enumeration and isolation of strains were more difficult, especially if incubations were extended beyond the minimal three days (39°C) and starch or maltose requi ...
... The RGCA medium contained .2 percent each of glucose and cellobiose which resulted in very large colony formation and spreading such that enumeration and isolation of strains were more difficult, especially if incubations were extended beyond the minimal three days (39°C) and starch or maltose requi ...
age of the mammoth - Lorain County Metro Parks
... 12. Explain ways in which humans have had a major effect on other species (e.g., the influence of humans on other organisms occurs through land use, which decreases space available to other species and pollution, which changes the chemical composition of air, soil and water). Life Sciences Benchmar ...
... 12. Explain ways in which humans have had a major effect on other species (e.g., the influence of humans on other organisms occurs through land use, which decreases space available to other species and pollution, which changes the chemical composition of air, soil and water). Life Sciences Benchmar ...
Ecology Introduction 1. Ecology
... few sample ploys of 1 km2 each. The larger the number and size of sample plots, the more accurate the estimates. In some cases, population densities are estimated not by counts of organisms but by indirect indicators, such as number of bird nests or rodent burrows. Within a population’s geographic r ...
... few sample ploys of 1 km2 each. The larger the number and size of sample plots, the more accurate the estimates. In some cases, population densities are estimated not by counts of organisms but by indirect indicators, such as number of bird nests or rodent burrows. Within a population’s geographic r ...
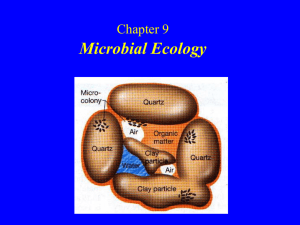
Microbial Ecology 微生物生态学
... • Methods used to study microbial interaction and microbial ecology provide information on environmental characteristics; microbial biomass. Numbers, types and activity, and community structure. Microscopic, chemical, enzymatic and molecular techniques are used in these studies. ...
... • Methods used to study microbial interaction and microbial ecology provide information on environmental characteristics; microbial biomass. Numbers, types and activity, and community structure. Microscopic, chemical, enzymatic and molecular techniques are used in these studies. ...
INTERVET/SCHERING-PLOUGH ANIMAL HEALTH OTOMAX
... Gentamicin: Gentamicin sulfate is an aminoglycoside antibiotic active against a wide variety of pathogenic gram-negative an bacteria. In vitro tests have determined that gentamicin is bactericidal and acts by inhibiting normal protein synthesis in susce Specifically, gentamicin is active against the ...
... Gentamicin: Gentamicin sulfate is an aminoglycoside antibiotic active against a wide variety of pathogenic gram-negative an bacteria. In vitro tests have determined that gentamicin is bactericidal and acts by inhibiting normal protein synthesis in susce Specifically, gentamicin is active against the ...
Chapter 11 packet
... The steps to succession in water are 1. Smaller organisms die and fill the bottom of the water bed. 2. These bodies build up and make the lake shallow. 3. __________________________________________ 4. The pond becomes a marsh 5. ___________________________________________ ...
... The steps to succession in water are 1. Smaller organisms die and fill the bottom of the water bed. 2. These bodies build up and make the lake shallow. 3. __________________________________________ 4. The pond becomes a marsh 5. ___________________________________________ ...
MSDS - Dudley Chemical Corporation
... Canada - DSL/NDSL CAS# 10101-41-4 is not listed on Canada’s DSL List. Canada – WHMIS: Not available. This product has been classified in accordance with the hazard criteria of the Controlled Products Regulations and the MSDS contains all of the information required by those regulations. CAS# 10101-4 ...
... Canada - DSL/NDSL CAS# 10101-41-4 is not listed on Canada’s DSL List. Canada – WHMIS: Not available. This product has been classified in accordance with the hazard criteria of the Controlled Products Regulations and the MSDS contains all of the information required by those regulations. CAS# 10101-4 ...
Document
... especially important in the medical community to determine the cause of disease and effectively treat patients. To identify unknown bacteria, Microbiologists use a diverse collection of tests including stains, biochemical tests, and selective and differential media. In general, the identification be ...
