Endocrine System
... B. Adrenal Glands - There are two adrenal glands, each superior to a kidney. Each adrenal gland has two parts -- an outer adrenal cortex and an inner adrenal medulla. Each section produces its own hormones. The adrenal cortex appears yellow in color due to the presence of lipids. It produces more th ...
... B. Adrenal Glands - There are two adrenal glands, each superior to a kidney. Each adrenal gland has two parts -- an outer adrenal cortex and an inner adrenal medulla. Each section produces its own hormones. The adrenal cortex appears yellow in color due to the presence of lipids. It produces more th ...
Health -- Primary Causes of Failing
... breathing more air than adults, acquire chemical body burdens faster than adults.” The Center for Disease Control found pesticides in 100% of the people tested. The average person in this group carried a toxic cocktail of 13 of the 23 pesticides that were analyzed. Many of the pesticides found in te ...
... breathing more air than adults, acquire chemical body burdens faster than adults.” The Center for Disease Control found pesticides in 100% of the people tested. The average person in this group carried a toxic cocktail of 13 of the 23 pesticides that were analyzed. Many of the pesticides found in te ...
The Peripheral Endocrine Glands
... Urinary excretion of glucose (occurs only abnormally, when blood glucose level becomes so high it exceeds the reabsorptive capacity of kidney tubules during urine formation) ...
... Urinary excretion of glucose (occurs only abnormally, when blood glucose level becomes so high it exceeds the reabsorptive capacity of kidney tubules during urine formation) ...
Unit P: Endocrine System
... DIABETES MELLITUS Caused by secretion of insulin Can be insulin dependent (juvenile) or noninsulin dependent Symps – polyuria, polyphagia, polydipsia, weight loss, blurred vision, and possible diabetic coma If not treated, excess glucose in blood (hyperglycemia) and glucose secreted in uri ...
... DIABETES MELLITUS Caused by secretion of insulin Can be insulin dependent (juvenile) or noninsulin dependent Symps – polyuria, polyphagia, polydipsia, weight loss, blurred vision, and possible diabetic coma If not treated, excess glucose in blood (hyperglycemia) and glucose secreted in uri ...
Endocrine System
... DIABETES MELLITUS Caused by secretion of insulin Can be insulin dependent (juvenile) or noninsulin dependent Symps – polyuria, polyphagia, polydipsia, weight loss, blurred vision, and possible diabetic coma If not treated, excess glucose in blood (hyperglycemia) and glucose secreted in uri ...
... DIABETES MELLITUS Caused by secretion of insulin Can be insulin dependent (juvenile) or noninsulin dependent Symps – polyuria, polyphagia, polydipsia, weight loss, blurred vision, and possible diabetic coma If not treated, excess glucose in blood (hyperglycemia) and glucose secreted in uri ...
9 Endocrine Physiology
... • When LH is released, it stimulates the release of more LH, and more LH, until it reaches a maximum level, then negative feedback kicks in. LH is the hormone that causes fluid to rush into the follicle surrounding a woman’s egg, and when enough fluid rushes in, the follicle pops like a balloon, rel ...
... • When LH is released, it stimulates the release of more LH, and more LH, until it reaches a maximum level, then negative feedback kicks in. LH is the hormone that causes fluid to rush into the follicle surrounding a woman’s egg, and when enough fluid rushes in, the follicle pops like a balloon, rel ...
The Endocrine System
... Fasting glucose concentration > 126 mg/dl Abnormal oral glucose tolerance test ( glucose >200mg.dL 2 hours after a standard carbohydrate load “pre-diabetes” ...
... Fasting glucose concentration > 126 mg/dl Abnormal oral glucose tolerance test ( glucose >200mg.dL 2 hours after a standard carbohydrate load “pre-diabetes” ...
9 Endocrine - bloodhounds Incorporated
... Thyroid hormones are basically a "double" tyrosine with the critical incorporation of 3 or 4 iodine atoms. Thyroid hormone is produced by the thyroid gland and is lipid soluble Thyroid hormones are produced by modification of a tyrosine residue contained in thyroglobulin, posttranslationally m ...
... Thyroid hormones are basically a "double" tyrosine with the critical incorporation of 3 or 4 iodine atoms. Thyroid hormone is produced by the thyroid gland and is lipid soluble Thyroid hormones are produced by modification of a tyrosine residue contained in thyroglobulin, posttranslationally m ...
View/Open
... Appetite, food preferences, and the regulation of food intake are key aspects of energy balance and weight homeostasis. There is an ever growing list of peptides, receptors, and other gene products associated with appetite and the regulation of food intake, and investigating their interrelated roles ...
... Appetite, food preferences, and the regulation of food intake are key aspects of energy balance and weight homeostasis. There is an ever growing list of peptides, receptors, and other gene products associated with appetite and the regulation of food intake, and investigating their interrelated roles ...
