No Slide Title
... • Growth hormone antagonists – Growth hormone analog with one binding site mutated – Dominant negative activity – Disadvantages: • GH levels not suppressed • Difficult to monitor • Effect on tumor unknown – May actually stimulate tumor growth ...
... • Growth hormone antagonists – Growth hormone analog with one binding site mutated – Dominant negative activity – Disadvantages: • GH levels not suppressed • Difficult to monitor • Effect on tumor unknown – May actually stimulate tumor growth ...
Hormones and the Endocrine System
... the embryo. Within the larval caterpillar, they are nourished as islands of tissues that will eventually become the eyes, wings, brain, and other structures of the butterfly. Once the plump, crawling caterpillar becomes a stationary pupa, the adult cells take over. They complete their program of deve ...
... the embryo. Within the larval caterpillar, they are nourished as islands of tissues that will eventually become the eyes, wings, brain, and other structures of the butterfly. Once the plump, crawling caterpillar becomes a stationary pupa, the adult cells take over. They complete their program of deve ...
Endocrine Pathology
... Papillary carcinoma This is another papillary carcinoma of thyroid. Note the small psammoma body in the center. The cells of the neoplasm have clear nuclei. Papillary carcinomas are indolent tumors that have a long survival, even with metastases. The most favorite site of metastasis is to local lym ...
... Papillary carcinoma This is another papillary carcinoma of thyroid. Note the small psammoma body in the center. The cells of the neoplasm have clear nuclei. Papillary carcinomas are indolent tumors that have a long survival, even with metastases. The most favorite site of metastasis is to local lym ...
Agenesis of isthmus of thyroid gland with bilateral levator glandulae
... Thyroid gland is the first endocrine gland to start developing in the embryo. It is well known for its developmental anomalies ranging from common to rare. Common anomalies include persistence of pyramidal lobe and thyroglossal duct cyst. Rare anomalies are agenesis or hemi-agenesis of thyroid gland ...
... Thyroid gland is the first endocrine gland to start developing in the embryo. It is well known for its developmental anomalies ranging from common to rare. Common anomalies include persistence of pyramidal lobe and thyroglossal duct cyst. Rare anomalies are agenesis or hemi-agenesis of thyroid gland ...
The Endocrine System
... (each 9 amino acids long) • Small proteins • Growth hormone (GH; 191 amino acids) and prolactin (PRL; 198 amino acids) • Includes all hormones secreted by: • Hypothalamus, heart, thymus, digestive tract, pancreas, and posterior lobe of the pituitary gland, as well as several hormones produced in oth ...
... (each 9 amino acids long) • Small proteins • Growth hormone (GH; 191 amino acids) and prolactin (PRL; 198 amino acids) • Includes all hormones secreted by: • Hypothalamus, heart, thymus, digestive tract, pancreas, and posterior lobe of the pituitary gland, as well as several hormones produced in oth ...
Hormones and the Endocrine System
... caterpillar becomes a stationary pupa, the adult cells take over. They complete their program of development, while many larval tissues undergo programmed cell death. The end result is a butterfly, a delicate, free-flying adult that bears little resemblance to the larval and pupal forms from which i ...
... caterpillar becomes a stationary pupa, the adult cells take over. They complete their program of development, while many larval tissues undergo programmed cell death. The end result is a butterfly, a delicate, free-flying adult that bears little resemblance to the larval and pupal forms from which i ...
Human Physiology
... Human Physiology Endocrine System, Neurohormones • Hypothalamus and Anterior Pituitary ▫ The hypothalamus also secretes hormones that control the secretion of ALL the anterior pituitary hormones. The basic pattern is as follows: Secretion of a hypothalamic hormone, which controls secretion of A ...
... Human Physiology Endocrine System, Neurohormones • Hypothalamus and Anterior Pituitary ▫ The hypothalamus also secretes hormones that control the secretion of ALL the anterior pituitary hormones. The basic pattern is as follows: Secretion of a hypothalamic hormone, which controls secretion of A ...
