My Pituitary Gland
... ADH (Anti-diuretic Hormone) This hormone regulates the normal amount of water in the body. Lack of ADH: causes loss of large amounts of water through the kidneys so that very dilute urine is formed. As a result there is increased thirst and large amounts of water are drunk. These symptoms may contin ...
... ADH (Anti-diuretic Hormone) This hormone regulates the normal amount of water in the body. Lack of ADH: causes loss of large amounts of water through the kidneys so that very dilute urine is formed. As a result there is increased thirst and large amounts of water are drunk. These symptoms may contin ...
AnS SI 214 Practice Exam 3 Female Reproduction, Male
... More than likely, the questions we DO go over in review will help you answer at least one of the essay questions per unit on the exam. These questions were written to call your attention to other important concepts that are slightly less likely to make it into your exam essay pool, but will be benef ...
... More than likely, the questions we DO go over in review will help you answer at least one of the essay questions per unit on the exam. These questions were written to call your attention to other important concepts that are slightly less likely to make it into your exam essay pool, but will be benef ...
Hormonal Imbalance In Men And Women
... in a person's body. They interact with each other and often cause imbalances. They are produced by a group of glands called the endocrine system. These glands are located in different parts of the body but are considered part of the same system. They are powerful substances secreted into the bloodst ...
... in a person's body. They interact with each other and often cause imbalances. They are produced by a group of glands called the endocrine system. These glands are located in different parts of the body but are considered part of the same system. They are powerful substances secreted into the bloodst ...
The Endocrine System
... You’ve probably heard of diabetes Type 1, that happens when the pancreas can’t produce enough insulin to control your blood sugar. The thymus helps your body fight off infections. It’s a key player in the production of T-cells, which identify and kill germs in your blood. ...
... You’ve probably heard of diabetes Type 1, that happens when the pancreas can’t produce enough insulin to control your blood sugar. The thymus helps your body fight off infections. It’s a key player in the production of T-cells, which identify and kill germs in your blood. ...
Lecture Slides - Austin Community College
... synthesis and release of hormones – TRH - Thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) >> release of TSH – CRH - Corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH) >> release of ACTH – GnRH - Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GNRH) >> release of FSH and LH ...
... synthesis and release of hormones – TRH - Thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) >> release of TSH – CRH - Corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH) >> release of ACTH – GnRH - Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GNRH) >> release of FSH and LH ...
Endo_Emergencies
... Prevention of Acute Adrenal Crisis For patients on chronic steroid Rx: –Double their normal daily dose before and for at least 2 - 3 days after a stressful procedure or when an active infection is present ...
... Prevention of Acute Adrenal Crisis For patients on chronic steroid Rx: –Double their normal daily dose before and for at least 2 - 3 days after a stressful procedure or when an active infection is present ...
The Endocrine System - An Overview
... The thyroid gland produces two main hormones which are very important for growth and development. One is called thyroxine (T4) and the other is called triiodothyronine (T3). T4 is converted to T3 in the body’s cells and tissues. T3 is an active hormone and is needed by all of the cells and tissues ...
... The thyroid gland produces two main hormones which are very important for growth and development. One is called thyroxine (T4) and the other is called triiodothyronine (T3). T4 is converted to T3 in the body’s cells and tissues. T3 is an active hormone and is needed by all of the cells and tissues ...
Adrenal Insufficiency (Adrenal gland failure)
... Under conditions of mild physical stress such as bronchitis with fever, intestinal infection or food poisoning causing diarrhea, or sinus infection, the oral hydrocortisone/prednisone dose should be doubled until the mild stress has resolved-this usually takes from 2 to 3 days. You should also try t ...
... Under conditions of mild physical stress such as bronchitis with fever, intestinal infection or food poisoning causing diarrhea, or sinus infection, the oral hydrocortisone/prednisone dose should be doubled until the mild stress has resolved-this usually takes from 2 to 3 days. You should also try t ...
