
The Endocrine System
... united by the isthmus. Average size of each lobe is 4cm long and 2cm across but these sizes may vary considerably. The secretion of this gland is thyroxine and tri-iodothyronine. Thyroxine controls the general metabolism. Both hormones contain iodine but thyronine is more active than thyroxin. Under ...
... united by the isthmus. Average size of each lobe is 4cm long and 2cm across but these sizes may vary considerably. The secretion of this gland is thyroxine and tri-iodothyronine. Thyroxine controls the general metabolism. Both hormones contain iodine but thyronine is more active than thyroxin. Under ...
Lymphatic System
... Diabetes Mellitus Type two • results when the pancreas produces insulin, but not enough to meet the needs of the body. This type of diabetes is linked with obesity and is most common in adults over the age of 45. Treatment may involve oral medication, exercise, weight loss, and insulin injections. ...
... Diabetes Mellitus Type two • results when the pancreas produces insulin, but not enough to meet the needs of the body. This type of diabetes is linked with obesity and is most common in adults over the age of 45. Treatment may involve oral medication, exercise, weight loss, and insulin injections. ...
comp3_unit7_audio_transcript
... Hormones are natural chemicals produced and released by the endocrine glands. Hormones are thought of as our body’s chemical messengers. The eight endocrine glands secrete hormones into our bloodstream. In the bloodstream these chemical messengers go to various organs and tissues to generate a spec ...
... Hormones are natural chemicals produced and released by the endocrine glands. Hormones are thought of as our body’s chemical messengers. The eight endocrine glands secrete hormones into our bloodstream. In the bloodstream these chemical messengers go to various organs and tissues to generate a spec ...
The Endocrine System Chapter 10
... slower response (minutes to hours) potentially long duration of effects (hours to days) works via chemical signals (“hormones”) which are released through interstitial fluid into blood capillaries affects multiple cells throughout the body that have specific hormone receptors (“target cells” ...
... slower response (minutes to hours) potentially long duration of effects (hours to days) works via chemical signals (“hormones”) which are released through interstitial fluid into blood capillaries affects multiple cells throughout the body that have specific hormone receptors (“target cells” ...
Endocrine System
... The thyroid is in the front part of the lower neck, and is shaped like a butterfly. It produces the hormones known as thyroxine and triiodothyronine. These control the rate at which cells burn fuels from food to produce energy. Thyroid hormones are important because they participate in the growth an ...
... The thyroid is in the front part of the lower neck, and is shaped like a butterfly. It produces the hormones known as thyroxine and triiodothyronine. These control the rate at which cells burn fuels from food to produce energy. Thyroid hormones are important because they participate in the growth an ...
1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3Receptors in Human
... D and calcium intake to be inversely correlated with the risk of 1,25-Dihydroxy vitamin Dj |1,25-(OH)2D.,| receptor concentration was colorectal cancer (12). In a study of primary carcinoma of the measured by an accurate immunoradiometric assay in primary tumors breast, VDR-positive tumors were foun ...
... D and calcium intake to be inversely correlated with the risk of 1,25-Dihydroxy vitamin Dj |1,25-(OH)2D.,| receptor concentration was colorectal cancer (12). In a study of primary carcinoma of the measured by an accurate immunoradiometric assay in primary tumors breast, VDR-positive tumors were foun ...
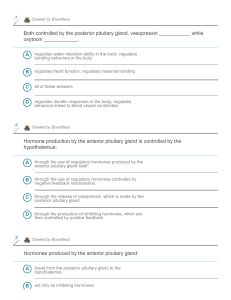
Both controlled by the posterior pituitary gland, vasopressin ______
... The adrenal medulla produces cortisol and corticosterone hormones. ...
... The adrenal medulla produces cortisol and corticosterone hormones. ...
Chapter 11
... What else can trigger their release? Name some Gluccocorticoids. Which zone secretes these hormones? sex hormones: Sex hormones, produced in the _________________zone, are mostly of the ___________ type but can be converted to ________________ hormones in the skin, liver, and adipose tissues. b. The ...