Study Guide for Endocrine
... 50. What precursor is required for the manufacture of all corticoid hormones? 51. What is the principle mineralocorticoid? 52. What are its effects? 53. When would it be released? High or low blood pressure 54. What is the most important glucocorticoid hormone in the body? 55. What is the definition ...
... 50. What precursor is required for the manufacture of all corticoid hormones? 51. What is the principle mineralocorticoid? 52. What are its effects? 53. When would it be released? High or low blood pressure 54. What is the most important glucocorticoid hormone in the body? 55. What is the definition ...
The Endocrine System
... C. Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)- stimulates production of egg and sperm D. Leutinizing Hormone (LH)stimulates ovaries to release egg and testes to produce ...
... C. Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)- stimulates production of egg and sperm D. Leutinizing Hormone (LH)stimulates ovaries to release egg and testes to produce ...
Bio 100-Ch 15
... A.regulate glucose levels B.regulate salt/water balance C.are the sex hormones testosterone and estrogen 67. Which of the following hormones will use cAMP to cause a cellular effect? A.estrogen B.progesterone C.testosterone D.cortisol ...
... A.regulate glucose levels B.regulate salt/water balance C.are the sex hormones testosterone and estrogen 67. Which of the following hormones will use cAMP to cause a cellular effect? A.estrogen B.progesterone C.testosterone D.cortisol ...
Endocrine Ch 16-Fall 2016-StudentRevised
... 1. Regulation: Humoral Stimulation: Inhibition: Low blood glucose 2. Actions: Enhances membrane transport Inhibits glycogen breakdown ...
... 1. Regulation: Humoral Stimulation: Inhibition: Low blood glucose 2. Actions: Enhances membrane transport Inhibits glycogen breakdown ...
chap9_SBI4U
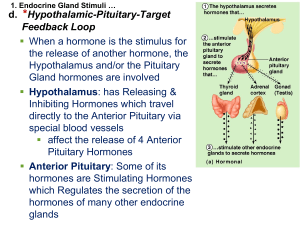
... The hypothalamus secretes a releasing hormone into the anterior pituitary Causes the anterior pituitary to release a second tropic hormone into the bloodstream The second tropic hormone stimulates the target gland to release a third hormone into the blood This hormone travels to another target tissu ...
... The hypothalamus secretes a releasing hormone into the anterior pituitary Causes the anterior pituitary to release a second tropic hormone into the bloodstream The second tropic hormone stimulates the target gland to release a third hormone into the blood This hormone travels to another target tissu ...
Bio 30 Endocrine Unit Plan Day Outcome Tasks 1 30–A2.1k identify
... 30–A2.3s analyze data and apply mathematical and conceptual models to develop and assess possible solutions infer the role of ADH and aldosterone in the maintenance of water and ions, using the analysis and interpretation of data on blood and urine composition (AI– NS6) [ICT C7–4.2] infer the ro ...
... 30–A2.3s analyze data and apply mathematical and conceptual models to develop and assess possible solutions infer the role of ADH and aldosterone in the maintenance of water and ions, using the analysis and interpretation of data on blood and urine composition (AI– NS6) [ICT C7–4.2] infer the ro ...
homeostasis
... • Produces two related hormones • Epinephrine (adrenaline) • Norepinephrine (noradrenaline) ...
... • Produces two related hormones • Epinephrine (adrenaline) • Norepinephrine (noradrenaline) ...
Lesson Overview
... pancreas releases insulin. Insulin stimulates cells to take glucose out of the blood, preventing blood glucose levels from rising too rapidly and ensuring that glucose is stored for future use. Insulin signals the liver and skeletal muscles to store glucose as glycogen. In fat tissue, glucose is con ...
... pancreas releases insulin. Insulin stimulates cells to take glucose out of the blood, preventing blood glucose levels from rising too rapidly and ensuring that glucose is stored for future use. Insulin signals the liver and skeletal muscles to store glucose as glycogen. In fat tissue, glucose is con ...
Urinary bladder Urinary bladder empties into the cloaca Ureters
... – 2 outer ones are the color of the frog’s body and do not move – 3rd eyelid is a transparent membrane that protects the eye while permitting the frog to see under water • It also keeps the eye moist when the frog is on land ...
... – 2 outer ones are the color of the frog’s body and do not move – 3rd eyelid is a transparent membrane that protects the eye while permitting the frog to see under water • It also keeps the eye moist when the frog is on land ...
LECTURE OUTLINE
... 20.6 Other Endocrine Glands Testes and Ovaries The testes produce androgens, which are the male sex hormones. The female sex hormones, estrogen and progesterone, are produced by the ovaries. Thymus Gland The thymus gland secretes thymosins which aid in the differentiation of T lymphocytes. Pineal Gl ...