Endocrine Test - The Science of Payne
... 22. Glands that release their secretion into ducts leading to a body surface are called _______________. 23. The central portion of the adrenal gland is the adrenal ____________. 24. A group of lipids called __________ have powerful, regulating effects on a variety of tissues. 25. The hormone that s ...
... 22. Glands that release their secretion into ducts leading to a body surface are called _______________. 23. The central portion of the adrenal gland is the adrenal ____________. 24. A group of lipids called __________ have powerful, regulating effects on a variety of tissues. 25. The hormone that s ...
Endocrine system Lesson: Endocrine system Lesson Developer
... Figure 1: Types of chemical communication between cells. Source: ILLL in house In some tissues, a type of localized chemical communication between cells occurs through the chemical messenger, which is not transported any distance in blood but acts in a highly circumscribed area. These secretory cell ...
... Figure 1: Types of chemical communication between cells. Source: ILLL in house In some tissues, a type of localized chemical communication between cells occurs through the chemical messenger, which is not transported any distance in blood but acts in a highly circumscribed area. These secretory cell ...
1 Part Ten: Thyroid / Parathyroid Chapter 133: Anatomy Daniel O
... original intent and the most effective technique of preventing recurrence of thyroglossal duct cysts (Deane and Telander, 1978). Development of the Parafollicular Cells In addition to the principal cells of the thyroid gland, which form the thyroid follicles and produce thyroglobulin, there is a se ...
... original intent and the most effective technique of preventing recurrence of thyroglossal duct cysts (Deane and Telander, 1978). Development of the Parafollicular Cells In addition to the principal cells of the thyroid gland, which form the thyroid follicles and produce thyroglobulin, there is a se ...
Gl Glands, Hormones Diabetes
... prolactin (released when female is suckled during lactation) and growth hormones. It also produces other hormones that control the adrenal and thyroid glands. The thyroid gland is located on the front of the trachea in the neck just below the Adam’s apple. It releases the hormone thyroxine which con ...
... prolactin (released when female is suckled during lactation) and growth hormones. It also produces other hormones that control the adrenal and thyroid glands. The thyroid gland is located on the front of the trachea in the neck just below the Adam’s apple. It releases the hormone thyroxine which con ...
The Endocrine System
... Lesson 8.1: Functions and Control of the Endocrine System Lesson 8.2: Major Endocrine Organs Lesson 8.3: Endocrine Disorders and ...
... Lesson 8.1: Functions and Control of the Endocrine System Lesson 8.2: Major Endocrine Organs Lesson 8.3: Endocrine Disorders and ...
Endocrine System
... 2. Most of the receptors are bound to the cell membrane but it can be intracellular receptor. E. g. of intracellular receptor hormone:- Steroid hormone , Thyroid hormone , Vit. D 3. Combine with high affinity with the hormone concentrate the hormone in the cell (This is one of the ways to detect h ...
... 2. Most of the receptors are bound to the cell membrane but it can be intracellular receptor. E. g. of intracellular receptor hormone:- Steroid hormone , Thyroid hormone , Vit. D 3. Combine with high affinity with the hormone concentrate the hormone in the cell (This is one of the ways to detect h ...
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... Steroid Hormones ~ from cholesterol Gonadal hormones ~ estrogen, testosterone Adrenalcorticoids hormones ~ corticosteroids Eicosanoids (eye cos an oids) Increase inflammation & cause swelling NON-CIRCULATING hormones ~ act locally only Released from most cell membranes & have a highly localized resp ...
... Steroid Hormones ~ from cholesterol Gonadal hormones ~ estrogen, testosterone Adrenalcorticoids hormones ~ corticosteroids Eicosanoids (eye cos an oids) Increase inflammation & cause swelling NON-CIRCULATING hormones ~ act locally only Released from most cell membranes & have a highly localized resp ...
Endocrine System
... Growth hormone (GH) stimulates body cells to grow and reproduce; it also speeds the rate at which cells use carbohydrates and fats. a. ...