The Endocrine System - An Overview
... The pea-sized pineal gland is near the centre of the brain. The pineal gland produces a hormone called melatonin. Melatonin is produced when it is dark so more is produced at night and in the winter. When nights are longer, the body makes more melatonin. Melatonin is the hormone which is responsible ...
... The pea-sized pineal gland is near the centre of the brain. The pineal gland produces a hormone called melatonin. Melatonin is produced when it is dark so more is produced at night and in the winter. When nights are longer, the body makes more melatonin. Melatonin is the hormone which is responsible ...
Endocrine System
... increase until signals are sent to glands to stop secretion of that hormone) • Endocrine glands: – Pituitary – “master gland,” growth hormone – Thyroid – metabolic rate – Adrenal – salt and carbohydrate metabolism – Pancreas – sugar metabolism – Gonads – sex hormones ...
... increase until signals are sent to glands to stop secretion of that hormone) • Endocrine glands: – Pituitary – “master gland,” growth hormone – Thyroid – metabolic rate – Adrenal – salt and carbohydrate metabolism – Pancreas – sugar metabolism – Gonads – sex hormones ...
Saladin, Human Anatomy 3e
... 18.1 Overview of the Endocrine System (p. 498) 1. Hormones are chemical messengers that are secreted into the bloodstream and stimulate distant cells and organs. The glands and cells that secrete hormones constitute the endocrine system, and the branch of biology and medicine that deals with them is ...
... 18.1 Overview of the Endocrine System (p. 498) 1. Hormones are chemical messengers that are secreted into the bloodstream and stimulate distant cells and organs. The glands and cells that secrete hormones constitute the endocrine system, and the branch of biology and medicine that deals with them is ...
Hormones and the Endocrine System
... The hypothalamus regulates the neuroendocrine system, maintaining homeostasis in the body. The hypothalamus can use motor nerves to send shortlived electrical messages or hormones to send chemical messages with a longer duration. ...
... The hypothalamus regulates the neuroendocrine system, maintaining homeostasis in the body. The hypothalamus can use motor nerves to send shortlived electrical messages or hormones to send chemical messages with a longer duration. ...
Hormones and the Endocrine System
... diabetes) is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system destroys the beta cells of the pancreas. Type II diabetes mellitus (non-insulindependent diabetes) is characterized either by a deficiency of insulin or, more commonly, by reduced responsiveness of target cells due to some change in in ...
... diabetes) is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system destroys the beta cells of the pancreas. Type II diabetes mellitus (non-insulindependent diabetes) is characterized either by a deficiency of insulin or, more commonly, by reduced responsiveness of target cells due to some change in in ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... Type I results from an inability to produce insulin and is classified as an autoimmune disorder. Since the body does not produce insulin, blood sugars rise and cannot be pulled out of the blood and stored. Most cases of diabetes, roughly 90%, are type II. Type II is when the liver and muscle cells d ...
... Type I results from an inability to produce insulin and is classified as an autoimmune disorder. Since the body does not produce insulin, blood sugars rise and cannot be pulled out of the blood and stored. Most cases of diabetes, roughly 90%, are type II. Type II is when the liver and muscle cells d ...
2. Physiology of the testis 2015
... B. Medication that interfere with autonomic function C. Problem with blood flow to the penis. Sildenafil (Vigra): prescribed to treat erectile dysfunction. It does not produce an erection but it amplifies and prolongs an erectile response triggered by usual means of stimulation. ...
... B. Medication that interfere with autonomic function C. Problem with blood flow to the penis. Sildenafil (Vigra): prescribed to treat erectile dysfunction. It does not produce an erection but it amplifies and prolongs an erectile response triggered by usual means of stimulation. ...
9 Endocrine Physio flashcards
... make Thyroglobin? 57.Where does thyroglobulin (TG) go when it first leaves the cell? 58.How is TG changed after it leaves the cell, while it is on its way to the thyroid follicle for storage? 59.When iodine is attached to TG, what is ...