... What else can trigger their release? Name some Gluccocorticoids. Which zone secretes these hormones? sex hormones: Sex hormones, produced in the _________________zone, are mostly of the ___________ type but can be converted to ________________ hormones in the skin, liver, and adipose tissues. b. The ...
endocrine
... • Act on receptors in the plasma membrane • Amino acid–based hormones – e.g., epinephrine- binds to smooth muscle cells in blood vessels - causing contraction ...
... • Act on receptors in the plasma membrane • Amino acid–based hormones – e.g., epinephrine- binds to smooth muscle cells in blood vessels - causing contraction ...
chapt14-endocrine system
... Addison disease develops when the adrenal cortex is under active, and Cushing syndrome develops when the adrenal cortex is overactive. ...
... Addison disease develops when the adrenal cortex is under active, and Cushing syndrome develops when the adrenal cortex is overactive. ...
PMHS
... – The endocrine system works in parallel with the nervous system to control _____________________. Two major categories of glands in the body • Exocrine – Exocrine glands have ________________that carry their secretory product to a surface • Endocrine – The endocrine glands do ______________________ ...
... – The endocrine system works in parallel with the nervous system to control _____________________. Two major categories of glands in the body • Exocrine – Exocrine glands have ________________that carry their secretory product to a surface • Endocrine – The endocrine glands do ______________________ ...
Lecture_36_2014_noquiz
... Most are carnivorous; have a large mouth or long tongue for catching prey; short gut specialized for digesting proteins ...
... Most are carnivorous; have a large mouth or long tongue for catching prey; short gut specialized for digesting proteins ...
Chapter 9 Outline
... processes, and blood chemistry. Through the use of hormones, the endocrine system maintains balance within the body in a relatively leisurely and profound way. Hormones circulate in the blood until reaching the target organs upon which they are designed to act, bind with the awaiting cells, and imme ...
... processes, and blood chemistry. Through the use of hormones, the endocrine system maintains balance within the body in a relatively leisurely and profound way. Hormones circulate in the blood until reaching the target organs upon which they are designed to act, bind with the awaiting cells, and imme ...
The Endocrine System
... Langerhans; endocrine cells within the pancreas that secrete 2 hormones essential for maintaining blood sugar levels: • Insulin –stimulates the liver to remove glucose from the blood and convert it into glycogen for storage, thus lowering blood sugar levels • Glucagon – stimulates the liver to conve ...
... Langerhans; endocrine cells within the pancreas that secrete 2 hormones essential for maintaining blood sugar levels: • Insulin –stimulates the liver to remove glucose from the blood and convert it into glycogen for storage, thus lowering blood sugar levels • Glucagon – stimulates the liver to conve ...
x biology unit test 3
... 5.Blinking when a beam of light is suddenly focussed on the eyes and sudden withdrawal of hand upon touching a hot body are some of the examples of reflex actions. Which part of the central nervous system acts as the centre these actions? i) Forebrain ii) Spinal cord iii) Hindbrain iv) Synapse II. W ...
... 5.Blinking when a beam of light is suddenly focussed on the eyes and sudden withdrawal of hand upon touching a hot body are some of the examples of reflex actions. Which part of the central nervous system acts as the centre these actions? i) Forebrain ii) Spinal cord iii) Hindbrain iv) Synapse II. W ...
Chapter 45
... The Body’s Long-Distance Regulators • Animal __________ are chemical signals that are secreted into the circulatory system and communicate regulatory messages within the body. • Hormones mediate responses to environmental stimuli and regulate growth, development, and reproduction. • Stimuli can inc ...
... The Body’s Long-Distance Regulators • Animal __________ are chemical signals that are secreted into the circulatory system and communicate regulatory messages within the body. • Hormones mediate responses to environmental stimuli and regulate growth, development, and reproduction. • Stimuli can inc ...