... Growth hormone (GH) stimulates body cells to grow and reproduce; it also speeds the rate at which cells use carbohydrates and fats. a. ...
Endocrine System
... Growth hormone (GH) stimulates body cells to grow and reproduce; it also speeds the rate at which cells use carbohydrates and fats. a. ...
... Growth hormone (GH) stimulates body cells to grow and reproduce; it also speeds the rate at which cells use carbohydrates and fats. a. ...
HMC Pulse
... – The Hypothalamus produces hormones that: – Are released by the posterior pituitary – Raise or lower production of anterior pituitary hormones – The pituitary gland: – Produces hormones that regulate other endocrine glands in the body – Each of these hormones has a feedback loop that maintains ...
... – The Hypothalamus produces hormones that: – Are released by the posterior pituitary – Raise or lower production of anterior pituitary hormones – The pituitary gland: – Produces hormones that regulate other endocrine glands in the body – Each of these hormones has a feedback loop that maintains ...
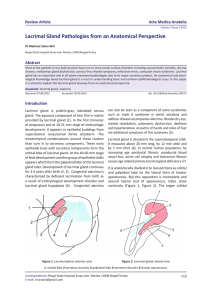
Lacrimal Gland Pathologies from an Anatomical Perspective
... of lacrimal gland functions. By the stimulation of parasympathetic nerves, acetylcholine released which activate M3 muscarinic receptors located at acinar basal and lateral membranes result in increase in intracellular concentration of calcium in activation of several protein kinase C. Protein secre ...
... of lacrimal gland functions. By the stimulation of parasympathetic nerves, acetylcholine released which activate M3 muscarinic receptors located at acinar basal and lateral membranes result in increase in intracellular concentration of calcium in activation of several protein kinase C. Protein secre ...
ch_09_lecture_presentation
... triggers the release of more hormone Hormone release stops once an appropriate level in the blood is reached ...
... triggers the release of more hormone Hormone release stops once an appropriate level in the blood is reached ...
8. Endocrine System 8.1 Basic Concepts The endocrine system is
... from the cadavers and hence is available only in limited amount. It is now possible to produce GH using genetic engineering techniques in bacteria. Actions of GH. GH affects the metabolic activity of most of the tissues of the body. Its growth-promoting effect is due to its ability to stimulate the ...
... from the cadavers and hence is available only in limited amount. It is now possible to produce GH using genetic engineering techniques in bacteria. Actions of GH. GH affects the metabolic activity of most of the tissues of the body. Its growth-promoting effect is due to its ability to stimulate the ...
hypothalamic-pituitary axis
... Secreted by lactotrophs of ant. Pituitary Lactation: only known function Inhibits reproductive hormone secretion Release inhibited by dopamine “prolactin inhibitory factor” • Animals: osmoregulation, growth • Stalk transection prolactin ...
... Secreted by lactotrophs of ant. Pituitary Lactation: only known function Inhibits reproductive hormone secretion Release inhibited by dopamine “prolactin inhibitory factor” • Animals: osmoregulation, growth • Stalk transection prolactin ...
20. Endocrine System
... mammary gland; that is, some cells in the mammary gland have receptors that pick up and respond to the prolactin by producing milk to nourish an infant. However, other organs (such as the heart and lungs) do not respond to prolactin because they do not have receptors that bind this hormone. The stud ...
... mammary gland; that is, some cells in the mammary gland have receptors that pick up and respond to the prolactin by producing milk to nourish an infant. However, other organs (such as the heart and lungs) do not respond to prolactin because they do not have receptors that bind this hormone. The stud ...
Mammary gland

A mammary gland is an organ in female mammals that produces milk to feed young offspring. Mammals get their name from the word ""mammary."" In humans, the mammary glands are situated in the breasts. In ruminants such as cows, goats, and deer, the mammary glands are contained in the udders. The mammary glands of mammals other than primates, such as dogs and cats, are sometimes called dugs.