... make Thyroglobin? 57.Where does thyroglobulin (TG) go when it first leaves the cell? 58.How is TG changed after it leaves the cell, while it is on its way to the thyroid follicle for storage? 59.When iodine is attached to TG, what is ...
draft `low testosterone pathway`
... Low testosterone levels indicate hypogonadism, which can be primary or secondary. Primary is a failure of the testes to produce testosterone, and this can be caused by many factors (see below), and secondary is related to a lack of pituitary signal. The LH (luteinising hormone) assay will be high in ...
... Low testosterone levels indicate hypogonadism, which can be primary or secondary. Primary is a failure of the testes to produce testosterone, and this can be caused by many factors (see below), and secondary is related to a lack of pituitary signal. The LH (luteinising hormone) assay will be high in ...
Endocrine part 2
... (c) Infections are generally masked until they become overwhelmingly severe. e. Hyposecretion: (1) Addison’s disease, hyposecretion of both glucocorticoids and mineralocoritcoids, (2) Symptoms: weight loss, severe dehydration and hypotension are common. 3. Gonadocorticoids a. most common gonadocorti ...
... (c) Infections are generally masked until they become overwhelmingly severe. e. Hyposecretion: (1) Addison’s disease, hyposecretion of both glucocorticoids and mineralocoritcoids, (2) Symptoms: weight loss, severe dehydration and hypotension are common. 3. Gonadocorticoids a. most common gonadocorti ...
عرض تقديمي من PowerPoint
... to produce an b. Alter protein or regulatory molecule activity: enhance a. membrane Myxedema: transport hypothyroid of glucose disorder into chemical ...
... to produce an b. Alter protein or regulatory molecule activity: enhance a. membrane Myxedema: transport hypothyroid of glucose disorder into chemical ...
Endocrine system
... Cushing’s syndrome Causes: Administration of exogenous glucocorticoids – most common Pituitary hypersecretion of ACTH (Cushing’s disease) – adenoma Ectopic ACTH secretion – small cell carcinoma !! Histology: Crooke’s hyaline changes within pituitary basophils Clinically: Central obesity, ...
... Cushing’s syndrome Causes: Administration of exogenous glucocorticoids – most common Pituitary hypersecretion of ACTH (Cushing’s disease) – adenoma Ectopic ACTH secretion – small cell carcinoma !! Histology: Crooke’s hyaline changes within pituitary basophils Clinically: Central obesity, ...
Document
... Usually an AM cortisol level of > 10-12 ug/dL and no signs of adrenal insufficiency would lead me to start a taper. Most cured patients can get off cortisol in 6-12 months. I taper HC down 2.5 mg to 5 mg every 2 weeks. I often get a morning cortisol level after taper, but usually don’t restart if pa ...
... Usually an AM cortisol level of > 10-12 ug/dL and no signs of adrenal insufficiency would lead me to start a taper. Most cured patients can get off cortisol in 6-12 months. I taper HC down 2.5 mg to 5 mg every 2 weeks. I often get a morning cortisol level after taper, but usually don’t restart if pa ...
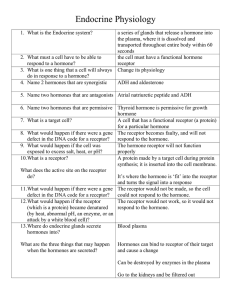
Endocrine System Study Questions with answers
... 19. What does the pancreas secrete when blood glucose levels are too high? insulin 20.What do the gonads secrete and for what functions? The testes produce testosterone, which produces sperm and develops the male reproductive system. The ovaries produce eggs, and estrogen and progesterone, which dev ...
... 19. What does the pancreas secrete when blood glucose levels are too high? insulin 20.What do the gonads secrete and for what functions? The testes produce testosterone, which produces sperm and develops the male reproductive system. The ovaries produce eggs, and estrogen and progesterone, which dev ...