PowerPoint to accompany
... • The pineal gland (epiphysis cerebri) is attached to the roof of the third ventricle, inside the brain (Figure 18.1). • Histologically, it consists of secretory parenchymal cells called pinealocytes, neuroglia cells, and scattered postganglionic sympathetic fibers. The pineal secrets melatonin in a ...
... • The pineal gland (epiphysis cerebri) is attached to the roof of the third ventricle, inside the brain (Figure 18.1). • Histologically, it consists of secretory parenchymal cells called pinealocytes, neuroglia cells, and scattered postganglionic sympathetic fibers. The pineal secrets melatonin in a ...
How do they work? Intercellular Communication Endocrine Signaling
... Same receptors but different intracellular proteins (not shown) ...
... Same receptors but different intracellular proteins (not shown) ...
Endocrine System
... Endocrine System A. Endocrine System: Overview 1. Endocrine system: Body's 2nd great control system; influences cellular metabolism via hormones 2. Endocrine glands: Pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pineal, and thymus 3. Pancreas & Gonads produce hormones and exocrine products 4. Hypothalam ...
... Endocrine System A. Endocrine System: Overview 1. Endocrine system: Body's 2nd great control system; influences cellular metabolism via hormones 2. Endocrine glands: Pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pineal, and thymus 3. Pancreas & Gonads produce hormones and exocrine products 4. Hypothalam ...
Principle of Endocrine & Metabolic Diseases
... Suppression test:on hyperfunction disease. eg. dexmethasone suppression test on Cushing syndrome. ...
... Suppression test:on hyperfunction disease. eg. dexmethasone suppression test on Cushing syndrome. ...
The Endocrine System
... Langerhans; endocrine cells within the pancreas that secrete 2 hormones essential for maintaining blood sugar levels: • Insulin –stimulates the liver to remove glucose from the blood and convert it into glycogen for storage, thus lowering blood sugar levels • Glucagon – stimulates the liver to conve ...
... Langerhans; endocrine cells within the pancreas that secrete 2 hormones essential for maintaining blood sugar levels: • Insulin –stimulates the liver to remove glucose from the blood and convert it into glycogen for storage, thus lowering blood sugar levels • Glucagon – stimulates the liver to conve ...
c42[1] - MizFamous21
... Hormones, endocrine glands, target cells, and target cell receptors. ---most endocrine glands/tissues contain neurosecretory cells that secrete hormones --hormone is chemical signal that communicates regulatory messages within body ---hormones may reach all parts of body, but only certain types of c ...
... Hormones, endocrine glands, target cells, and target cell receptors. ---most endocrine glands/tissues contain neurosecretory cells that secrete hormones --hormone is chemical signal that communicates regulatory messages within body ---hormones may reach all parts of body, but only certain types of c ...
The Endocrine System
... • It lies just below the hypothalamus in the middle of the brain. • It secretes hormones that include human growth hormone, prolactin, and oxytocin. • Some pituitary hormones stimulate other endocrine glands such as the adrenals, thyroid, and ovaries or testes. ...
... • It lies just below the hypothalamus in the middle of the brain. • It secretes hormones that include human growth hormone, prolactin, and oxytocin. • Some pituitary hormones stimulate other endocrine glands such as the adrenals, thyroid, and ovaries or testes. ...
Neuroendocrine tumor

Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are neoplasms that arise from cells of the endocrine (hormonal) and nervous systems. Many are benign, while some are malignant. They most commonly occur in the intestine, where they are often called carcinoid tumors, but they are also found in the pancreas, lung and the rest of the body.Although there are many kinds of NETs, they are treated as a group of tissue because the cells of these neoplasms share common features, such as looking similar, having special secretory granules, and often producing biogenic amines and polypeptide hormones.

















![c42[1] - MizFamous21](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010068630_1-2a5207be9f057bdfa8789626bb26f24e-300x300.png)