... 20.6 Other Endocrine Glands Testes and Ovaries The testes produce androgens, which are the male sex hormones. The female sex hormones, estrogen and progesterone, are produced by the ovaries. Thymus Gland The thymus gland secretes thymosins which aid in the differentiation of T lymphocytes. Pineal Gl ...
Lecture5
... muscles, coronary arteries, liver and brain. The level of blood sugar rises and metabolic rate increases. The bronchi dilates, permitting easier passage of air to and from the lungs. The pupils of the eye dilate and there is tendency for the body hair to stand. (ii) ...
... muscles, coronary arteries, liver and brain. The level of blood sugar rises and metabolic rate increases. The bronchi dilates, permitting easier passage of air to and from the lungs. The pupils of the eye dilate and there is tendency for the body hair to stand. (ii) ...
Assessment and Management of Patients with Endocrine Disorders Dr Ibraheem Bashayreh 29/11/2010
... 2-De Quervain's Thyroiditis. (also called subacute or granulomatous thyroiditis). The thyroid gland generally swells rapidly and is very painful and tender.] Patients will experience a hyperthyroid period as the cellular lining of colloid spaces fails, allowing abundant colloid into the circulation, ...
... 2-De Quervain's Thyroiditis. (also called subacute or granulomatous thyroiditis). The thyroid gland generally swells rapidly and is very painful and tender.] Patients will experience a hyperthyroid period as the cellular lining of colloid spaces fails, allowing abundant colloid into the circulation, ...
CHAPTER 15 LECTURE QUESTIONS
... a. Where does aldosterone have its effects? _______________________________ b. Aldosterone causes reabsorption of ___________________________________ 40. The two classes of sex hormones are _________________________________ and _______________________________________. 41. Epinephrine and norepinephr ...
... a. Where does aldosterone have its effects? _______________________________ b. Aldosterone causes reabsorption of ___________________________________ 40. The two classes of sex hormones are _________________________________ and _______________________________________. 41. Epinephrine and norepinephr ...
Endocrinology Features of Endocrine system:
... – Some estrogens (female sex hormones) are also formed ...
... – Some estrogens (female sex hormones) are also formed ...
The Endocrine System
... 333. Glycogen is synthesized and stored primarily in ____. A. liver B. kidneys C. neurons ...
... 333. Glycogen is synthesized and stored primarily in ____. A. liver B. kidneys C. neurons ...
Facts about sugars - Brochure
... as type 2 diabetes, is much debated. However, overweight and obesity risk relates more closely to energy balance (calories in exceeding calories out), than to the sugar content of the diet25.The development of overweight and obesity is due to an energy intake greater than energy expenditure, which i ...
... as type 2 diabetes, is much debated. However, overweight and obesity risk relates more closely to energy balance (calories in exceeding calories out), than to the sugar content of the diet25.The development of overweight and obesity is due to an energy intake greater than energy expenditure, which i ...
Glycemic index

The glycemic index or glycaemic index (GI) is a number associated with a particular type of food that indicates the food's effect on a person's blood glucose (also called blood sugar) level. A value of 100 represents the standard, an equivalent amount of pure glucose.The GI represents the total rise in a person's blood sugar level following consumption of the food; it may or may not represent the rapidity of the rise in blood sugar. The steepness of the rise can be influenced by a number of other factors, such as the quantity of fat eaten with the food. The GI is useful for understanding how the body breaks down carbohydrates and only takes into account the available carbohydrate (total carbohydrate minus fiber) in a food. Although the food may contain fats and other components that contribute to the total rise in blood sugar, these effects are not reflected in the GI.The glycemic index is usually applied in the context of the quantity of the food and the amount of carbohydrate in the food that is actually consumed. A related measure, the glycemic load (GL), factors this in by multiplying the glycemic index of the food in question by the carbohydrate content of the actual serving. Watermelon has a high glycemic index, but a low glycemic load for the quantity typically consumed. Fructose, by contrast, has a low glycemic index, but can have a high glycemic load if a large quantity is consumed.GI tables are available that list many types of foods and their GIs. Some tables also include the serving size and the glycemic load of the food per serving.A practical limitation of the glycemic index is that it does not measure insulin production due to rises in blood sugar. As a result, two foods could have the same glycemic index, but produce different amounts of insulin. Likewise, two foods could have the same glycemic load, but cause different insulin responses. Furthermore, both the glycemic index and glycemic load measurements are defined by the carbohydrate content of food. For example when eating steak, which has no carbohydrate content but provides a high protein intake, up to 50% of that protein can be converted to glucose when there is little to no carbohydrate consumed with it. But because it contains no carbohydrate itself, steak cannot have a glycemic index. For some food comparisons, the ""insulin index"" may be more useful.