... especially important in the medical community to determine the cause of disease and effectively treat patients. To identify unknown bacteria, Microbiologists use a diverse collection of tests including stains, biochemical tests, and selective and differential media. In general, the identification be ...
ECOSYSTEMS AND BIODIVERSITY
... A forest is an area with a high density of trees. World’s total land area is 13,076 million hectares - (Source: FAO; 1989) Of which total forests account for about 31% of the world’s land area. In India, the forest cover is roughly 19% of the total land area. The forest ecosystems are of g ...
... A forest is an area with a high density of trees. World’s total land area is 13,076 million hectares - (Source: FAO; 1989) Of which total forests account for about 31% of the world’s land area. In India, the forest cover is roughly 19% of the total land area. The forest ecosystems are of g ...
Fig. 1. Common shapes of bacteria Fig. 2: Different arrangements of
... Table 1: Differences between cell wall of Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria. ...
... Table 1: Differences between cell wall of Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria. ...
Nitrogen cycle review - North Penn School District
... a. A wetland ecosystem (grassland) with invasive species of plant such as Purple Loosestrife. Other aquatic plants would have to compete with the invasive for sunlight, and habitat. Species that rely on native aquatic plants for food may not be able to survive by eating the purple loosestrife. The p ...
... a. A wetland ecosystem (grassland) with invasive species of plant such as Purple Loosestrife. Other aquatic plants would have to compete with the invasive for sunlight, and habitat. Species that rely on native aquatic plants for food may not be able to survive by eating the purple loosestrife. The p ...
Ecology Review Answers
... large herbivores population will boom, and they in turn will eat up the producers, which will affect the smaller herbivores that rely on the producers. Ultimately, all the organisms in the food web will be affected and the populations will shift dramatically. The lack of a top predator leads to an u ...
... large herbivores population will boom, and they in turn will eat up the producers, which will affect the smaller herbivores that rely on the producers. Ultimately, all the organisms in the food web will be affected and the populations will shift dramatically. The lack of a top predator leads to an u ...
MARINE BIOACTIVE COMPOUNDS
... from the extracts of marine organisms. • Many of them have novel chemical structures which may lead to the development of entirely new drugs and therapeutic agents. • Anti-cancer agents have been isolated from algae, sponges, jellyfish, corals, shark cartilage and shellfish. • The Pacific oyster con ...
... from the extracts of marine organisms. • Many of them have novel chemical structures which may lead to the development of entirely new drugs and therapeutic agents. • Anti-cancer agents have been isolated from algae, sponges, jellyfish, corals, shark cartilage and shellfish. • The Pacific oyster con ...
printer-friendly version
... increased solar energy. This results in air masses that expand creating low pressure systems. As the air mass rises, it cools, and it loses its moisture. These air masses then move away from the poles, cool, condense, and sink creating a high pressure system. The increased air pressure and dryness c ...
... increased solar energy. This results in air masses that expand creating low pressure systems. As the air mass rises, it cools, and it loses its moisture. These air masses then move away from the poles, cool, condense, and sink creating a high pressure system. The increased air pressure and dryness c ...
2.4 Bacteria - gooyers3cbiology
... After division, many bacteria stay together in groups or clusters rather than remain as individual cells. Cocci (singular: coccus), bacilli (singular: bacillus), and sometimes spirilla (singular: spirillum), form pairs, cluster colonies, or chains (filaments) of cells. For example, Streptococcus mut ...
... After division, many bacteria stay together in groups or clusters rather than remain as individual cells. Cocci (singular: coccus), bacilli (singular: bacillus), and sometimes spirilla (singular: spirillum), form pairs, cluster colonies, or chains (filaments) of cells. For example, Streptococcus mut ...
Triclocarban

Triclocarban is an antibacterial agent common in personal care products like soaps and lotions as well as in the medical field, for which it was originally developed. Studies on its antibacterial qualities and mechanisms are growing. Research suggests that it is similar in its mechanism to triclosan and is effective in fighting infections by targeting the growth of bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus. Additional research seeks to understand its potential for causing antibacterial resistance and its effects on organismal and environmental health.